0x00 前言
groupcache 是一个分布式缓存库,支持多节点互备热数据,有良好的稳定性和较高的并发性。测试用例,可以参考此文章:Playing with groupcache;此外,还可以参考作者的幻灯片:dl.google.com: Powered by Go
先前讨论缓存更新时,分布式场景下需要解决 缓存更新导致的缓存一致性问题,而 GroupCache 仅支持外部 get,不支持外部 set/update/delete(当然有内部 Set 操作),自然就没有更新导致的缓存一致性问题。由于 GroupCache 只能 get,不能 update 和 delete,也无法设置过期时间,只能通过 lru 算法淘汰最近最少访问的数据;因而 Groupcache 比较适合那些数据长时间不变更的缓存。典型的应用场景是为下载服务提供静态资源缓存
0x01 groupcache-db-experiment 的应用
goupcache 仅仅是缓存库,业务逻辑需要自己构建。文章 给出的部署架构如下:
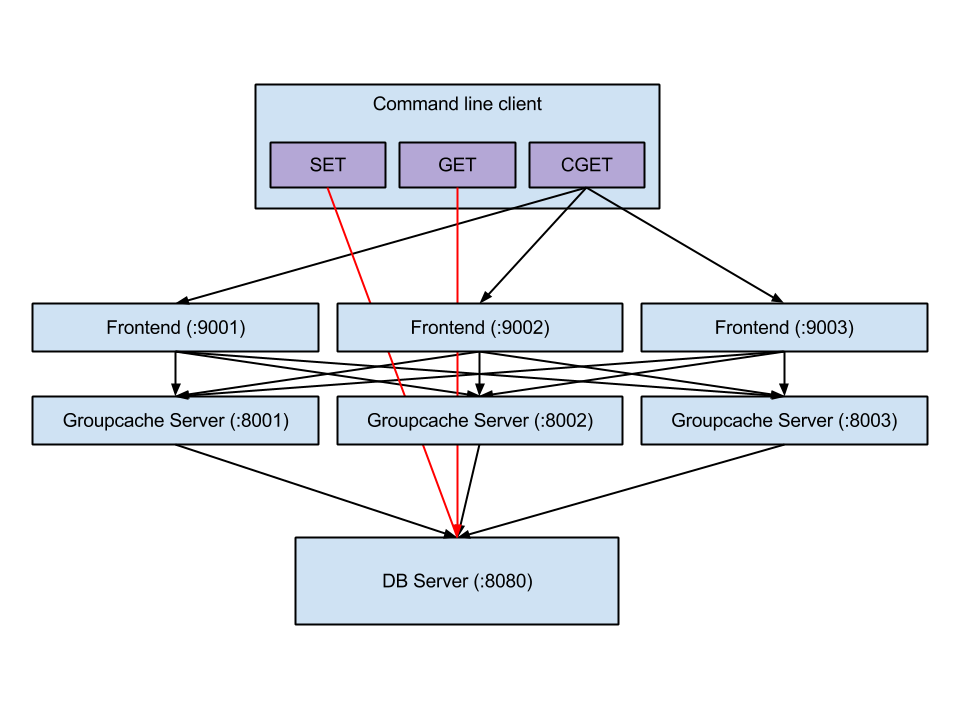
如图,客户端使用 set/get 指令时,直接操作存取的是数据源(数据库 DB Server);使用 cget 指令,则是从 groupcache 中查找数据。该 demo 封装了 groupcache,有如下组件:
- DB-server:模拟本地存储
- frontend-Server(内置了 groupCache Server):监听了
2个 tcp 端口,一个用于和客户端通信,另一个用于和 groupcache peer 进行通信 - Client 客户端:模拟客户端请求
其中,客户端和 groupcache 通过 rpc(net/rpc)进行通信,而 groupcache 的各个 peer 之间通过 http 协议进行通信。set/get 是直接针对数据存储服务器 DB Server 的存取,cget 是通过一个前端 frontend 的 rpc 接口间接访问 groupcache-server 来获取数据,假如 groupcache server 中没有数据,那么就进一步访问数据存储服务器来获取数据,将数据存储在缓存中,并返还给客户端。上述的逻辑如下 代码:
func (s *Frontend) Get(args *api.Load, reply *api.ValueResult) error {
var data []byte
fmt.Printf("cli asked for %s from groupcache\n", args.Key)
// 从 groupcache 中获取缓存数据
err := s.cacheGroup.Get(nil, args.Key,
groupcache.AllocatingByteSliceSink(&data))
reply.Value = string(data)
return err
}
模拟运行
./cli -set -key foo -value bar ## 模拟写入本地存储
./cli -get -key foo should see bar in 300 ms ## 模拟从本地存储读数据
./cli -cget -key foo should see bar in 300ms (cache is loaded) ##
./cli -cget -key foo should see bar instantly ## 从 groupcache 读取并返回
组件分析
[root@VM_120_245_centos ~/tw/groupcache-db-experiment]# tree -a
.
├── api
│ └── api.go #存储数据的基本格式
├── build.sh
├── cli
│ ├── cli
│ └── cli.go #客户端实现的多种方式存取数据,指令实现:cget,get,set
├── client
│ └── client.go #直接从数据存储服务器(dbserver)中的存取数据实现
├── dbserver
│ ├── dbserver
│ ├── dbserver.go #RPC 服务器,实现了针对数据存取服务器的操作,提供 rpc 接口调用
│ └── .DS_Store
├── frontend
│ ├── frontend
│ └── frontend.go #RPC 服务器,客户端发起 CGET 查询请求,首先到 frontend 端,frontend 查询占据 8001 端口的 groupcache 服务器获取查询值,如果没有,访问数据存取服务器 dbserver 来填充 groupcache,然后再返回给客户端
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
└── slowdb
└── slowdb.go #服务器端的具体存取数据,模拟慢 db
cget 流程
CGET 的调用路径如下:
func main(){
//...
if *cget {
// 调用 Frontend.Get 方法获取缓存
client, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "localhost:"+*port)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error %s", err)
}
args := &api.Load{*key}
var reply api.ValueResult
err = client.Call("Frontend.Get", args, &reply)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error %s", err)
}
fmt.Println(string(reply.Value))
return
}
}
func (s *Frontend) Get(args *api.Load, reply *api.ValueResult) error {
var data []byte
fmt.Printf("cli asked for %s from groupcache\n", args.Key)
// 调用 groupcache 的 Get 接口获取
err := s.cacheGroup.Get(nil, args.Key,
groupcache.AllocatingByteSliceSink(&data))
reply.Value = string(data)
return err
}
调用 groupcache 的代码分析
整个封装都在 frontend.go 中,初始化的代码如下:
type Frontend struct {
cacheGroup *groupcache.Group
}
func main() {
var port = flag.String("port", "8001", "groupcache port")
flag.Parse()
// 构建 NewHTTPPool
peers := groupcache.NewHTTPPool("http://localhost:" + *port)
client := new(client.Client)
var stringcache = groupcache.NewGroup("SlowDBCache", 64<<20, groupcache.GetterFunc(
func(ctx groupcache.Context, key string, dest groupcache.Sink) error {
result := client.Get(key)
fmt.Printf("asking for %s from dbserver\n", key)
dest.SetBytes([]byte(result))
return nil
}))
peers.Set("http://localhost:8001", "http://localhost:8002", "http://localhost:8003")
frontendServer := NewServer(stringcache)
i, err := strconv.Atoi(*port)
if err != nil {
// handle error
fmt.Println(err)
os.Exit(2)
}
var frontEndport = ":" + strconv.Itoa(i+1000)
go frontendServer.Start(frontEndport)
fmt.Println(stringcache)
fmt.Println("cachegroup slave starting on" + *port)
fmt.Println("frontend starting on" + frontEndport)
http.ListenAndServe("127.0.0.1:"+*port, http.HandlerFunc(peers.ServeHTTP))
}
func NewServer(cacheGroup *groupcache.Group) *Frontend {
server := new(Frontend)
server.cacheGroup = cacheGroup
return server
}
func (s *Frontend) Get(args *api.Load, reply *api.ValueResult) error {
var data []byte
fmt.Printf("cli asked for %s from groupcache\n", args.Key)
err := s.cacheGroup.Get(nil, args.Key,
groupcache.AllocatingByteSliceSink(&data))
reply.Value = string(data)
return err
}
0x02 GroupCache 库:介绍
前面已经介绍了 groupcache 是个 kv 存储库,最大的特点是没有删除接口;kv 一旦设置,那么用户端是无法更新和删除(没有接口)已经缓存的内容。此库的优点如下:
- client & server
- 缓存一致性:consistent
- 防击穿:singleflight
- group 的机制
- 协商填充
- 预热机制
- 热点数据多节点备份
- LRU
再看一个例子
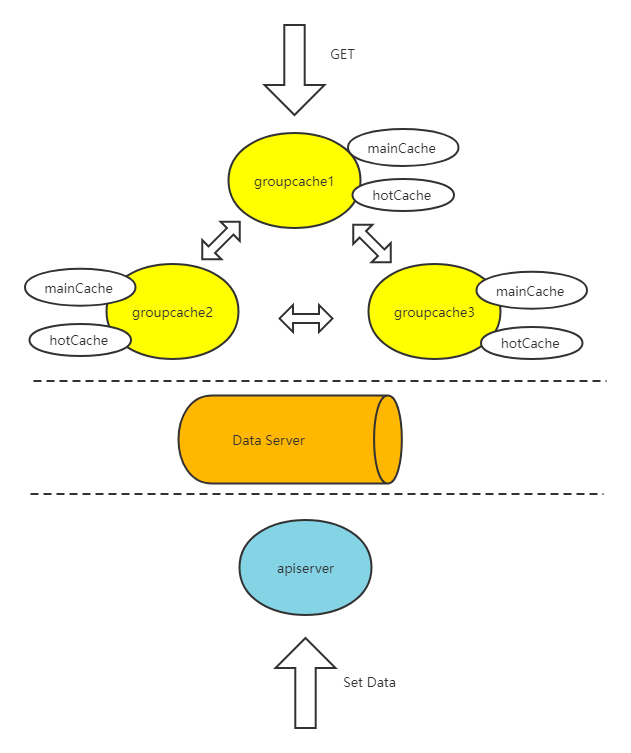
如上图,有4个groupcache节点,当 GET foo 请求到 groupcache-1 后
- groupcache-1 先看看自己的 cache 里有没有
foo,有的话直接返回 - 若无,则检查此
foo请求是否自己管理,检查的方法是利用consistent一致性算法:一致性hash将所有节点平均打散,然后当foo进来后用相同hash算法就会得到一个值(就是foo这个key最终会落到哪个groupcache节点上),落在哪个区间就属于哪个节点- 若是,去 DataSever 获取,然后本地缓存一份后返回客户端
- 否则问 group-2(假设
foo由此节点管理) 索要数据,成功返回后 groupcache-1 本地也会缓存一份
- 在
2的过程中,所有当前并发请求到 groupcache-1 的 GETfoo请求都会阻塞,直到第一个请求返回
基础数据结构及实现
1、byteView
byteview 对字符串数组和 string 进行封装,存储何种形式的字符串对用户透明
type struct {
b []byte
s string
}
func at(i){
if b!=nil
return b[i]
return s[i]
}
2、consistenthash:一致性 hash
groupcache 中,consistenthash 将 key 按照一致性 hash 分布在各个实例中,主要作用是实例(groupcache 节点)加入离开时不会导致映射关系发生重大变化
type Hash func(data []byte) uint32
type Map struct {
hash Hash
replicas int
keys []int // Sorted
hashMap map[int]string
}
3、LRU 算法
LRU 的作用是,groupcache 没有更新和删除接口,提供了避免空间只增不减的缓存淘汰机制
Group结构体的cache成员即LRU的Cache实现:
type cache struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
nbytes int64 // of all keys and values
lru *lru.Cache
nhit, nget int64
nevict int64 // number of evictions
}
4、singleflight 机制
singleflight 保证同时多个并发请求下,多个同参数的 get 请求只执行一次操作功能
5、group 分组
group 是 key-value 的容器,每个 group 都有一个名字,相当于一批 key-value 的家族标识。当用户访问某个 key 时,group 现在本地内存中维护的 hashmap 中查找,如果没有则从远端的 peerNode 或者本地的文件系统(DBserver)处进行加载。group 类似于命名空间的设计,不同的命名空间是相互隔离的。
groupcache支持多个group:groups = make(map[string]*Group)
// A Group is a cache namespace and associated data loaded spread over
// a group of 1 or more machines.
type Group struct {
name string
getter Getter
peersOnce sync.Once
peers PeerPicker
cacheBytes int64 // limit for sum of mainCache and hotCache size
// mainCache is a cache of the keys for which this process
// (amongst its peers) is authoritative. That is, this cache
// contains keys which consistent hash on to this process's
// peer number.
mainCache cache //lru缓存结构
// hotCache contains keys/values for which this peer is not
// authoritative (otherwise they would be in mainCache), but
// are popular enough to warrant mirroring in this process to
// avoid going over the network to fetch from a peer. Having
// a hotCache avoids network hotspotting, where a peer's
// network card could become the bottleneck on a popular key.
// This cache is used sparingly to maximize the total number
// of key/value pairs that can be stored globally.
hotCache cache //lru缓存结构
// loadGroup ensures that each key is only fetched once
// (either locally or remotely), regardless of the number of
// concurrent callers.
loadGroup flightGroup
_ int32 // force Stats to be 8-byte aligned on 32-bit platforms
// Stats are statistics on the group.
Stats Stats
}
6、httppool
httppool 是 groupcache 中各个 peerNode 通讯的封装,开启通讯 http,group 的 getFromPeer 便调用相对应 peer 的 httpool 提供的服务。httppool 同时保存了所有的远端 peerNode 实例的请求地址,实现 pickPeer 安装一致性 hash 取得某 key 对应的远端 peerNode 实例的地址。
groupcache:架构总览
1、API接口
groupcache 的对外接口,即Group的3个方法:
Get:用户侧,传入一个 key,获取 valueName方法:返回group的名字(允许多个group)CacheStats方法:统计数据,比如命中率
2、client && server
Groupcache 库既是服务器,也是客户端,当在本地 groupcache 缓存中没有查找的数据时,通过一致性哈希,查找到该 key 所对应的 peer 服务器,再通过 http 协议,从该 peer 服务器上获取所需要的数据;还有一点就是当多个客户端同时访问 groupcache 中不存在的键时,groupcache 只会有一个客户端从 mysql 获取数据,其他客户端阻塞,直到第一个客户端获取到数据之后,再返回给多个客户端
groupcache 实现的是一个分布式的无中心化的缓存集群。每个节点,既作为 server ,对外提供 API 访问,返回 key 的数据;节点(peerNode)之间,也是可以C/S 模式互相访问
groupCache的缓存一致性
0x03 groupCache源码走读
Group及其成员
Group会缓存自己节点的数据和访问比较频繁的 peer节点 的数据,用LRU算法控制cache容量,当 cache 未命中时,首先看看这个请求归不归该节点管(后面讨论),若是就是调用 getter:
type Group struct {
name string
getter Getter // cache 没有命中,从数据库获取的通用回调方法,需要开发者自行实现!
peersOnce sync.Once
peers PeerPicker // peer 节点调度器
cacheBytes int64 // 最大cache字节数
mainCache cache // 此节点缓存
hotCache cache // 其他节点缓存
loadGroup flightGroup // 请求并发控制器
Stats Stats // 统计数据
}
Getter定义了一个Cache如何从数据库中获取到相应的数据,比如是通过网络还是本地IO等方法,通常由开发者传入这个回调实现,比如前文例子中的stringcache;ctx Context 是操作的附带信息,key 请求的 id,Sink抽象了数据载体的行为(类型)。groupcache 提供了一些常用的 Sink 如 StringSink,BytesSliceSink 和 ProtoSink等
type Getter interface {
Get(ctx Context, key string, dest Sink) error
}
type Sink interface {
// SetString 写入 string
SetString(s string) error
// SetBytes 写入字节数组,调用者会保留 v 引用
SetBytes(v []byte) error
// SetProto 写入proto.Message,调用者会保留 m 应用
SetProto(m proto.Message) error
}
成员PeerPicker的定义如下,该结构是对节点调度器抽象。调度器主要负责根据管理 key 和节点的一致性映射。groupcache 实现了一个基于HTTP 的 PeerPicker,即HTTPPool结构,至此,groupcache 通过 Getter、PeerPicker和ProtoGetter这3个通用结构定义了cache,节点和调度器之间的连接方式,可以有效地控制耦合度,提供了比较大的灵活性。
// PeerPicker is the interface that must be implemented to locate
// the peer that owns a specific key.
type PeerPicker interface {
// PickPeer returns the peer that owns the specific key
// and true to indicate that a remote peer was nominated.
// It returns nil, false if the key owner is the current peer.
// PickPeer 根据 key 返回应该处理这个 key 的节点
// ok 为 true 代表找到了节点
// nil, false 代表当前节点就是 key 的处理器
PickPeer(key string) (peer ProtoGetter, ok bool)
}
最后,看下ProtoGetter结构。groupcache 规定内部 peerNode 节点间数据通信格式使用 google/protobuf,为了抽象 peer 节点,定义了 ProtoGetter。groupcache提供了httpGetter的实现
//pb.GetRequest 和 pb.GetResponse 定义了请求和响应 struct,这个抽象可以分离底层传输方式
type ProtoGetter interface {
Get(context Context, in *pb.GetRequest, out *pb.GetResponse) error
}
httpGetter的实例化实现,Get方法:
var bufferPool = sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} { return new(bytes.Buffer) },
}
func (h *httpGetter) Get(ctx context.Context, in *pb.GetRequest, out *pb.GetResponse) error {
u := fmt.Sprintf(
"%v%v/%v",
h.baseURL,
url.QueryEscape(in.GetGroup()),
url.QueryEscape(in.GetKey()),
)
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", u, nil)
if err != nil {
return err
}
req = req.WithContext(ctx)
tr := http.DefaultTransport
if h.transport != nil {
tr = h.transport(ctx)
}
res, err := tr.RoundTrip(req)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer res.Body.Close()
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return fmt.Errorf("server returned: %v", res.Status)
}
//optimistic
b := bufferPool.Get().(*bytes.Buffer)
b.Reset()
defer bufferPool.Put(b)
_, err = io.Copy(b, res.Body)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("reading response body: %v", err)
}
err = proto.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), out)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("decoding response body: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
0x04 PeerPicker的实例化结构:HTTPPool分析
如上一小节所述,groupcache定义了PeerPicker,该结构是对节点调度器抽象。调度器主要负责根据管理 key 和节点的一致性映射。本小节分析HTTPPool实现
HTTPPool结构
每一个groupcache节点都包含一个HTTPPool,此结构关联一个peers *consistenthash.Map结构,里面保存了集群所有节点对应的一致性hash构建的hashring
// HTTPPool implements PeerPicker for a pool of HTTP peers.
type HTTPPool struct {
// Context optionally specifies a context for the server to use when it
// receives a request.
// If nil, the server uses the request's context
Context func(*http.Request) context.Context
// Transport optionally specifies an http.RoundTripper for the client
// to use when it makes a request.
// If nil, the client uses http.DefaultTransport.
Transport func(context.Context) http.RoundTripper
// this peer's base URL, e.g. "https://example.net:8000"
self string
// opts specifies the options.
opts HTTPPoolOptions
mu sync.Mutex // guards peers and httpGetters
peers *consistenthash.Map
httpGetters map[string]*httpGetter // keyed by e.g. "http://10.0.0.2:8008"
}
通过指定虚拟节点副本数和hash计算方法对consistent-hash结构进行初始化:
p.peers = consistenthash.New(p.opts.Replicas, p.opts.HashFn)
HTTPPool.Set方法:更新本node的consistent-hash结构
// Set updates the pool's list of peers.
// Each peer value should be a valid base URL,
// for example "http://example.net:8000".
func (p *HTTPPool) Set(peers ...string) {
p.mu.Lock()
defer p.mu.Unlock()
p.peers = consistenthash.New(p.opts.Replicas, p.opts.HashFn)
p.peers.Add(peers...)
p.httpGetters = make(map[string]*httpGetter, len(peers))
for _, peer := range peers {
p.httpGetters[peer] = &httpGetter{transport: p.Transport, baseURL: peer + p.opts.BasePath}
}
}
HTTPPool.PickPeer方法:根据一致性hash查找到对应的groupcache节点
本方法根据一致性hash的原理,以查询的key为计算参数,查找到负责此key存储的groupcache后端节点,然后调用对应的p.httpGetters[peer]方法,获取数据并返回
func (p *HTTPPool) PickPeer(key string) (ProtoGetter, bool) {
p.mu.Lock()
defer p.mu.Unlock()
if p.peers.IsEmpty() {
return nil, false
}
if peer := p.peers.Get(key); peer != p.self {
return p.httpGetters[peer], true
}
return nil, false
}
HTTPPool.ServeHTTP方法:本节点为其他节点提供查询服务的处理方法
func (p *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Parse request.
if !strings.HasPrefix(r.URL.Path, p.opts.BasePath) {
panic("HTTPPool serving unexpected path: " + r.URL.Path)
}
parts := strings.SplitN(r.URL.Path[len(p.opts.BasePath):], "/", 2)
if len(parts) != 2 {
http.Error(w, "bad request", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
groupName := parts[0]
key := parts[1]
// Fetch the value for this group/key.
group := GetGroup(groupName)
if group == nil {
http.Error(w, "no such group: "+groupName, http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
var ctx context.Context
if p.Context != nil {
ctx = p.Context(r)
} else {
ctx = r.Context()
}
group.Stats.ServerRequests.Add(1)
var value []byte
err := group.Get(ctx, key, AllocatingByteSliceSink(&value))
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// Write the value to the response body as a proto message.
body, err := proto.Marshal(&pb.GetResponse{Value: value})
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/x-protobuf")
w.Write(body)
}
groupcache节点的客户端功能
type httpGetter struct {
transport func(context.Context) http.RoundTripper //http客户端
baseURL string
}
httpGetter.Get方法:向其他节点请求数据
本方法对应上面的HTTPPool.ServeHTTP方法,可以一起结合来看,是属于http客户端的功能封装
func (h *httpGetter) Get(ctx context.Context, in *pb.GetRequest, out *pb.GetResponse) error {
u := fmt.Sprintf(
"%v%v/%v",
h.baseURL,
url.QueryEscape(in.GetGroup()),
url.QueryEscape(in.GetKey()),
)
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", u, nil)
if err != nil {
return err
}
req = req.WithContext(ctx)
tr := http.DefaultTransport
if h.transport != nil {
tr = h.transport(ctx)
}
res, err := tr.RoundTrip(req)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer res.Body.Close()
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return fmt.Errorf("server returned: %v", res.Status)
}
b := bufferPool.Get().(*bytes.Buffer)
b.Reset()
defer bufferPool.Put(b)
_, err = io.Copy(b, res.Body)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("reading response body: %v", err)
}
err = proto.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), out)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("decoding response body: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
0x05 核心方法分析
核心方法:Group.Get分析
整个Group.Get的流程图如下:
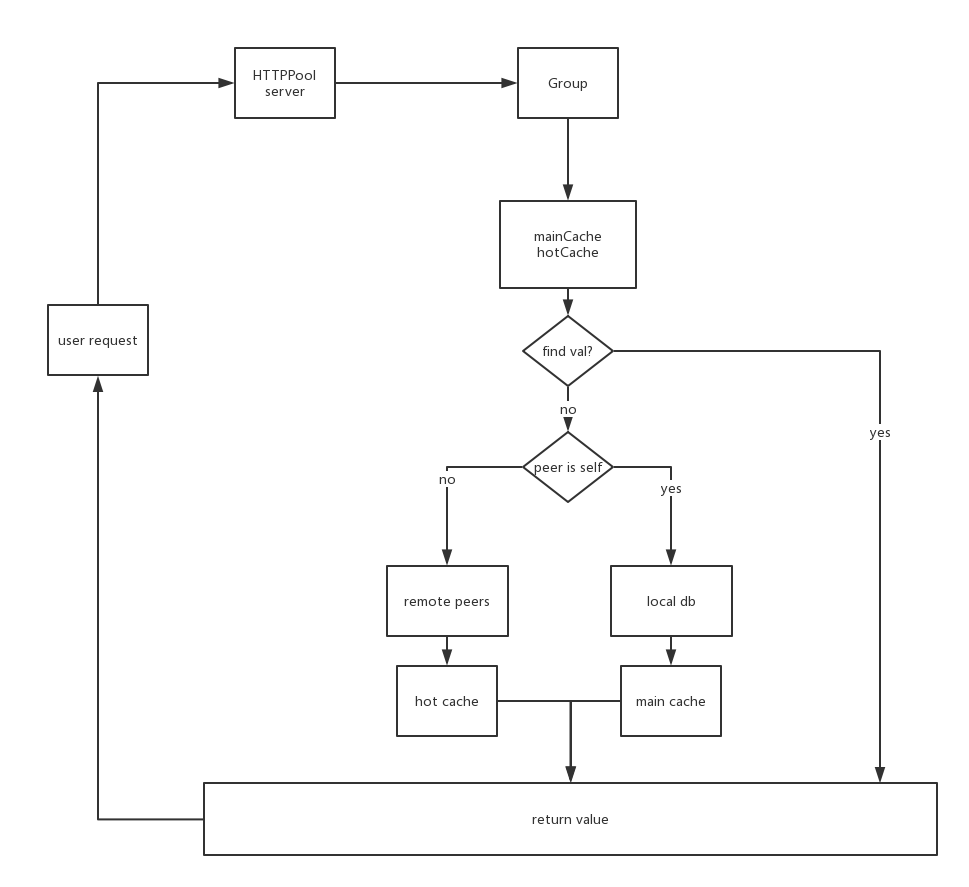
func (g *Group) Get(ctx context.Context, key string, dest Sink) error {
g.peersOnce.Do(g.initPeers)
g.Stats.Gets.Add(1)
if dest == nil {
return errors.New("groupcache: nil dest Sink")
}
value, cacheHit := g.lookupCache(key)
if cacheHit {
g.Stats.CacheHits.Add(1)
return setSinkView(dest, value)
}
// Optimization to avoid double unmarshalling or copying: keep
// track of whether the dest was already populated. One caller
// (if local) will set this; the losers will not. The common
// case will likely be one caller.
destPopulated := false
value, destPopulated, err := g.load(ctx, key, dest)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if destPopulated {
return nil
}
return setSinkView(dest, value)
}
0x04 groupcache VS memcache
Groupcache 库既是服务器,也是客户端,当在本地 groupcache 缓存中没有查找的数据时,通过一致性哈希,查找到该 key 所对应的 peer 服务器,再通过 http 协议,从该 peer 服务器上获取所需要的数据;还有一点就是当多个客户端同时访问 memcache 中不存在的键时,会导致多个客户端从 mysql 获取数据并同时插入 memcache 中,而在相同情况下,groupcache 只会有一个客户端从 mysql 获取数据,其他客户端阻塞,直到第一个客户端获取到数据之后,再返回给多个客户端
0x0 思考
1、HTTPPool的consistent节点能否动态设置?
比如groupcache节点发生了上/下线,如何实现一致性hash的动态调整?