0x00 前言
net/http 实现了 HTTP 客户端和服务端,分别对应 http.RoundTripper 和 http.Handler 两个接口。
http.RoundTripper:用来表示执行 HTTP 请求的接口,调用方将请求作为参数可以获取请求对应的响应http.Handler主要用于 HTTP 服务器响应客户端的请求
http.RoundTripper 是用来表示执行 HTTP 请求的接口,而 HTTP 请求的接收方可以实现 http.Handler 接口,其中实现了处理 HTTP 请求的逻辑,处理的过程中会调用 http.ResponseWriter 接口的方法构造 HTTP 响应,它提供的三个接口 Header、Write 和 WriteHeader 分别会获取 HTTP 响应、将数据写入负载以及写入响应头,如下
type RoundTripper interface {
RoundTrip(*Request) (*Response, error)
}
type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)
}
type ResponseWriter interface {
Header() Header
Write([]byte) (int, error)
WriteHeader(statusCode int)
}
HTTP 的客户端中包含几个比较重要的结构体,
http.Client:HTTP 客户端,它的默认值是使用 net/http.DefaultTransport 的 HTTP 客户端http.Transport:是http.RoundTripper接口的实现,主要作用就是支持 HTTP/HTTPS 请求和 HTTP 代理http.persistConn:封装了一个 TCP 的持久连接,是与远程交换消息的句柄(Handle)
客户端 http.Client 是级别较高的抽象,提供了 HTTP 的一些细节,包括 Cookies 和重定向;而 http.Transport 会处理 HTTP/HTTPS 协议的底层实现细节,其中会包含连接重用、构建请求以及发送请求等功能。本篇主要分析下客户端的 transport 实现。
0x01 一个客户端的基础例子
func doRequest(addr string, port int) error {
client := &http.Client{
Transport: &http.Transport{
Proxy: http.ProxyFromEnvironment,
DialContext: (&net.Dialer{
Timeout: 30 * time.Second,
KeepAlive: 30 * time.Second,
DualStack: true,
}).DialContext,
MaxIdleConns: 100,
MaxIdleConnsPerHost: 100,
IdleConnTimeout: 90 * time.Second,
},
}
// construct encoded endpoint
Url, err := url.Parse(fmt.Sprintf("http://%s:%d", addr, port))
if err != nil {
return err
}
Url.Path += "/some_apipath"
endpoint := Url.String()
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", endpoint, nil)
if err != nil {
return err
}
rsp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// close the connection to reuse it
defer rsp.Body.Close()
if rsp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return fmt.Errorf("get rsp error: %v", rsp)
}
return err
}
0x01 http.RoundTripper
http.RoundTripper 包含如下所示的层级结构,每个 http.RoundTripper 接口的实现都包含了一种向远程发出请求的过程;http.Handler 的多种实现为客户端的 HTTP 请求提供不同的服务。
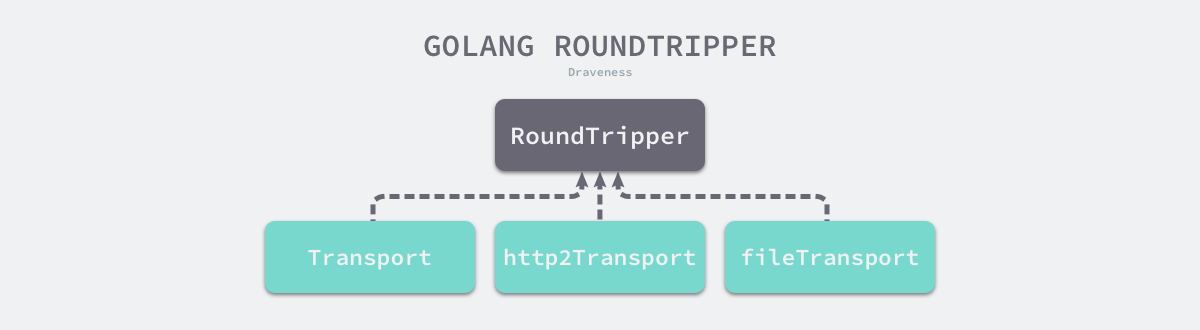
net/http 库发送 http 请求,最后都是调用 transport 的 RoundTrip 方法,说白了,就是你给它一个 Request, 它给你一个 Response:
//RoundTrip executes a single HTTP transaction, returning the Response for the request req.
//(RoundTrip 代表一个 http 事务,给一个请求返回一个响应)
type RoundTripper interface {
RoundTrip(*Request) (*Response, error)
}
0x02 http.Client 结构
0x03 http.Transport 结构
http.Transport实现了http.RoundTripper,支持 HTTP/HTTPS 以及 HTTP Proxy(for either HTTP or HTTPS with CONNECT)http.Transport默认实现了 TCP 连接池,会复用底层 TCP 连接,这个特性的指导意义是,在现网的场景时,初始化一次http.Transport为全局变量,然后重复使用,这样可以避免大量创建连接http.Transport对 HTTP URLs 使用 HTTP/1.1 协议;对 HTTPS URLs 使用 HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2,具体使用哪种协议要取决于 Transport 的配置以及服务端是否支持 HTTP/2 协议http.Transport只有在遇到网络故障的情况下会重试幂等的请求。另外,http Transport 实现了 goroutine-safe
// Transport is an implementation of RoundTripper that supports HTTP,
// HTTPS, and HTTP proxies (for either HTTP or HTTPS with CONNECT).
//
// By default, Transport caches connections for future re-use.
// This may leave many open connections when accessing many hosts.
// This behavior can be managed using Transport's CloseIdleConnections method
// and the MaxIdleConnsPerHost and DisableKeepAlives fields.
//
// Transports should be reused instead of created as needed.
// Transports are safe for concurrent use by multiple goroutines.
//
// A Transport is a low-level primitive for making HTTP and HTTPS requests.
// For high-level functionality, such as cookies and redirects, see Client.
//
// Transport uses HTTP/1.1 for HTTP URLs and either HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2
// for HTTPS URLs, depending on whether the server supports HTTP/2,
// and how the Transport is configured. The DefaultTransport supports HTTP/2.
// To explicitly enable HTTP/2 on a transport, use golang.org/x/net/http2
// and call ConfigureTransport. See the package docs for more about HTTP/2.
//
// Responses with status codes in the 1xx range are either handled
// automatically (100 expect-continue) or ignored. The one
// exception is HTTP status code 101 (Switching Protocols), which is
// considered a terminal status and returned by RoundTrip. To see the
// ignored 1xx responses, use the httptrace trace package's
// ClientTrace.Got1xxResponse.
//
// Transport only retries a request upon encountering a network error
// if the request is idempotent and either has no body or has its
// Request.GetBody defined. HTTP requests are considered idempotent if
// they have HTTP methods GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, or TRACE; or if their
// Header map contains an "Idempotency-Key" or "X-Idempotency-Key"
// entry. If the idempotency key value is an zero-length slice, the
// request is treated as idempotent but the header is not sent on the
// wire.
type Transport struct {
idleMu sync.Mutex
closeIdle bool // user has requested to close all idle conns
idleConn map[connectMethodKey][]*persistConn // most recently used at end
idleConnWait map[connectMethodKey]wantConnQueue // waiting getConns
idleLRU connLRU
reqMu sync.Mutex
reqCanceler map[*Request]func(error)
altMu sync.Mutex // guards changing altProto only
altProto atomic.Value // of nil or map[string]RoundTripper, key is URI scheme
connsPerHostMu sync.Mutex
connsPerHost map[connectMethodKey]int
connsPerHostWait map[connectMethodKey]wantConnQueue // waiting getConns
// Proxy specifies a function to return a proxy for a given
// Request. If the function returns a non-nil error, the
// request is aborted with the provided error.
//
// The proxy type is determined by the URL scheme. "http",
// "https", and "socks5" are supported. If the scheme is empty,
// "http" is assumed.
//
// If Proxy is nil or returns a nil *URL, no proxy is used.
Proxy func(*Request) (*url.URL, error)
// DialContext specifies the dial function for creating unencrypted TCP connections.
// If DialContext is nil (and the deprecated Dial below is also nil),
// then the transport dials using package net.
//
// DialContext runs concurrently with calls to RoundTrip.
// A RoundTrip call that initiates a dial may end up using
// a connection dialed previously when the earlier connection
// becomes idle before the later DialContext completes.
DialContext func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// Dial specifies the dial function for creating unencrypted TCP connections.
//
// Dial runs concurrently with calls to RoundTrip.
// A RoundTrip call that initiates a dial may end up using
// a connection dialed previously when the earlier connection
// becomes idle before the later Dial completes.
//
// Deprecated: Use DialContext instead, which allows the transport
// to cancel dials as soon as they are no longer needed.
// If both are set, DialContext takes priority.
Dial func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// DialTLS specifies an optional dial function for creating
// TLS connections for non-proxied HTTPS requests.
//
// If DialTLS is nil, Dial and TLSClientConfig are used.
//
// If DialTLS is set, the Dial hook is not used for HTTPS
// requests and the TLSClientConfig and TLSHandshakeTimeout
// are ignored. The returned net.Conn is assumed to already be
// past the TLS handshake.
DialTLS func(network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// TLSClientConfig specifies the TLS configuration to use with
// tls.Client.
// If nil, the default configuration is used.
// If non-nil, HTTP/2 support may not be enabled by default.
TLSClientConfig *tls.Config
// TLSHandshakeTimeout specifies the maximum amount of time waiting to
// wait for a TLS handshake. Zero means no timeout.
TLSHandshakeTimeout time.Duration
// DisableKeepAlives, if true, disables HTTP keep-alives and
// will only use the connection to the server for a single
// HTTP request.
//
// This is unrelated to the similarly named TCP keep-alives.
DisableKeepAlives bool
// DisableCompression, if true, prevents the Transport from
// requesting compression with an "Accept-Encoding: gzip"
// request header when the Request contains no existing
// Accept-Encoding value. If the Transport requests gzip on
// its own and gets a gzipped response, it's transparently
// decoded in the Response.Body. However, if the user
// explicitly requested gzip it is not automatically
// uncompressed.
DisableCompression bool
// MaxIdleConns controls the maximum number of idle (keep-alive)
// connections across all hosts. Zero means no limit.
MaxIdleConns int
// MaxIdleConnsPerHost, if non-zero, controls the maximum idle
// (keep-alive) connections to keep per-host. If zero,
// DefaultMaxIdleConnsPerHost is used.
MaxIdleConnsPerHost int
// MaxConnsPerHost optionally limits the total number of
// connections per host, including connections in the dialing,
// active, and idle states. On limit violation, dials will block.
//
// Zero means no limit.
MaxConnsPerHost int
// IdleConnTimeout is the maximum amount of time an idle
// (keep-alive) connection will remain idle before closing
// itself.
// Zero means no limit.
IdleConnTimeout time.Duration
// ResponseHeaderTimeout, if non-zero, specifies the amount of
// time to wait for a server's response headers after fully
// writing the request (including its body, if any). This
// time does not include the time to read the response body.
ResponseHeaderTimeout time.Duration
// ExpectContinueTimeout, if non-zero, specifies the amount of
// time to wait for a server's first response headers after fully
// writing the request headers if the request has an
// "Expect: 100-continue" header. Zero means no timeout and
// causes the body to be sent immediately, without
// waiting for the server to approve.
// This time does not include the time to send the request header.
ExpectContinueTimeout time.Duration
// TLSNextProto specifies how the Transport switches to an
// alternate protocol (such as HTTP/2) after a TLS NPN/ALPN
// protocol negotiation. If Transport dials an TLS connection
// with a non-empty protocol name and TLSNextProto contains a
// map entry for that key (such as "h2"), then the func is
// called with the request's authority (such as"example.com"
// or "example.com:1234") and the TLS connection. The function
// must return a RoundTripper that then handles the request.
// If TLSNextProto is not nil, HTTP/2 support is not enabled
// automatically.
TLSNextProto map[string]func(authority string, c *tls.Conn) RoundTripper
// ProxyConnectHeader optionally specifies headers to send to
// proxies during CONNECT requests.
ProxyConnectHeader Header
// MaxResponseHeaderBytes specifies a limit on how many
// response bytes are allowed in the server's response
// header.
//
// Zero means to use a default limit.
MaxResponseHeaderBytes int64
// WriteBufferSize specifies the size of the write buffer used
// when writing to the transport.
// If zero, a default (currently 4KB) is used.
WriteBufferSize int
// ReadBufferSize specifies the size of the read buffer used
// when reading from the transport.
// If zero, a default (currently 4KB) is used.
ReadBufferSize int
// nextProtoOnce guards initialization of TLSNextProto and
// h2transport (via onceSetNextProtoDefaults)
nextProtoOnce sync.Once
h2transport h2Transport // non-nil if http2 wired up
tlsNextProtoWasNil bool // whether TLSNextProto was nil when the Once fired
// ForceAttemptHTTP2 controls whether HTTP/2 is enabled when a non-zero
// Dial, DialTLS, or DialContext func or TLSClientConfig is provided.
// By default, use of any those fields conservatively disables HTTP/2.
// To use a custom dialer or TLS config and still attempt HTTP/2
// upgrades, set this to true.
ForceAttemptHTTP2 bool
}
RoundTrip 方法
下面代码是 httputil.ReverseProxy 中用来转发请求的逻辑,最终还是调用 transport.RoundTrip(outreq) 来发送 http 请求:
func (p *ReverseProxy) ServeHTTP(rw http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
//...
transport := p.Transport
if transport == nil {
transport = http.DefaultTransport
}
// 向下游发起请求
res, err := transport.RoundTrip(outreq)
if err != nil {
p.getErrorHandler()(rw, outreq, err)
return
}
//...
}
看下 roundTrip 方法的实现,完全遵守了原生库的约定:
// RoundTrip implements the RoundTripper interface.
//
// For higher-level HTTP client support (such as handling of cookies
// and redirects), see Get, Post, and the Client type.
//
// Like the RoundTripper interface, the error types returned
// by RoundTrip are unspecified.
func (t *Transport) RoundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error) {
return t.roundTrip(req)
}
// roundTrip implements a RoundTripper over HTTP.
func (t *Transport) roundTrip(req *Request) (*Response, error) {
t.nextProtoOnce.Do(t.onceSetNextProtoDefaults)
ctx := req.Context()
trace := httptrace.ContextClientTrace(ctx)
if req.URL == nil {
req.closeBody()
return nil, errors.New("http: nil Request.URL")
}
if req.Header == nil {
req.closeBody()
return nil, errors.New("http: nil Request.Header")
}
scheme := req.URL.Scheme
isHTTP := scheme == "http" || scheme == "https"
if isHTTP {
for k, vv := range req.Header {
if !httpguts.ValidHeaderFieldName(k) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid header field name %q", k)
}
for _, v := range vv {
if !httpguts.ValidHeaderFieldValue(v) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid header field value %q for key %v", v, k)
}
}
}
}
if t.useRegisteredProtocol(req) {
altProto, _ := t.altProto.Load().(map[string]RoundTripper)
if altRT := altProto[scheme]; altRT != nil {
if resp, err := altRT.RoundTrip(req); err != ErrSkipAltProtocol {
return resp, err
}
}
}
if !isHTTP {
req.closeBody()
return nil, &badStringError{"unsupported protocol scheme", scheme}
}
if req.Method != "" && !validMethod(req.Method) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("net/http: invalid method %q", req.Method)
}
if req.URL.Host == "" {
req.closeBody()
return nil, errors.New("http: no Host in request URL")
}
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
req.closeBody()
return nil, ctx.Err()
default:
}
// treq gets modified by roundTrip, so we need to recreate for each retry.
treq := &transportRequest{Request: req, trace: trace}
cm, err := t.connectMethodForRequest(treq)
if err != nil {
req.closeBody()
return nil, err
}
// Get the cached or newly-created connection to either the
// host (for http or https), the http proxy, or the http proxy
// pre-CONNECTed to https server. In any case, we'll be ready
// to send it requests.
pconn, err := t.getConn(treq, cm)
if err != nil {
t.setReqCanceler(req, nil)
req.closeBody()
return nil, err
}
var resp *Response
if pconn.alt != nil {
// HTTP/2 path.
t.setReqCanceler(req, nil) // not cancelable with CancelRequest
resp, err = pconn.alt.RoundTrip(req)
} else {
resp, err = pconn.roundTrip(treq)
}
if err == nil {
return resp, nil
}
// Failed. Clean up and determine whether to retry.
_, isH2DialError := pconn.alt.(http2erringRoundTripper)
if http2isNoCachedConnError(err) || isH2DialError {
t.removeIdleConn(pconn)
t.decConnsPerHost(pconn.cacheKey)
}
if !pconn.shouldRetryRequest(req, err) {
// Issue 16465: return underlying net.Conn.Read error from peek,
// as we've historically done.
if e, ok := err.(transportReadFromServerError); ok {
err = e.err
}
return nil, err
}
testHookRoundTripRetried()
// Rewind the body if we're able to.
if req.GetBody != nil {
newReq := *req
var err error
newReq.Body, err = req.GetBody()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req = &newReq
}
}
}