0x00 前言
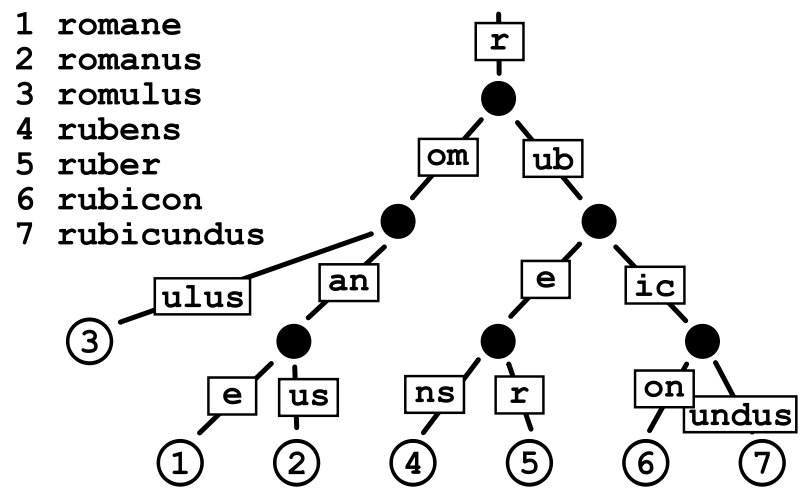
本文着重介绍 bm(gin) 框架的路由树构造算法。
从前几篇文章已知,bm(gin) 框架也是使用了压缩的 Trie 树 作为路由 Path 的存储结构,本文分析根据设置的路由请求构建路由压缩 Trie 树的代码实现 细节。
相较于普通的 Trie 树,压缩版本的树能显著减少树的层数,同时因为每个节点上数据存储也比通常的 Trie 树要多。
0x01 HTTPRouter 及示例
关于 HTTPRouter,在设计路由的时候需要规避一些会导致路由冲突的情况。一般而言,如果两个路由拥有一致的 HTTP 方法 (指 GET/POST/PUT/DELETE 等) 和请求路径前缀,且在某个位置出现了 A 路由是 wildcard(指 :id 这种形式)参数,B 路由则是普通字符串,那么就会发生路由冲突。路由冲突会在初始化阶段直接 panic。下面给出了冲突的路由示例:
conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
GET /user/:id
no conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
POST /user/:id
压缩字典树的构造
本小节基于下面的路由来构建一颗压缩 Trie 树:
PUT /user/installations/:installation_id/repositories/:repository_id
GET /marketplace_listing/plans/
GET /marketplace_listing/plans/:id/accounts
GET /search
GET /status
GET /support
// 附:补充路由:
GET /marketplace_listing/plans/ohyes
插入部分的代码 主要在此:
1、node 节点的结构
Radix Tree 的节点类型为 *bm.node:
type node struct {
path string
indices string
children []*node
handlers []HandlerFunc
priority uint32
nType nodeType
maxParams uint8
wildChild bool
}
关键的字段说明如下:
children:保存该节点所有子节点 node 的指针path:当前节点对应的路径中的字符串(相对路径)wildChild:子节点是否为参数节点,即 wildcard node,或者说:id这种类型的节点indices:子节点索引,当子节点为非参数类型,即本节点的 wildChild 为false时,会将每个子节点的首字母放在该索引数组(在 golang 中为string)nType: 当前节点类型,有四个枚举值:分别为static/root/param/catchAllstatic:非根节点的普通字符串节点root:根节点param:参数节点,例如:idcatchAll:通配符节点,例如*anyway
2、root 节点创建(PUT)
本例子中路由有 GET 和 POST 两种方法,那么每一种方法对应的都是一棵独立的压缩 Trie 树,这些树之间是独立的。任何 HTTP 方法首次插入的路由就会导致对应字典树的根节点(Root)被创建,如下:
r := httprouter.New()
// 创建 PUT 的 root 节点
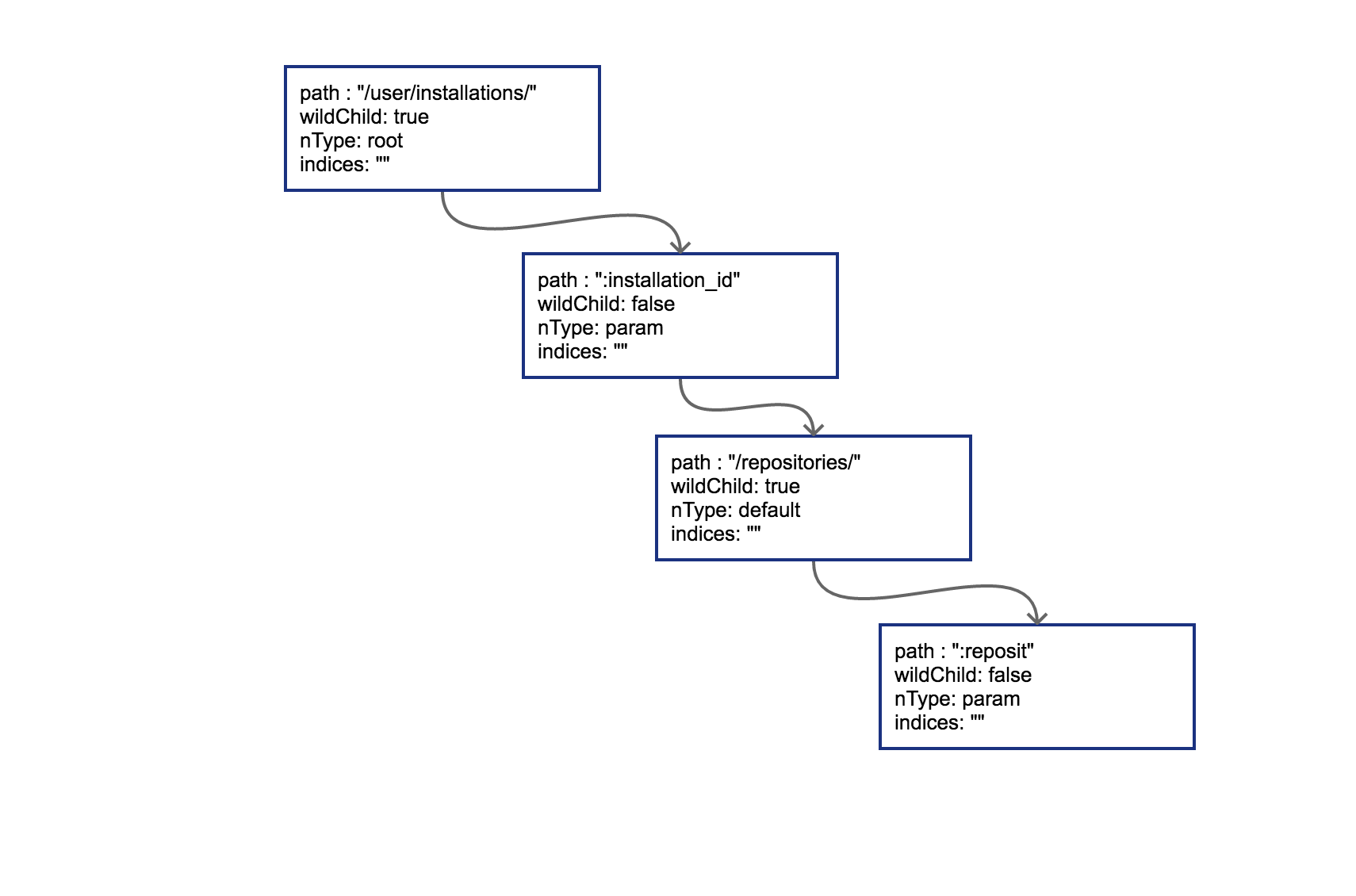
r.PUT("/user/installations/:installation_id/repositories/:reposit", Hello)
该 PUT 方法对应的树如下,根据 代码构建的逻辑,PUT 对应的根节点被创建出来,此外,根据 wildcard 的规则,该路由 /user/installations/:installation_id/repositories/:reposit 被构建为一棵有 4 个节点的树,Root 节点的 Path 信息为 /user/installations/:
3、root 节点创建(GET)
插入第一条 GET 路由,当插入 GET /marketplace_listing/plans 时,类似前面 PUT 的过程,建立了一棵 GET 树,因为第一个路由没有 wildcard 参数,path 都被存储到 Root 节点上了。目前只有一个 Root 节点:

对应的关键信息如下:
path: /marketplace_listing/plans
wildChild: false
indices: ""
nType: root
4、插入普通节点(GET):新路由可以直接作为原路由的子节点进行插入
然后插入路由 GET /marketplace_listing/plans/:id/accounts,新的路径与之前的路径有共同的前缀(和现有树的 node 进行比较,找到共同的前缀),且可以直接在之前叶子节点后进行插入,不过由于本路径存在 wildcard,所以需要对此路由进行拆分:
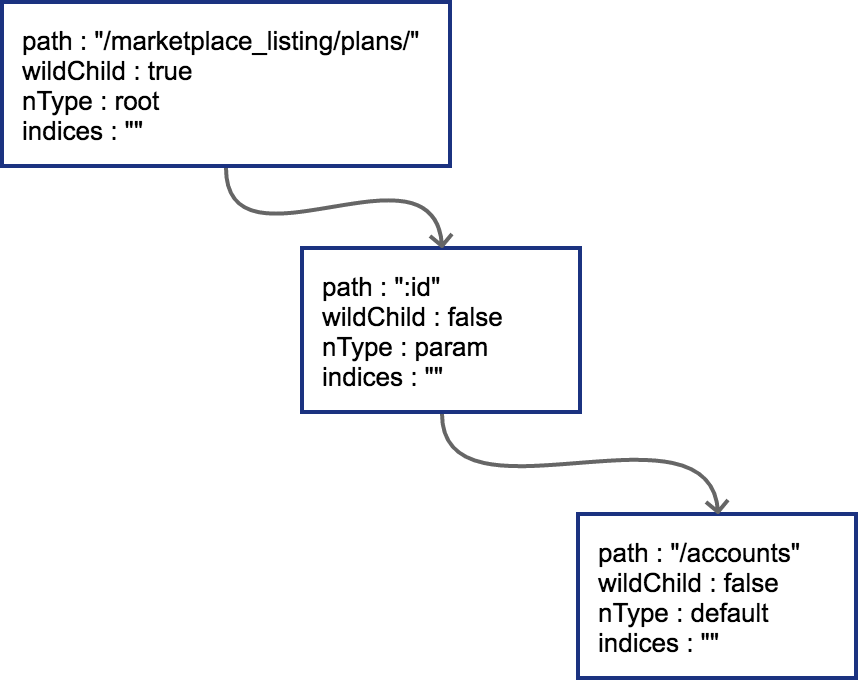
PS:由于 :id 这个节点只有一个字符串的普通子节点,所以目前不需要处理 indices
5、导致边分裂的情况(GET)
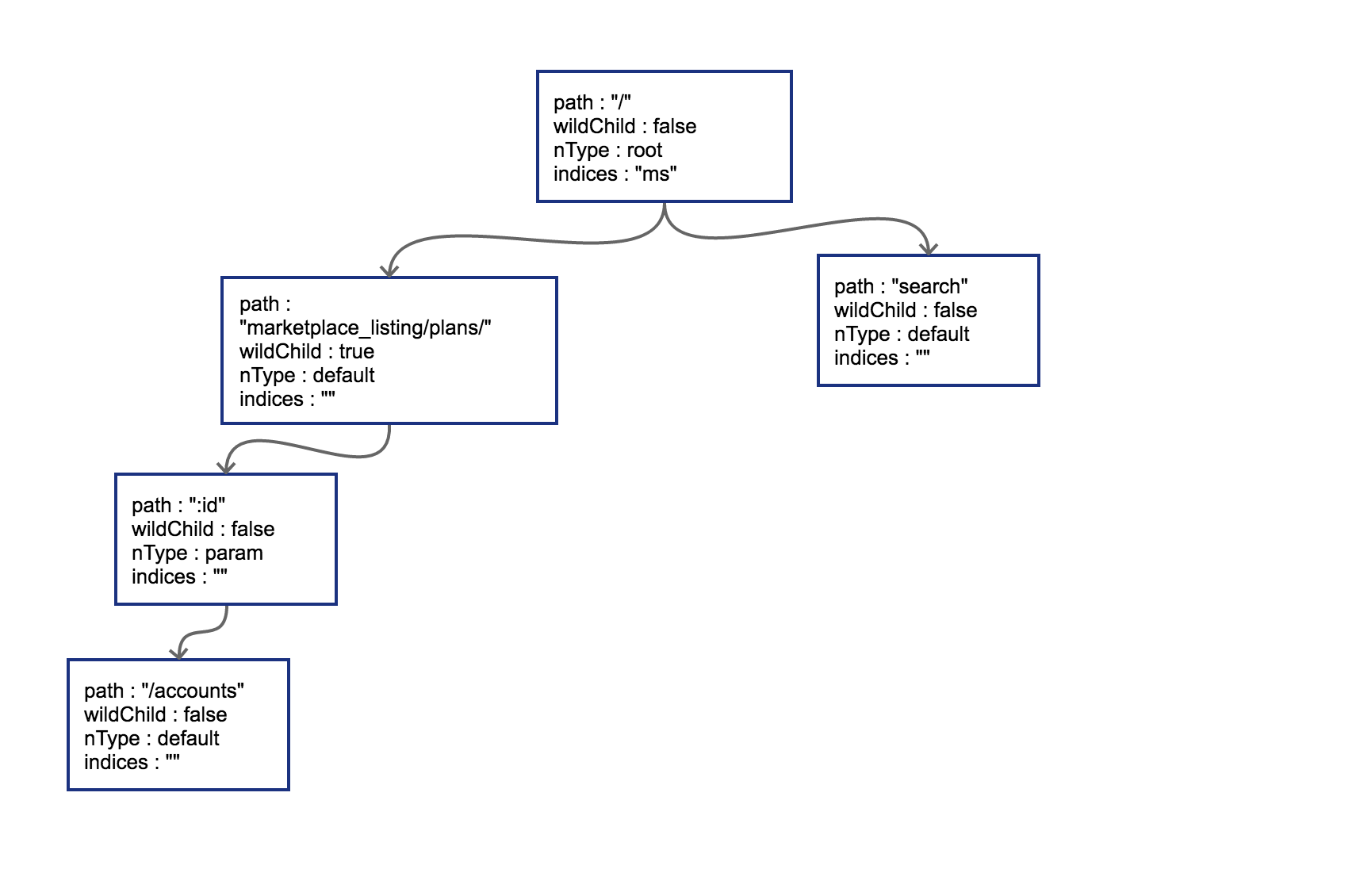
下一条插入路由为 GET /search,这时 会导致树的边分裂 。原有树的 node 路径和新的路径在初始的 / 位置发生分裂,这样需要把原有的 root 节点内容下移,再将新路由 search 同样作为子节点挂在 root 节点之下。这时候因为子节点出现多个,root 节点的 indices 提供子节点索引,即 ms 代表子节点的首字母分别为 m(marketplace)和 s(search):
6、继续导致边分裂的情况(GET)
继续插入录入 GET /status 和 GET /support 这两个路由。这时候会导致在 search 节点上再次发生分裂:
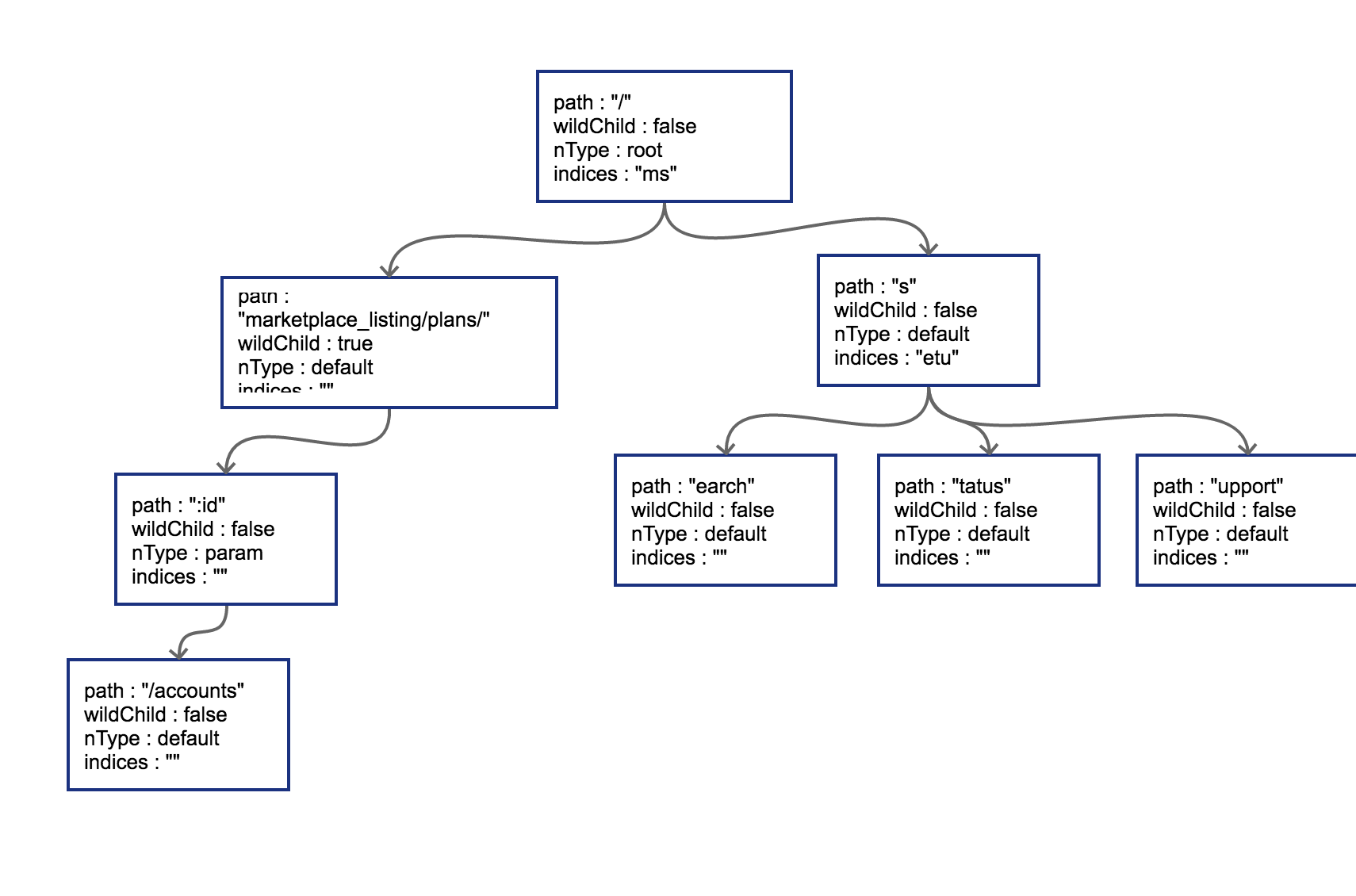
子节点冲突处理
从上面插入的 case 来看,理解子节点冲突处理的规则对理解路由树算法有非常大的帮助,只要发生冲突,都会在初始化的时候 panic。在路由本身只有字符串的情况下,不会发生任何冲突。只有当路由中含有 wildcard(类似 :id)或者 catchAll 的情况下才可能冲突。子节点的冲突处理的规则分几种情况:
- 在插入 wildcard 节点时,父节点的
children数组非空且wildChild被设置为false时。例如:(先插入)GET /user/getAll和 (再插入)GET /user/:id/getAddr,或者GET /user/*aaa和GET /user/:id - 在插入 wildcard 节点时,父节点的
children数组非空且wildChild被设置为true,但该父节点的 wildcard 子节点要插入的 wildcard 名字(:后面的字符串)不一样。例如:GET /user/:id/info和GET /user/:name/info - 在插入 catchAll 节点时,父节点的
children非空。例如:GET /src/abc和GET /src/*filename,或者GET /src/:id和GET /src/*filename - 在插入 static 节点时,父节点的
wildChild字段被设置为true - 在插入 static 节点时,父节点的
children非空,且子节点nType为 catchAll
例如,在上面的树中,插入路由 GET /marketplace_listing/plans/ohyes 时,出现第 4 种冲突情况:它的父节点 marketplace_listing/plans/ 的 wildChild 字段为 true
0x02 路由结构
在 bm.Engine 成员中,trees 是一个 Slice,不同的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST/DELETE 等),都会创建一个 methodTree,每个 methodTree 即为 Trie 树,即每个 HTTP Method 对应一棵 Trie 树。树的节点按照 URL 中的 / 符号进行层级划分,URL 支持 :name 形式的名称匹配,还支持 *subpath 形式的路径通配符。
每个节点都会挂接若干请求处理函数构成一个请求处理链 HandlersChain。当一个请求到来时,在这棵树上找到请求 URL 对应的节点,拿到对应的请求处理链来执行就完成了请求的处理。
type Engine struct {
......
trees methodTrees
// 不同的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST/DELETE 等)都对应一棵树
......
}
type methodTrees []methodTree
// 方法树的定义
type methodTree struct {
method string
root *node
}
node 的定义
每个 tree 的节点代表了一条实际注册的路由 PATH,节点(node)的定义如下。根节点 root 通过 node 及包含 children 的 node 数组的结构形成了整个框架的路由树结构。
type node struct {
path string // 当前节点的 path
indices string //
children []*node
handlers HandlersChain
priority uint32
nType nodeType
maxParams uint8
wildChild bool
fullPath string
}
path:表示当前节点的 path; indices:通常情况下维护了 children 列表的 path 的各首字符组成的 string,之所以是通常情况,是在处理包含通配符的 path 处理中会有一些例外情况; priority:代表了有几条路由会经过此节点,用于在节点进行排序时使用; nType:是节点的类型,默认是 static 类型,还包括了 root 类型,对于 path 包含冒号通配符的情况,nType 是 param 类型,对于包含 * 通配符的情况,nType 类型是 catchAll 类型;wildChild:默认是 false,当 children 是 通配符类型时,wildChild 为 true; fullPath:是从 root 节点到当前节点的全部 path 部分;如果此节点为终结节点 handlers 为对应的处理链,否则为 nil;maxParams 是当前节点到各个叶子节点的包含的通配符的最大数量。
Trie 树实例
如下路由创建的代码,对应了 2 棵 Trie 树(POST 和 GET):
engine.GET("/admin/model/get", api.GetTemplate)
engine.GET("/admin/model/query", api.QueryTemplate)
engine.POST("/admin/model/set", api.SetTemplate)
engine.POST("/admin/model/upload", api.UploadTemplate)
engine.POST("/admin/model/uploadv2", api.GetTemplateWithSignature)
engine.POST("/admin/model/update", api.UpdateTemplate)
0x03 路由初始化
路由初始化过程中构建 Trie 树的核心流程如下:
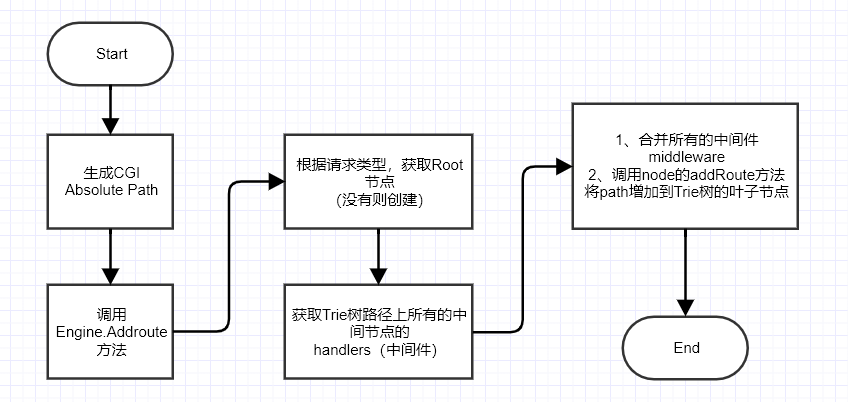
路由的初始化过程,首先生成绝对 path,然后调用 Engine 的 addRoute 方法,根据请求的 method 类型,找到根节点。再调用 node 的 addRoute 方法,将 path 增加到树的合适节点。这个过程是路由初始化过程中构建前缀树的核心流程
Engine.addRoute 方法
首先,注意 addRoute 方法 是一个内部方法,参数中 handlers(多个,最后一个为业务 logic)为中间件:
func (engine *Engine) addRoute(method, path string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) {
// 参数校验
if path[0] != '/' {
panic("blademaster: path must begin with'/'")
}
if method == "" {
panic("blademaster: HTTP method can not be empty")
}
if len(handlers) == 0 {
panic("blademaster: there must be at least one handler")
}
if _, ok := engine.metastore[path]; !ok {
engine.metastore[path] = make(map[string]interface{})
}
engine.metastore[path]["method"] = method
// 获取对应 method 的 Trie 树的 root 根节点,如果不存在则创建
root := engine.trees.get(method)
if root == nil {
// 新的 root 节点
root = new(node)
engine.trees = append(engine.trees, methodTree{method: method, root: root})
}
prelude := func(c *Context) {
c.method = method
c.RoutePath = path
}
handlers = append([]HandlerFunc{prelude}, handlers...)
// 调用 root 节点的 addRoute 方法添加到路由树,path 为绝对路径
root.addRoute(path, handlers)
}
node.insertChild:增加孩子节点
上面的 root.addRoute 中 https://github.com/go-kratos/kratos/blob/master/pkg/net/http/blademaster/tree.go#L254
func (n *node) insertChild(numParams uint8, path string, fullPath string, handlers []HandlerFunc) {
var offset int // already handled bytes of the path
// find prefix until first wildcard (beginning with ':' or '*')
for i, max := 0, len(path); numParams > 0; i++ {
c := path[i]
if c != ':' && c != '*' {
continue
}
// find wildcard end (either '/' or path end)
end := i + 1
for end <max && path[end] != '/' {
switch path[end] {
// the wildcard name must not contain ':' and '*'
case ':', '*':
panic("only one wildcard per path segment is allowed, has:'" +
path[i:] + "'in path'" + fullPath + "'")
default:
end++
}
}
// check if this Node existing children which would be
// unreachable if we insert the wildcard here
if len(n.children) > 0 {
panic("wildcard route'" + path[i:end] +
"'conflicts with existing children in path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
// check if the wildcard has a name
if end-i < 2 {
panic("wildcards must be named with a non-empty name in path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
if c == ':' { // param
// split path at the beginning of the wildcard
if i > 0 {
n.path = path[offset:i]
offset = i
}
child := &node{
nType: param,
maxParams: numParams,
}
n.children = []*node{child}
n.wildChild = true
n = child
n.priority++
numParams--
// if the path doesn't end with the wildcard, then there
// will be another non-wildcard subpath starting with '/'
if end < max {
n.path = path[offset:end]
offset = end
child := &node{
maxParams: numParams,
priority: 1,
}
n.children = []*node{child}
n = child
}
} else { // catchAll
if end != max || numParams > 1 {
panic("catch-all routes are only allowed at the end of the path in path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
if len(n.path) > 0 && n.path[len(n.path)-1] == '/' {
panic("catch-all conflicts with existing handle for the path segment root in path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
// currently fixed width 1 for '/'
i--
if path[i] != '/' {
panic("no / before catch-all in path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
n.path = path[offset:i]
// first node: catchAll node with empty path
child := &node{
wildChild: true,
nType: catchAll,
maxParams: 1,
}
n.children = []*node{child}
n.indices = string(path[i])
n = child
n.priority++
// second node: node holding the variable
child = &node{
path: path[i:],
nType: catchAll,
maxParams: 1,
handlers: handlers,
priority: 1,
}
n.children = []*node{child}
return
}
}
// insert remaining path part and handle to the leaf
n.path = path[offset:]
n.handlers = handlers
}
####
接下来,看下如何构建 Trie 树,前面已经给出了 Trie 树 node 节点 的结构,先看下 [node.addRoute 方法]((https://github.com/go-kratos/kratos/blob/master/pkg/net/http/blademaster/tree.go#L125):
// addRoute adds a node with the given handle to the path.
// Not concurrency-safe!
func (n *node) addRoute(path string, handlers []HandlerFunc) {
//path 为 CGI 绝对路径
fullPath := path
n.priority++
// 计算 path 中通配符的数量,即冒号和星号的数量
numParams := countParams(path)
// non-empty tree
if len(n.path) > 0 || len(n.children) > 0 {
walk:
for {
// Update maxParams of the current node
if numParams > n.maxParams {
n.maxParams = numParams
}
// Find the longest common prefix.
// This also implies that the common prefix contains no ':' or '*'
// since the existing key can't contain those chars.
// 计算 path 和当前节点的 path 的共同前缀长度
i := 0
max := min(len(path), len(n.path))
for i <max && path[i] == n.path[i] {
i++
}
// Split edge
if i <len(n.path) {
child := node{
path: n.path[i:],
wildChild: n.wildChild,
indices: n.indices,
children: n.children,
handlers: n.handlers,
priority: n.priority - 1,
}
// Update maxParams (max of all children)
for i := range child.children {
if child.children[i].maxParams > child.maxParams {
child.maxParams = child.children[i].maxParams
}
}
n.children = []*node{&child}
// []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65
n.indices = string([]byte{n.path[i]})
n.path = path[:i]
n.handlers = nil
n.wildChild = false
}
// Make new node a child of this node
if i <len(path) {
path = path[i:]
if n.wildChild {
n = n.children[0]
n.priority++
// Update maxParams of the child node
if numParams > n.maxParams {
n.maxParams = numParams
}
numParams--
// Check if the wildcard matches
if len(path) >= len(n.path) && n.path == path[:len(n.path)] {
// check for longer wildcard, e.g. :name and :names
if len(n.path) >= len(path) || path[len(n.path)] == '/' {
continue walk
}
}
pathSeg := path
if n.nType != catchAll {
pathSeg = strings.SplitN(path, "/", 2)[0]
}
prefix := fullPath[:strings.Index(fullPath, pathSeg)] + n.path
panic("'" + pathSeg +
"'in new path'" + fullPath +
"'conflicts with existing wildcard'" + n.path +
"'in existing prefix'" + prefix +
"'")
}
c := path[0]
// slash after param
if n.nType == param && c == '/' && len(n.children) == 1 {
n = n.children[0]
n.priority++
continue walk
}
// Check if a child with the next path byte exists
for i := 0; i <len(n.indices); i++ {
if c == n.indices[i] {
i = n.incrementChildPrio(i)
n = n.children[i]
continue walk
}
}
// Otherwise insert it
if c != ':' && c != '*' {
// []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65
n.indices += string([]byte{c})
child := &node{
maxParams: numParams,
}
n.children = append(n.children, child)
n.incrementChildPrio(len(n.indices) - 1)
n = child
}
n.insertChild(numParams, path, fullPath, handlers)
return
} else if i == len(path) { // Make node a (in-path) leaf
if n.handlers != nil {
panic("handlers are already registered for path'" + fullPath + "'")
}
n.handlers = handlers
}
return
}
} else { // Empty tree
n.insertChild(numParams, path, fullPath, handlers)
n.nType = root
}
}