0x00 前言
看看下面这个例子,将 map[string]interface{} 定义成一个类型,这样直接 newmap:=MD{} 生成的对象就是一个 map(虽然这种语法看起来很奇怪)。理解此用法是分析 Metadata 的基础。
type mdKey struct{}
type MD map[string]interface{}
func main(){
fmt.Println(mdKey{}) // 是一个空 struct
newmap:=MD{}
newmap["1"]=1
newmap["2"]=2
fmt.Println(newmap,len(newmap))
}
该例子输出的结果是:
{}
map[1:1 2:2] 2
0x01 Context 之传值
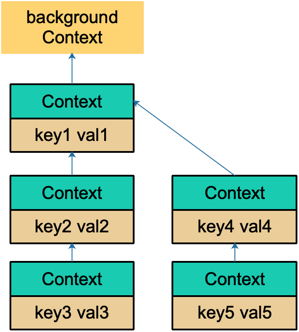
利用 Context 可以方便的进行 Value 传递和向上查找(虽然不推荐这么做),一棵使用了 context.WithValue 的 Context-Tree 可能像下面这样:
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
process(ctx)
// 左子树
lctx := context.WithValue(ctx, "key1", "val1")
process(lctx)
lctx = context.WithValue(lctx, "key2", "val2")
process(lctx)
lctx = context.WithValue(lctx, "key3", "val3")
process(lctx)
// 右子树
rctx:=context.WithValue(lctx, "key4", "val4")
process(rctx)
rctx =context.WithValue(rctx, "key5", "val5")
process(rctx)
}
func process(ctx context.Context) {
traceId, ok := ctx.Value("traceid1").(string)
if ok {
fmt.Printf("find trace_id=%s\n", traceId)
} else {
fmt.Printf("no trace_id\n")
}
}
0x02 Metadata 结构
Kratos Metadata 的 实现代码在此
基础定义
Metadata 的定义如下,一个是全局的 key:mdKey,另一个是 MD,它就是一个 map:
// MD is a mapping from metadata keys to values.
type MD map[string]interface{}
//MDKEY 是个空结构 struct{}
type mdKey struct{}
和 MD 相关的操作(不含 context)有如下几个:
New:通过传入的参数map[string]interface{}构造一个新的MDLen:返回 map 的 sizeCopy:原地复制一个新的MD结构(即不改变旧的结构)
// Len returns the number of items in md.
func (md MD) Len() int {
return len(md)
}
// Copy returns a copy of md.
func (md MD) Copy() MD {
return Join(md)
}
// New creates an MD from a given key-value map.
func New(m map[string]interface{}) MD {
md := MD{}
for k, val := range m {
md[k] = val
}
return md
}
// Join joins any number of mds into a single MD.
// The order of values for each key is determined by the order in which
// the mds containing those values are presented to Join.
func Join(mds ...MD) MD {
// 创建新的 MD
out := MD{}
// 复制
for _, md := range mds {
for k, v := range md {
out[k] = v
}
}
return out
}
此外,还提供了 Pairs 方法来生成一个 MD 结构,它传入的参数是 slice,要求长度必须为偶数(K-V):
// 测试用例
{[]MD{}, MD{}},
{[]MD{Pairs("foo", "bar")}, Pairs("foo", "bar")},
{[]MD{Pairs("foo", "bar"), Pairs("foo", "baz")}, Pairs("foo", "bar", "foo", "baz")},
{[]MD{Pairs("foo", "bar"), Pairs("foo", "baz"), Pairs("zip", "zap")}, Pairs("foo", "bar", "foo", "baz", "zip", "zap")},
// Pairs returns an MD formed by the mapping of key, value ...
// Pairs panics if len(kv) is odd.
func Pairs(kv ...interface{}) MD {
if len(kv)%2 == 1 {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("metadata: Pairs got the odd number of input pairs for metadata: %d", len(kv)))
}
md := MD{}
var key string
for i, s := range kv {
if i%2 == 0 {
key = s.(string)
continue
}
md[key] = s
}
return md
}
0x03 Metadata && Context
有了封装好的 MD 及方法,接下来就是如何和 context 进行搭配使用了。这里我们逐个方法来分析:
NewContext 方法,传入参数为 ctx context.Context 及 md MD,返回一个子 context,如下图所示:
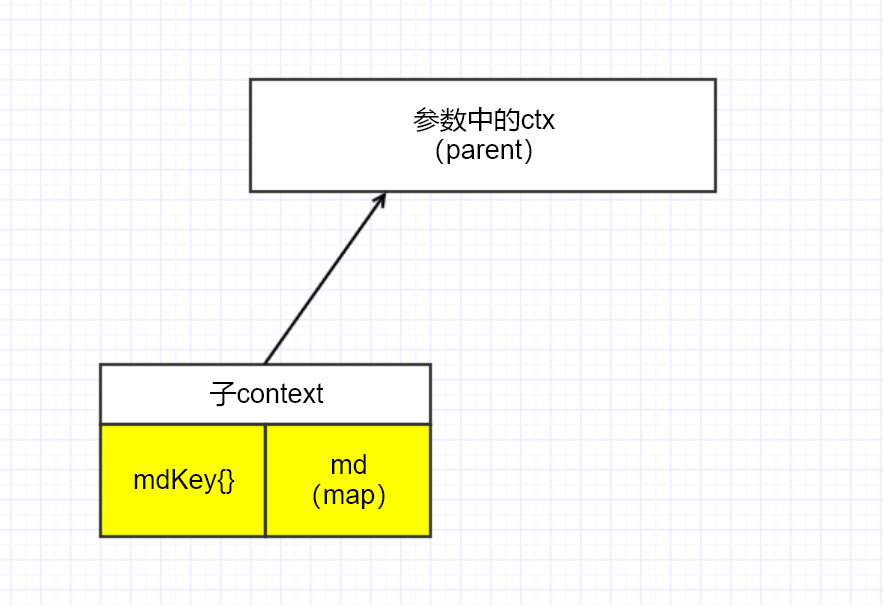
// NewContext creates a new context with md attached.
// 给 ctx 加入 md 的 kv 传递,返回一个子 ctx(excellent)
// func WithValue(parent Context, key, val interface{}) Context
func NewContext(ctx context.Context, md MD) context.Context {
// 以 mdKey{} 为 key 的意义:固定的全局变量
return context.WithValue(ctx, mdKey{}, md)
}
FromContext 方法,从当前的 ctx 向上遍历,查询 mdKey{} 对应的 Value 值,这个 mdKey{} 可以理解为全局唯一常量(Kratos 框架设置用此)。
// FromContext returns the incoming metadata in ctx if it exists. The
// returned MD should not be modified. Writing to it may cause races.
// Modification should be made to copies of the returned MD.
func FromContext(ctx context.Context) (md MD, ok bool) {
md, ok = ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
return
}
String 方法,是 FromContext 的拓展,它多传入一个 key string 参数,先查找 mdKey{} 对应的 Value(map),再在 map 中查找 key 对应的值:
// String get string value from metadata in context
func String(ctx context.Context, key string) string {
md, ok := ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
if !ok {
return ""
}
str, _ := md[key].(string)
return str
}
Int64 和 Value 方法,也是类似:
// Int64 get int64 value from metadata in context
func Int64(ctx context.Context, key string) int64 {
md, ok := ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
if !ok {
return 0
}
i64, _ := md[key].(int64)
return i64
}
// Value get value from metadata in context return nil if not found
func Value(ctx context.Context, key string) interface{} {
md, ok := ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
if !ok {
return nil
}
return md[key]
}
WithContext 方法,首先从传入的 context 中查找 mdKey{} 对应的 Value,如果不存在就返回 context.Background(),如果存在,先将 context 复制一份为 md,然后去掉 md 的 Trace 信息,然后使用 context.Background()+ context.WithValue(ctx, mdKey{}, md) 生成一份新的 context 返回。
// WithContext return no deadline context and retain metadata.
func WithContext(c context.Context) context.Context {
md, ok := FromContext(c)
if ok {
nmd := md.Copy()
// NOTE: temporary delete prevent asynchronous task reuse finished task
delete(nmd, Trace)
return NewContext(context.Background(), nmd)
}
return context.Background()
}
Bool 方法,查找 ctx context 中 mdKey{} 的 MAP 中,key 值是否为 bool 类型:
// Bool get boolean from metadata in context use strconv.Parse.
func Bool(ctx context.Context, key string) bool {
md, ok := ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
if !ok {
return false
}
switch md[key].(type) {
case bool:
return md[key].(bool)
case string:
ok, _ = strconv.ParseBool(md[key].(string))
return ok
default:
return false
}
}
Range 方法,该方法传入 rangeFunc 及 filterFunc,其中后者可以传入多个,filterFunc 过滤 key,rangeFunc 作用于 key 及 value:
// Range range value from metadata in context filtered by filterFunc.
func Range(ctx context.Context, rangeFunc func(key string, value interface{}), filterFunc ...func(key string) bool) {
var filter func(key string) bool
filterLen := len(filterFunc)
if filterLen > 1 {
panic(errors.New("metadata: Range got the lenth of filterFunc must less than 2"))
} else if filterLen == 1 {
filter = filterFunc[0]
}
md, ok := ctx.Value(mdKey{}).(MD)
if !ok {
return
}
for key, value := range md {
if filter == nil || filter(key) {
rangeFunc(key, value)
}
}
}
0x04 总结
本文分析了 Kratos 中 Metadata 及它和 Context 库的封装及使用,理解 Context 的原理对理解 Metadata 的实现非常有帮助。此外,后续文章将分析下 Metadata 在 Kratos-Opentracing 的使用。