0x00 前言
本文介绍下golang标准库中httputil.ReverseProxy的使用及排坑。
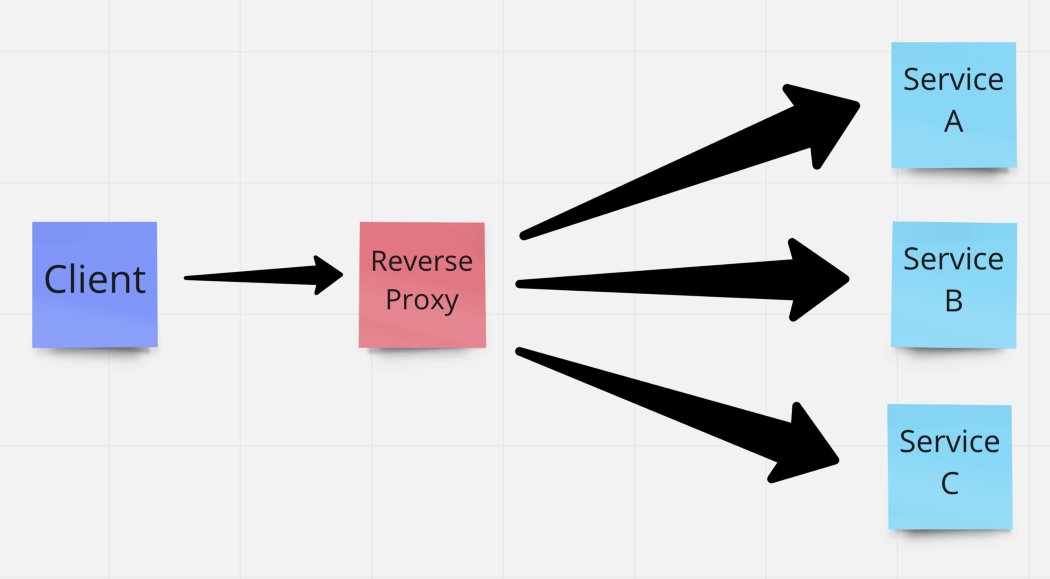
REVERSE PROXY USE CASES
-
Load balancing: a reverse proxy can provide a load balancing solution which will distribute the incoming traffic evenly among the different servers to prevent any single server from becoming overloaded
-
Preventing security attacks: since the actual web-servers never need to expose their public IP address, attacks such as DDoS can only target the reverse proxy which can be secured with more resources to fend off the cyber attack. Your actual servers are always safe.
-
Caching: Let’s say your actual servers are in a region far from your users, you can deploy regional reverse proxies which can cache content and serve to local users.
-
SSL encryption: As SSL communication with each client is computationally expensive, using a reverse proxy it can handle all your SSL related stuff and then freeing up valuable resources on your actual servers.
basic
如下面调用NewSingleHostReverseProxy创建代理的例子,将请求http://127.0.0.1:8080/test?id=1转发到http://1.2.3.4:8081/reverse/test?id=1:
func main() {
rs1 := "http://1.2.3.4:12345/reverse"
targetUrl , err := url.Parse(rs1)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("err")
}
//代理到哪个地址?
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(targetUrl)
//
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080",proxy);err != nil{
log.Fatal("Start server failed,err:",err)
}
}
假设目标URI是/base,请求的URI是/dir,那么原请求会被反向代理到http://x.x.x.x./base/dir;由于ReverseProxy实现了ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)方法,所以可以直接传入http.ListenAndServe方法中
NewSingleHostReverseProxy实现
参考此文
0x01 case1:基础用法
启动一个监听在端口12345的http服务:
python -c 'import BaseHTTPServer as bhs, SimpleHTTPServer as shs; bhs.HTTPServer(("127.0.0.1", 12345), shs.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler).serve_forever()'
- Step 1: Create origin server
- Step 2: Create a reverse proxy server
- Step 3: Forward a client request to the origin server (via reverse proxy)
- Step 4: Copy Origin Server Response
http.ReverseProxy提供了很多用户可以自定义的传参:
// 处理进来的请求,并发送转发至后端 server 实现反向代理,并将响应请求回传给客户端
type ReverseProxy struct {
// Director must be a function which modifies
// the request into a new request to be sent
// using Transport. Its response is then copied
// back to the original client unmodified.
// Director must not access the provided Request
// after returning.
Director func(*http.Request) // 通过 transport 可修改请求,响应体将原封不动的返回
// The transport used to perform proxy requests.
// If nil, http.DefaultTransport is used.
Transport http.RoundTripper // 通过 transport 设置转发 http-client 的参数
// FlushInterval specifies the flush interval
// to flush to the client while copying the
// response body.
// If zero, no periodic flushing is done.
// A negative value means to flush immediately
// after each write to the client.
// The FlushInterval is ignored when ReverseProxy
// recognizes a response as a streaming response, or
// if its ContentLength is -1; for such responses, writes
// are flushed to the client immediately.
FlushInterval time.Duration
// ErrorLog specifies an optional logger for errors
// that occur when attempting to proxy the request.
// If nil, logging is done via the log package's standard logger.
ErrorLog *log.Logger // Go 1.4 // 默认为 std.err,可用于自定义 logger
// BufferPool optionally specifies a buffer pool to
// get byte slices for use by io.CopyBuffer when
// copying HTTP response bodies.
BufferPool BufferPool // Go 1.6 // 用于执行 io.CopyBuffer 复制响应体,将其存放至 byte 切片
// ModifyResponse is an optional function that modifies the
// Response from the backend. It is called if the backend
// returns a response at all, with any HTTP status code.
// If the backend is unreachable, the optional ErrorHandler is
// called without any call to ModifyResponse.
//
// If ModifyResponse returns an error, ErrorHandler is called
// with its error value. If ErrorHandler is nil, its default
// implementation is used.
ModifyResponse func(*http.Response) error // Go 1.8 // 用于修改响应结果及 HTTP 状态码,当返回结果 error 不为空时,会调用 ErrorHandler
// ErrorHandler is an optional function that handles errors
// reaching the backend or errors from ModifyResponse.
//
// If nil, the default is to log the provided error and return
// a 502 Status Bad Gateway response.
ErrorHandler func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, error) // Go 1.11 // 用于处理后端和 ModifyResponse 返回的错误信息,默认将返回传递过来的错误信息,并返回 HTTP 502
}
接下来一一介绍:
修改请求:Director
Director用于将请求转发到后端服务器之前对其进行修改,可以在请求发送之前对其进行任何更改,但是务必要遵循基本的HTTP协议,否则,后端服务器不一定能接受该请求
// NewProxy takes target host and creates a reverse proxy
func NewProxy(targetHost string) (*httputil.ReverseProxy, error) {
url, err := url.Parse(targetHost)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
originalDirector := proxy.Director
proxy.Director = func(req *http.Request) {
originalDirector(req)
modifyRequest(req)
}
proxy.ModifyResponse = modifyResponse()
proxy.ErrorHandler = errorHandler()
return proxy, nil
}
//修改客户端的原始请求,注意到参数是*http.Request
func modifyRequest(req *http.Request) {
//在请求发送到服务器之前添加了一个 Header 头
req.Header.Set("X-Proxy", "Simple-Reverse-Proxy")
}
修改响应:ModifyResponse
可以利用成员ModifyResponse,修改从后端服务器获得的响应, 通常情况下根据应用场景来缓存或更改此响应:
- 修改响应header
- 读取响应体body,并对其进行修改或缓存,然后将其设置回客户端
// NewProxy takes target host and creates a reverse proxy
func NewProxy(targetHost string) (*httputil.ReverseProxy, error) {
url, err := url.Parse(targetHost)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
proxy.ModifyResponse = modifyResponse()
return proxy, nil
}
func modifyResponse() func(*http.Response) error {
return func(resp *http.Response) error {
//在响应回包中增加Header头
resp.Header.Set("X-Proxy", "Magical")
return nil
}
}
此外,在 modifyResponse 方法中,假设在处理响应时发生了错误,那么返回此错误( 如果设置了 proxy.ErrorHandler),modifyResponse 返回错误时会自动调用 ErrorHandler 进行错误处理。
// NewProxy takes target host and creates a reverse proxy
func NewProxy(targetHost string) (*httputil.ReverseProxy, error) {
url, err := url.Parse(targetHost)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(url)
proxy.ModifyResponse = modifyResponse()
//设置了proxy.ErrorHandler
proxy.ErrorHandler = errorHandler()
return proxy, nil
}
func errorHandler() func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, error) {
return func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request, err error) {
fmt.Printf("Got error while modifying response: %v \n", err)
return
}
}
func modifyResponse() func(*http.Response) error {
return func(resp *http.Response) error {
return errors.New("response body is invalid")
}
}
0x02 case2:修改响应包(支持缓存)
简单的修改response
示例3提供了修改response,加入自定义前缀的逻辑:注意修改了resp包体之后需要更新Content-Length的值。下图给出了前后请求的抓包:
resp.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(newData))
resp.ContentLength = int64(len(newData))
resp.Header.Set("Content-Length", fmt.Sprint(len(newData)))
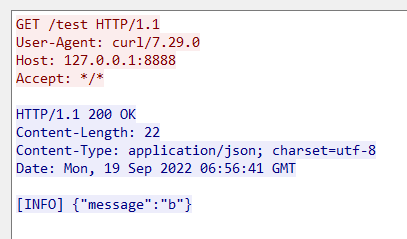
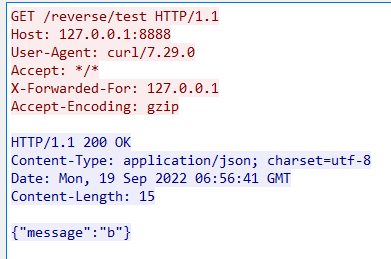
0x03 case3:给请求后端加上负载均衡
0x04 case4:给请求后端加上服务发现及探测
0x0 case: 基于fasthttp构建
基于fasthttp实现的反向代理项目:fasthttp-reverse-proxy
0x0 零信任代理网关
pomerium是一个基于零信任理念构建的代理网关,官方文档,其架构如下:
System Level
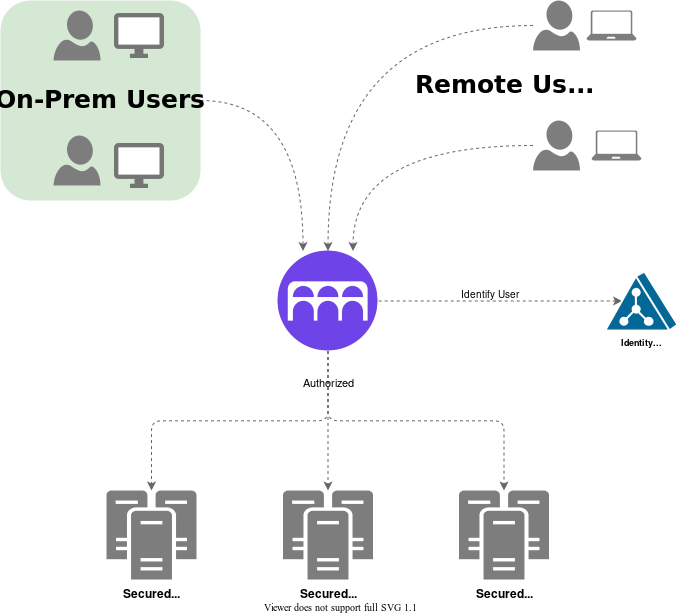
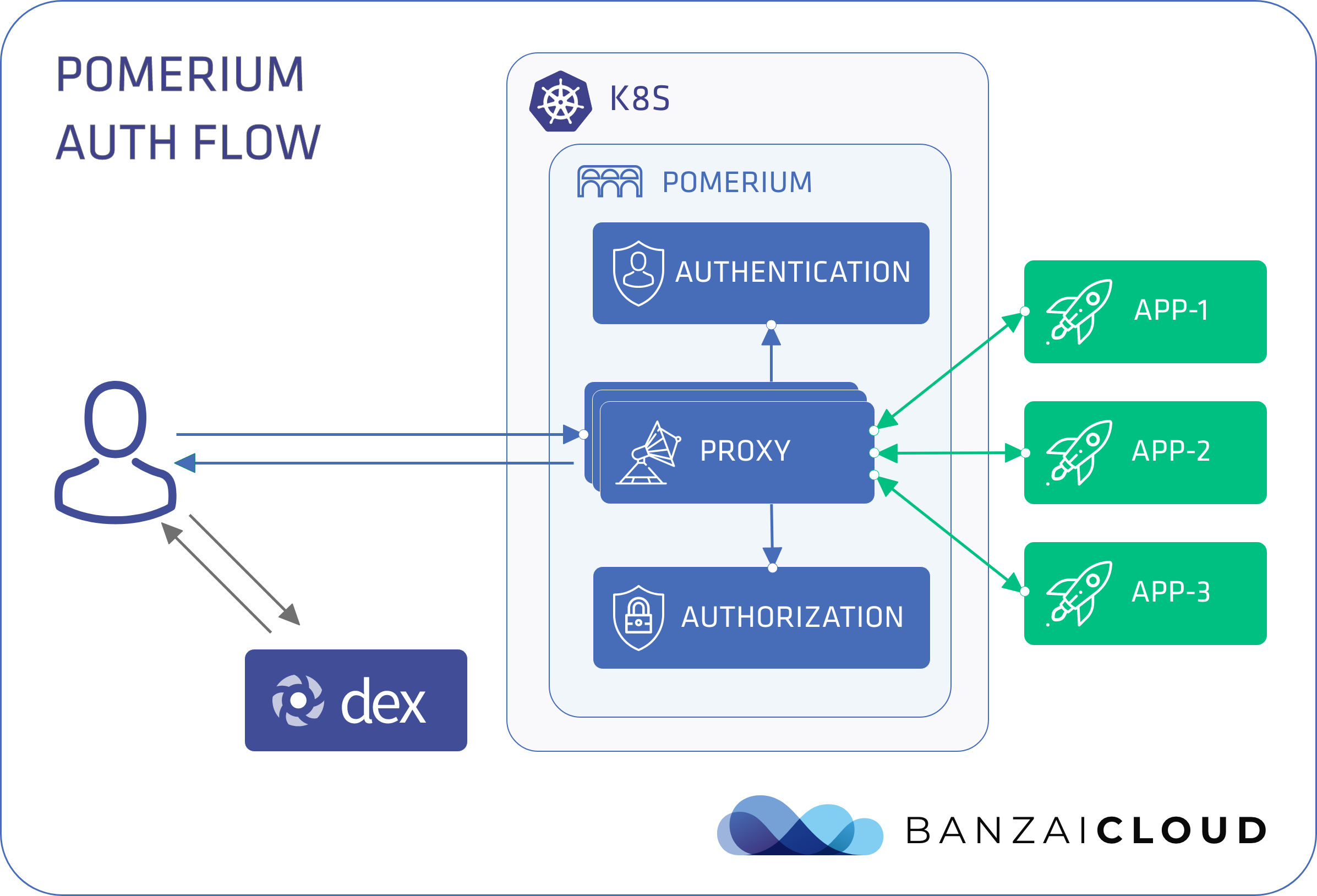
Component:组件
- Proxy Service: main proxy to direct users to establish identity
- Authentication Service (AuthN): verifies identity via identity provider (IdP)
- Authorization Service (AuthZ): determines permissions
- Cache Service: stores and refreshes IdP access and tokens
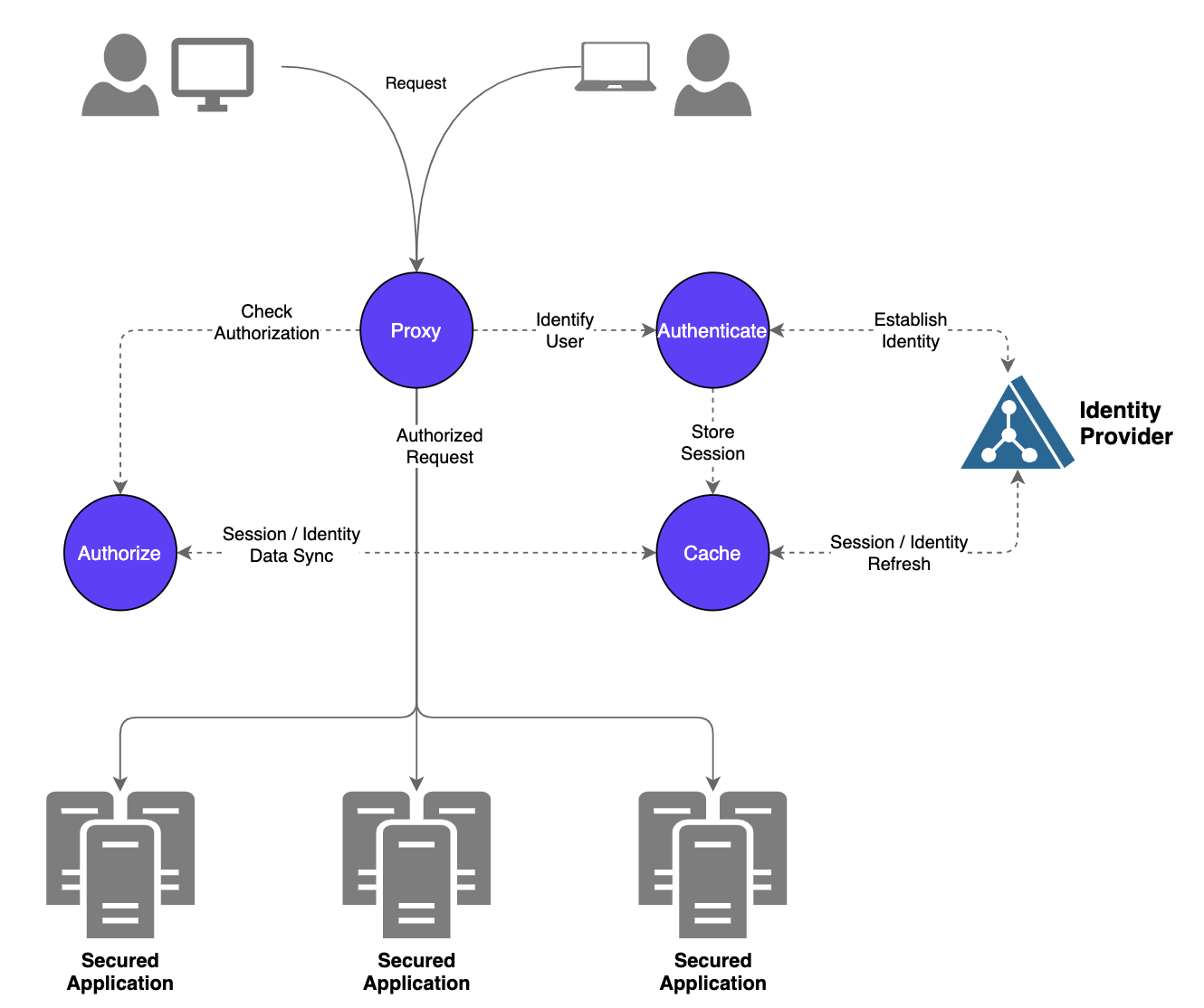
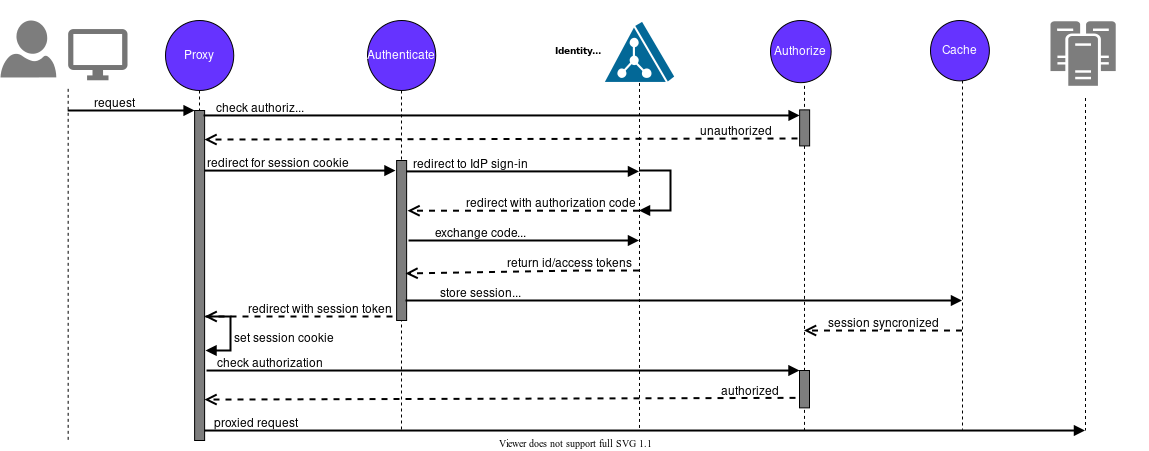
Authentication Flow
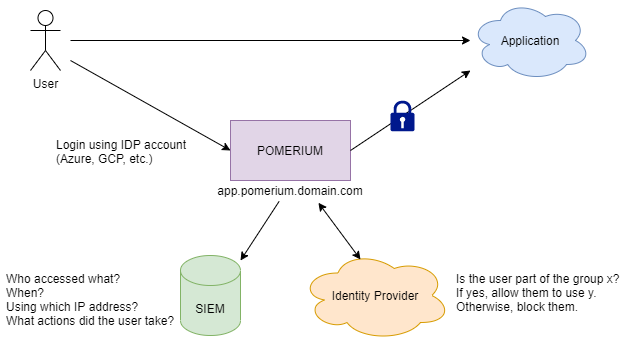
Data
0x0 case:reproxy
- reproxy:Simple edge server / reverse proxy
- ginproxy:A very simple proxy handler for gin-gonic
- ReverseProxy:ReverseProxy in golang
- gin-reverseproxy:Gin Reverse Proxy Middleware
- pomerium:Pomerium is an identity and context-aware access proxy
0x0 参考
- Is it possible to run python SimpleHTTPServer on localhost only?
- Golang Reverse Proxy
- The Right Use of ReverseProxy in Golang
- A simple reverse proxy in Go using Gin
- Golang gin gonic web framework proxy route to another backend
- Introduction to modern network load balancing and proxying
- Capturing Metrics with Go’s Reverse Proxy
- Build reverse proxy server in Go
- Architecture