0x00 前言
Nginx 中有个 reload 指令,提供了不重启服务下针对配置文件的热加载能力,本文讨论下在 golang 下的文件热加载实现。
- 通过 signal 手动触发
- 通过文件监听 notify 自动触发
0x01 golang 中的实现
手动触发
要点有如下几点:
- 配置文件指针化,并且加锁保护(配置的单例模式)
- 捕获信号,重新读配置
- 在代码逻辑引用配置文件的核心路径上,读出配置文件的字段
1、初始化配置
通常来说,在一个进程周期,配置文件仅需解析一次,建议使用单例模式实现 config 的解析,go 中可以使用 sync.Once 实现
var (
cfg * tomlConfig
once sync.Once
cfgLock = new(sync.RWMutex)
)
func Config() *tomlConfig {
once.Do(ReloadConfig)
cfgLock.RLock()
defer cfgLock.RUnlock()
return cfg
}
func ReloadConfig() {
filePath, err := filepath.Abs(configPath)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
config := new(tomlConfig)
if _ , err := toml.DecodeFile(filePath, config); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cfgLock.Lock()
defer cfgLock.Unlock()
cfg = config
}
2、捕获信号
func handleSignals(){
s := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(s, syscall.SIGUSR1)
for {
<-s
ReloadConfig()
}
}
3、重载后,在程序的路径中使用配置,注意需要调用上面的 Config 方法去获取全局配置(并发安全)
示例代码参见 这里
0x02 viper 库的动态监听实现(v1.13.0)
笔者项目中常用的配置文件解析库是 viper,其热更新机制基于 fsnotify 实现,通常使用如下代码,其中 ReloadConf 是需要开发者自行实现的配置文件解析逻辑:
viperInstance := viper.New() // viper 实例
viperInstance.WatchConfig()
viperInstance.OnConfigChange(func(e fsnotify.Event) {
log.Print("Config file updated.")
ReloadConf(viperInstance) // 加载配置的方法
})
更进一步,通常项目中是这样使用 viper 的:
- 定义配置文件指针为全局变量(配置 lock)
- 子 goroutine 通过全局指针读配置,通过读锁保护
- 当
OnConfigChange触发时,写锁保护重新加载配置
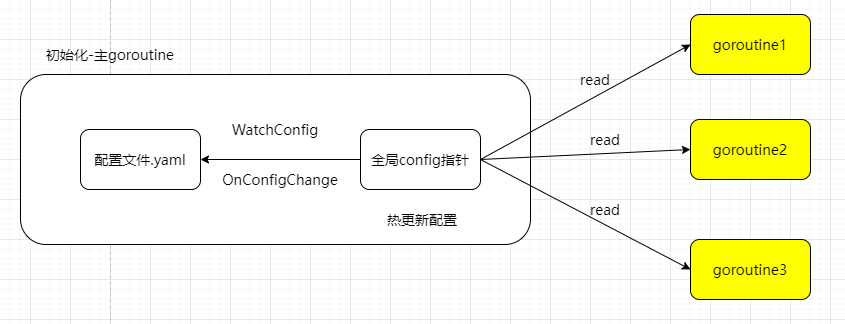
代码示例 在此,特别注意,在 viper 进行动态热更新的时候是否是 goroutine 安全的
viper 结构
viper 结构 定义 如下,注意有个 onConfigChange 成员:
// Note: Vipers are not safe for concurrent Get() and Set() operations.
type Viper struct {
// Delimiter that separates a list of keys
// used to access a nested value in one go
keyDelim string
// A set of paths to look for the config file in
configPaths []string
// The filesystem to read config from.
fs afero.Fs
// A set of remote providers to search for the configuration
remoteProviders []*defaultRemoteProvider
// Name of file to look for inside the path
configName string
configFile string
configType string
configPermissions os.FileMode
envPrefix string
// Specific commands for ini parsing
iniLoadOptions ini.LoadOptions
automaticEnvApplied bool
envKeyReplacer StringReplacer
allowEmptyEnv bool
config map[string]interface{}
override map[string]interface{}
defaults map[string]interface{}
kvstore map[string]interface{}
pflags map[string]FlagValue
env map[string][]string
aliases map[string]string
typeByDefValue bool
onConfigChange func(fsnotify.Event)
//...
}
WatchConfig 方法
WatchConfig方法 开启事件监听,确定用户操作文件后该文件是否可正常读取,并将内容注入到 viper 实例的 config 字段。任何文件的变更事件都可以从 Watcher.Events 这个 channel 中获取到,即 event, ok := <-watcher.Events,这里的 event 有如下属性:
event.Name:监听文件的绝对路径,如/root/xxxx.yamlevent.Op:对文件的操作
WatchConfig 关注的文件变更有两种:
- if the config file was modified or created:(对文件进行了创建操作或写操作)
- if the real path to the config file changed (eg: k8s ConfigMap replacement)
func (v *Viper) WatchConfig() {
initWG := sync.WaitGroup{}
initWG.Add(1)
go func() {
// 用来建立新的文件监听处理,会开启一个协程开始等待读取事件,完成 从 I/O 完成端口读取任务,将事件注入到 Event 对象中
watcher, err := newWatcher()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer watcher.Close()
// we have to watch the entire directory to pick up renames/atomic saves in a cross-platform way
filename, err := v.getConfigFile()
if err != nil {
log.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
initWG.Done()
return
}
configFile := filepath.Clean(filename)
configDir, _ := filepath.Split(configFile)
realConfigFile, _ := filepath.EvalSymlinks(filename)
eventsWG := sync.WaitGroup{}
eventsWG.Add(1)
go func() {
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-watcher.Events:
if !ok { // 'Events' channel is closed
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
currentConfigFile, _ := filepath.EvalSymlinks(filename)
// we only care about the config file with the following cases:
// 1 - if the config file was modified or created
// 2 - if the real path to the config file changed (eg: k8s ConfigMap replacement)
const writeOrCreateMask = fsnotify.Write | fsnotify.Create
// 用来判断操作的文件是否是 configFile,确保是同一个文件
if (filepath.Clean(event.Name) == configFile &&
event.Op&writeOrCreateMask != 0) ||
(currentConfigFile != "" && currentConfigFile != realConfigFile) {
realConfigFile = currentConfigFile
err := v.ReadInConfig()
if err != nil {
log.Printf("error reading config file: %v\n", err)
}
if v.onConfigChange != nil {
// 调用开发者设置的回调方法,处理变更 event
v.onConfigChange(event)
}
} else if filepath.Clean(event.Name) == configFile &&
event.Op&fsnotify.Remove != 0 {
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
case err, ok := <-watcher.Errors:
if ok { // 'Errors' channel is not closed
log.Printf("watcher error: %v\n", err)
}
eventsWG.Done()
return
}
}
}()
watcher.Add(configDir)
initWG.Done() // done initializing the watch in this go routine, so the parent routine can move on...
eventsWG.Wait() // now, wait for event loop to end in this go-routine...
}()
initWG.Wait() // make sure that the go routine above fully ended before returning
}
newWatcher 创建文件监听器:
import "github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify"
type watcher = fsnotify.Watcher
func newWatcher() (*watcher, error) {
return fsnotify.NewWatcher()
}
fsnotify
WatchConfig 开始时,会调用 fsnotify 的 NewWatcher 方法创建一个 file 监听器(以 UNIX 为例):
当监听的文件发生改变时,会通过 sendEvent 方法将 events 发送到 channel w.Events 中
// NewWatcher creates a new Watcher.
func NewWatcher() (*Watcher, error) {
// Create inotify fd
// Need to set the FD to nonblocking mode in order for SetDeadline methods to work
// Otherwise, blocking i/o operations won't terminate on close
fd, errno := unix.InotifyInit1(unix.IN_CLOEXEC | unix.IN_NONBLOCK)
if fd == -1 {
return nil, errno
}
w := &Watcher{
fd: fd,
inotifyFile: os.NewFile(uintptr(fd), ""),
watches: make(map[string]*watch),
paths: make(map[int]string),
Events: make(chan Event),
Errors: make(chan error),
done: make(chan struct{}),
doneResp: make(chan struct{}),
}
//https://github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify/blob/main/backend_inotify.go#L335
go w.readEvents()
return w, nil
}
// Returns true if the event was sent, or false if watcher is closed.
func (w *Watcher) sendEvent(e Event) bool {
select {
case w.Events <- e:
return true
case <-w.done:
}
return false
}
OnConfigChange 方法
OnConfigChange方法 是调用用户传入的方法,即执行 v.onConfigChange(event) 逻辑,通常我们不 care 这个 event 的内容(特殊情况下比如对文件做增量监控需要对 event 进行细化处理),直接读取所有配置再重新 reload 就好
func OnConfigChange(run func(in fsnotify.Event)) {
v.OnConfigChange(run)
}
func (v *Viper) OnConfigChange(run func(in fsnotify.Event)) {
v.onConfigChange = run
}
如果想完整的处理 events 事件,可以尝试如下代码:
// 监听配置变化
viper.WatchConfig()
// 配置改变时的回调
viper.OnConfigChange(func(in fsnotify.Event) {
switch in.Op {
case fsnotify.Create:
fmt.Println("notify file event Create")
case fsnotify.Remove:
fmt.Println("notify file event Remove")
case fsnotify.Rename:
fmt.Println("notify file event Rename")
case fsnotify.Write:
fmt.Println("notify file event Write")
case fsnotify.Chmod:
fmt.Println("notify file event Chmod")
}
})
讨论:viper 的 OnConfigChange 方法并发安全性?
关于这个话题,看到了不少讨论:
- viper dynamically loading config file has data race
- Concurrency-safe way to use viper.WatchConfig()? #378
0x03 ConfigMap/secrets 的(container)热更新
在 kubernetes 场景下,ConfigMap 更新时,希望其关联的 Deployment 的业务逻辑也能随之更新,有哪些可行且高效的方案?最好的办法是在当 ConfigMap 发生变更时,直接热更新,从而做到不影响 Pod 的正常运行;兜底方案是(假如无法热更新),就需要触发 Deployment 滚动更新
ConfigMap 更新的问题
ConfigMap volume 的更新机制如下,更新操作由 kubelet 的 Pod 同步循环触发。每次进行 Pod 同步时,Kubelet 都会将 Pod 的所有 ConfigMap volume 标记为 ** 需要重新挂载(RequireRemount)**,而 kubelet 的 volume 控制循环会发现这些需要重新挂载的 volume,去执行一次挂载操作。在 ConfigMap 的重新挂载过程中,kubelet 会先比较远端的 ConfigMap 与 volume 中的 ConfigMap 是否一致,不一致时再做更新。
上面的叙述中,获取远端 ConfigMap 这个可能是从缓存中获取(由配置中的 ConfigMapAndSecretChangeDetectionStrategy 决定),不一定能获取到最新版本(最终能完成自动更新,有延迟),最多的可能延迟时间是:
Pod 同步间隔(default 10s) + ConfigMap 本地缓存的 TTL
注意,假如使用了 subPath 将 ConfigMap 中的某个文件单独挂载到其它目录下,那这个文件是无法热更新的(这是 ConfigMap 的挂载逻辑决定的)
1、实时更新
deployment 对配置热更新有实时性要求,建议自行实现 Watch 逻辑
- 业务逻辑中通过 ApiServer 的 API Watch 对应的 ConfigMap 事件变更来做实时更新
- 使用远程配置中心(如 Etcd/Consul 配合 Confd 实现)来管理配置
2、非实时更新 如果没有实时性要求,那么可以依赖 ConfigMap 本身的更新逻辑来完成配置热更新
业务进程重载配置
更新完配置后,还需要通知应用重新读取配置进行业务逻辑上的更新,在 kubernetes 场景下有这么几种方式:
1、业务进程监听本地配置文件
可以在业务进程的实现中加入监听本地文件的变化,在文件变化时触发一次配置热更新。如本文提到的 viper 库,目前版本也支持对 ConfigMap 做 Watch 支持热更新
2、使用 sidecar 来监听本地配置文件变更
建议使用镜像 configmap-reload 来完成,它的逻辑是 Watch 本地文件的变更,并在发生变更时通过 HTTP 调用通知应用进行热更新
viper 支持 ConfigMap 的细节
从上一小节的描述,v1.13.0 也是支持 ConfigMap 更新的,当 ConfigMap 更改时,它所包含的配置文件的实际路径也更改了,所以在 WatchConfig 方法中调用了 filepath.EvalSymlinks 来检测,filepath.EvalSymlinks 会将所有路径的符号链接都解析出来,并且该方法返回的路径,是直接可访问的。
// 如果 path 或返回值是相对路径,则是相对于进程当前工作目录
// 在当前目录下创建一个 test.txt 文件和一个 symlink 目录,在 symlink 目录下对 test.txt 建一个符号链接 test.txt.link
fmt.Println(filepath.EvalSymlinks("symlink/test.txt.link"))
fmt.Println(os.Readlink("symlink/test.txt.link"))
// 输出为:
// test.txt <nil>
// ../test.txt <nil>
0x04 配置中心(远程更新)
基于分布式配置中心,远程更新也是一种方式,如下:
- Etcd + Confd
- Nacos
- Apollo
- Etcd + viper
0x05 小结
还有另外一种基于 atomic.Value实现 的热更方法,如下:
// 利用原子操作动态更新配置文件
var config Value // holds current server configuration
// Create initial config value and store into config.
config.Store(loadConfig()) //loadConfig 从文件读取配置
go func() {
// Reload config every 10 seconds
// and update config value with the new version.
for {
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
config.Store(loadConfig())
}
}()
// Create worker goroutines that handle incoming requests
// using the latest config value.
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
for r := range requests() {
c := config.Load()
// Handle request r using config c.
_, _ = r, c
}
}()
}