0x00 前言
gost 是一个非常有意思的项目,在笔者看来,像是乐高积木一样的代理连接器(多机端口转发器),其核心概念是四大模块:
Service:Service 是指一个网络服务,它可以是一个服务器或者一个客户端。每一个 service 都有一个特定的网络地址和网络协议,如 HTTP,SOCKS5 等。GOST 通过 service 来接收和发送网络数据Node:Node 代表一个代理服务器。一个 node 包含了代理服务器的地址、端口和协议等信息。一个 Service 可以由一个或多个 node 组成Hop:Hop 是指在 GOST 中数据传输过程中,从一个 node 到另一个 node 的跳转。每个 hop 都有一个特定的转发规则,例如从一个 HTTP 代理跳转到一个 SOCKS5 代理Chain:Chain 是指一个网络服务链路。一个 chain 可以包含多个 hop,数据在这些 hop 之间按照特定的顺序进行转发。通过 chain,GOST 可以实现数据的多次转发,从而实现复杂的网络代理功能
本文分析版本基于 v3.0.0-nightly.20240201,地址 gost-3.0.0
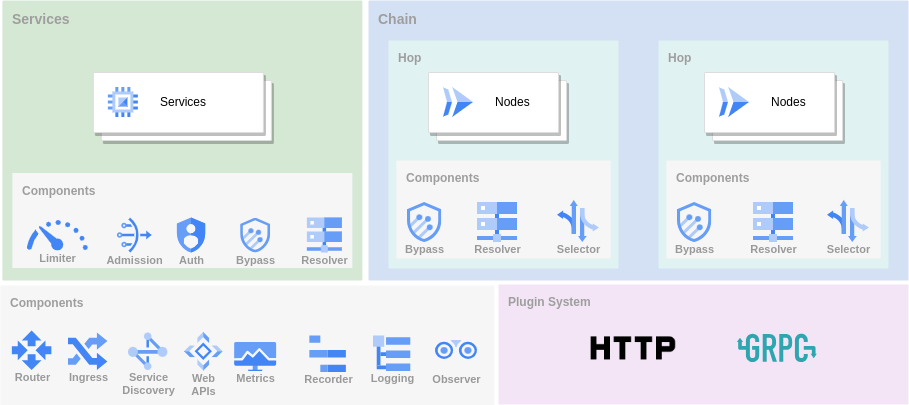
gost 源码的设计(结构)极佳,适合 golang 进阶使用
0x01 支持 tunnel 场景
GOST 作为隧道 tunnel 有三种主要使用方式:
正向代理
作为代理服务访问网络,可以组合使用多种协议组成转发链进行转发
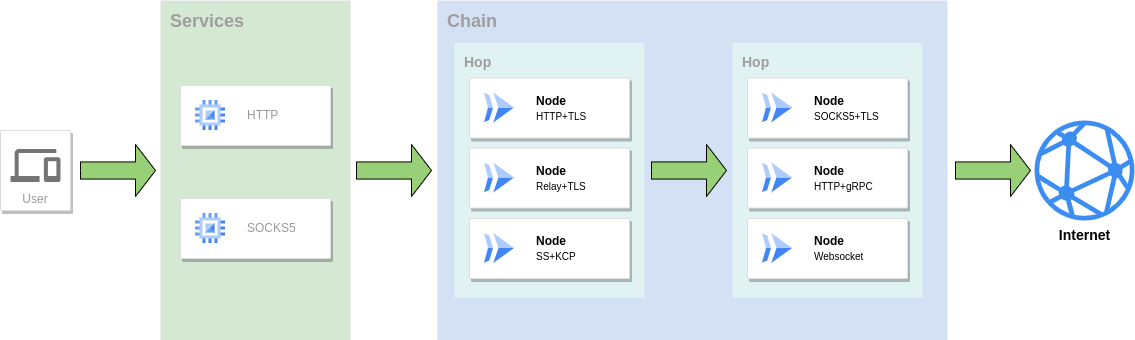
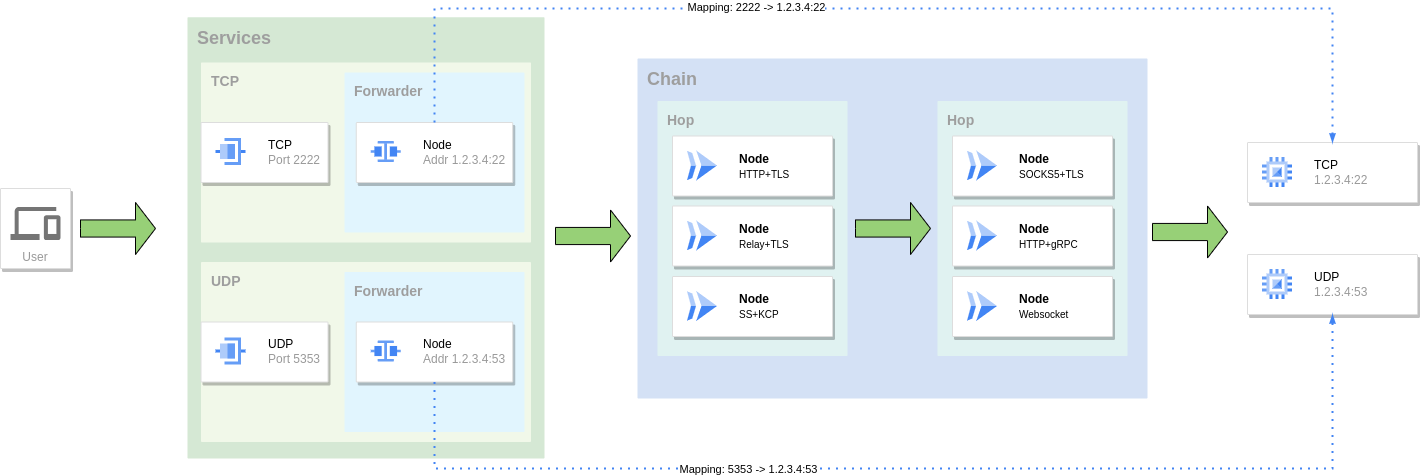
端口转发
将一个服务的端口映射到另外一个服务的端口,同样可以组合使用多种协议组成转发链进行转发
反向代理
利用隧道和内网穿透将内网服务暴露到公网访问
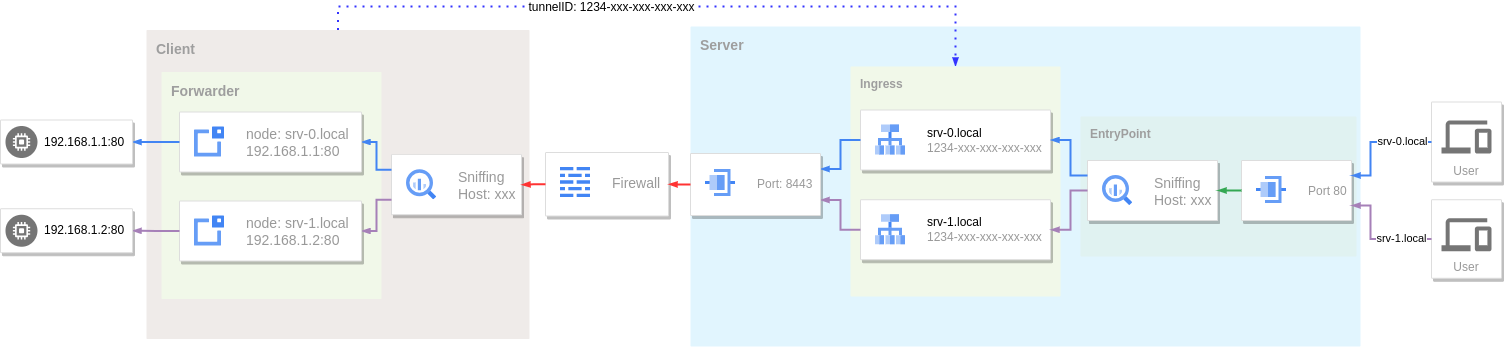
先看一个简单的 例子:
代理模式
1、代理 + 转发:监听在 8080 端口的 HTTP 代理服务,使用 192.168.1.1:8080 做为上级代理进行转发
services:
- name: service-0
addr: ":8080"
handler:
type: http
chain: chain-0
listener:
type: tcp
chains:
- name: chain-0
hops:
- name: hop-0
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.1:8080
connector:
type: http
dialer:
type: tcp
2、使用多级转发(转发链):GOST 按照设置 hop-0、hop-1 的顺序将请求最终转发给 192.168.1.2:1080 处理
services:
- name: service-0
addr: ":8080"
handler:
type: auto
chain: chain-0
listener:
type: tcp
chains:
- name: chain-0
hops:
- name: hop-0
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.1:8080
connector:
type: http
dialer:
type: tcp
- name: hop-1
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.2:1080
connector:
type: socks5
dialer:
type: tcp
转发模式
1、TCP 本地端口转发:将本地的 TCP 端口 8080 映射到 192.168.1.1 的 80 端口,即所有到本地 8080 端口的数据会被转发到 192.168.1.1:80
services:
- name: service-0
addr: :8080
handler:
type: tcp
listener:
type: tcp
forwarder:
nodes:
- name: target-0
addr: 192.168.1.1:80
2、UDP 本地端口转发:将本地的 UDP 端口 10053 映射到 192.168.1.1 的 53 端口,所有到本地 10053 端口的数据会被转发到 192.168.1.1:53
services:
- name: service-0
addr: :10053
handler:
type: udp
listener:
type: udp
forwarder:
nodes:
- name: target-0
addr: 192.168.1.1:53
3、TCP 本地端口转发(转发链):将本地的 TCP 端口 8080 通过转发链 chain-0 映射到 192.168.1.1 的 80 端口
services:
- name: service-0
addr: :8080
handler:
type: tcp
chain: chain-0
listener:
type: tcp
forwarder:
nodes:
- name: target-0
addr: 192.168.1.1:80
chains:
- name: chain-0
hops:
- name: hop-0
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.2:1080
connector:
type: socks5
dialer:
type: tcp
4、TCP 远程端口转发:在 192.168.1.2 上开启并监听 TCP 端口 2222,并将 192.168.1.2 上的 2222 端口映射到本地 TCP 端口 22,所有到 192.168.1.2:2222 的数据会被转发到本地端口 22
services:
- name: service-0
addr: :2222
handler:
type: rtcp
listener:
type: rtcp
chain: chain-0
forwarder:
nodes:
- name: target-0
addr: :22
chains:
- name: chain-0
hops:
- name: hop-0
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.2:1080
connector:
type: socks5
dialer:
type: tcp
5、UDP 远程端口转发:在 192.168.1.2 上开启并监听 UDP 端口 10053,并将 192.168.1.2 上的 10053 端口映射到本地 UDP 端口 53,所有到 192.168.1.2:10053 的数据会被转发到本地端口 53
services:
- name: service-0
addr: :10053
handler:
type: rudp
listener:
type: rudp
chain: chain-0
forwarder:
nodes:
- name: target-0
addr: :53
chains:
- name: chain-0
hops:
- name: hop-0
nodes:
- name: node-0
addr: 192.168.1.2:1080
connector:
type: socks5
dialer:
type: tcp
0x02 tunnel 实现
本小节分析下 gost 项目 的 tunnel 实现,所谓 tunnel,就是通过此传输一些其他协议的数据(变换协议)或者加速访问(和 frp 功能类似),可以抽象为如下模型:
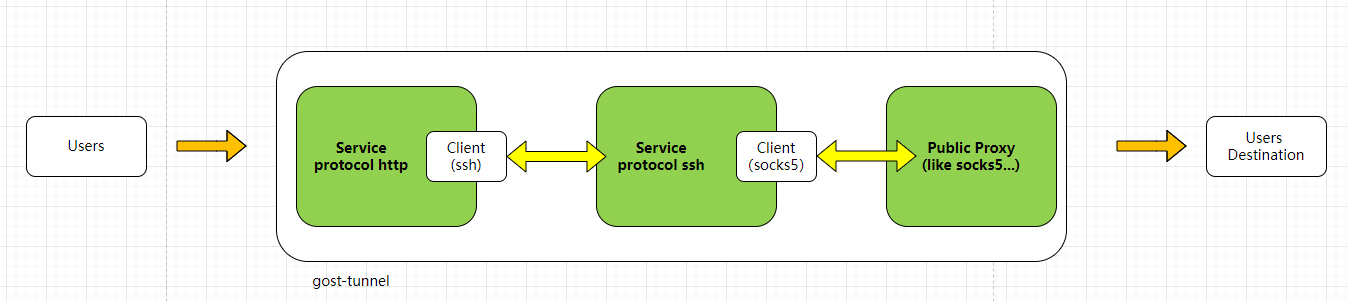
公共接口
gost 的 core 目录下面,定义了项目中所有的公共接口 interface 和重要结构体,重要的如下:
- admission:负责处理连接接入控制,例如限制并发连接数等
- auth:负责处理用户认证,例如用户名和密码验证
- bypass:负责处理直连规则,判断某个请求是否需要直接连接,而不经过代理
- chain:负责管理代理链路,包括多个节点(node)和跳转(hop)的顺序
- common:包含一些通用的工具和功能,例如解析配置文件、处理命令行参数等
- connector:处理已经建立的网络连接,例如协议升级、设置连接属性等
- dialer:负责建立网络连接,创建新的网络连接
- handler:负责处理网络请求,例如 HTTP 请求、SOCKS5 请求等
- hop:表示数据传输过程中,从一个节点(node)到另一个节点(node)的跳转
- hosts:负责处理自定义的域名解析规则,例如将某个域名解析为指定的 IP 地址
- ingress:负责处理入站连接,例如监听端口、接收客户端连接等
- limiter:负责处理流量控制,例如限制每个连接的速度、限制总流量等
- listener:负责监听网络端口,接收客户端连接
- logger:负责处理日志记录,输出调试信息和错误信息
- metrics:负责收集和处理统计信息,例如连接数、流量等
- metadata:负责处理元数据,例如连接的目标地址、协议类型等
- observer:负责实现观察者模式,让其他组件可以订阅和接收事件通知
- recorder:负责记录连接信息,例如连接时间、流量等
- registry:负责管理各种组件的注册和查找,例如注册新的协议处理器、查找已注册的处理器等
- resolver:负责处理域名解析,将域名转换为 IP 地址
- router:负责处理路由规则,判断某个请求应该通过哪个代理节点(node)
- sd:负责处理服务发现,例如从 Consul、Etcd 等服务发现系统获取代理节点信息
- selector:负责实现负载均衡策略,例如轮询、随机等
- service:表示一个网络服务,例如 HTTP 代理、SOCKS5 代理等
Dialer VS Connector
Dialer 和 Connector 通常会配合使用,例如当 GOST 需要建立一个新的网络连接时,它会首先使用 Dialer 的 Dial 方法创建一个新的网络连接,然后再使用 Connector 的 Connect 方法对这个新建的连接进行处理。这种设计使得 GOST 在处理网络连接时既灵活又高效。
Dialer:Dialer是用于建立网络连接的接口。它定义了一个Dial方法,该方法接受一个网络地址,然后返回一个已经建立好的网络连接。Dialer可以看作是一个网络连接的生产者,它的任务就是创建新的网络连接Connector:Connector则是用于处理已经建立的网络连接的接口。它定义了一个Connect方法,该方法接受一个已经建立好的网络连接,然后对这个连接进行一些后续处理,比如进行协议升级、设置连接属性等。Connector可以看作是一个网络连接的消费者,它的任务就是处理已经建立好的网络连接
代码定义
1、Service:通用实例化在 x/service,defaultService 为默认的 Service 实例化
type Service interface {
Serve() error
Addr() net.Addr
Close() error
}
type defaultService struct {
name string
listener listener.Listener // 关联 Listener 接口
handler handler.Handler // 关联 Handler 接口
status *Status
options options
}
任何支持的 Service,都可以通过此通用框架实现,只需要传入相关的 listener 和 handler 即可:
func NewService(name string, ln listener.Listener, h handler.Handler, opts ...Option) service.Service
2、Listener:gost 支持多种 listener 实现,均在 此,定义 在此
// Listener is a server listener, just like a net.Listener.
type Listener interface {
Init(metadata.Metadata) error
Accept() (net.Conn, error)
Addr() net.Addr
Close() error
}
3、Handler:所有 Handler 的实例化都在 此,Handler 的主要作用是处理 net.Conn,有几种典型的处理逻辑:
CONNECT代理- 仅建 tunnel,将
net.Conn和另外一个net.Connpipe 起来,进作为隧道 tunnel 转发数据
type Handler interface {
Init(metadata.Metadata) error
Handle(context.Context, net.Conn, ...HandleOption) error
}
4、Node:实例化单个节点 封装,比如隧道路径上的某个节点
// Node:实例化单个节点封装
type Node struct {
Name string
Addr string
marker selector.Marker
options NodeOptions
}
5、Route:Route 被抽象为一组 Node,同时需要至少提供 Dial、Bind 方法的实现
Bind:用来实现一个服务的 listenerDial:用来把一组Node进行打洞,提供最终的net.Conn
// Route:Chain 的通用封装,定义了 3 个方法
type Route interface {
Dial(ctx context.Context, network, address string, opts ...DialOption) (net.Conn, error)
Bind(ctx context.Context, network, address string, opts ...BindOption) (net.Listener, error)
Nodes() []*Node // 返回当前的 Node(按顺序)
}
补充下,gost 提供了默认的 Route 实例化实现,代码 有点意思,可以详细阅读下
// Router:是 Route 的实例化,实现了 Bind/Dial/Nodes 方法
type Router struct {
options RouterOptions
}
实例化的 Router 提供的 Bind实现、以及 Dial实现,下面再做分析
6、Chainer:Chainer 抽象为根据目的 IP(参数),构造出一条可以通的 Route
type Chainer interface {
Route(ctx context.Context, network, address string, opts ...RouteOption) Route
}
7、Metadata
type Metadata interface {
IsExists(key string) bool
Set(key string, value any)
Get(key string) any
}
8、Binder
type Binder interface {
Bind(ctx context.Context, conn net.Conn, network, address string, opts ...BindOption) (net.Listener, error)
}
9、Connector && Handshaker
// Connector is responsible for connecting to the destination address.
type Connector interface {
Init(metadata.Metadata) error
Connect(ctx context.Context, conn net.Conn, network, address string, opts ...ConnectOption) (net.Conn, error)
}
type Handshaker interface {
Handshake(ctx context.Context, conn net.Conn) (net.Conn, error)
}
10、Dialer && Handshaker
// Transporter is responsible for dialing to the proxy server.
type Dialer interface {
Init(metadata.Metadata) error
Dial(ctx context.Context, addr string, opts ...DialOption) (net.Conn, error)
}
type Handshaker interface {
Handshake(ctx context.Context, conn net.Conn, opts ...HandshakeOption) (net.Conn, error)
}
11、ingress
type Rule struct {
// Hostname is the hostname match pattern, e.g. example.com, *.example.org or .example.com.
Hostname string
// Endpoint is the tunnel ID for the hostname.
Endpoint string
}
type Ingress interface {
// SetRule adds or updates a rule for the ingress.
SetRule(ctx context.Context, rule *Rule, opts ...Option) bool
// GetRule queries a rule by host.
GetRule(ctx context.Context, host string, opts ...Option) *Rule
}
12、Resolver,定义用于 DNS解析
type Resolver interface {
// Resolve returns a slice of the host's IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
// The network should be 'ip', 'ip4' or 'ip6', default network is 'ip'.
Resolve(ctx context.Context, network, host string, opts ...Option) ([]net.IP, error)
}
实例化
上一小节中抽象的 interface 的实例化都在这个 目录
1、Service
2、Listener:实例化代码,提供了非常多的实现
3、Node/Router/Chain
// route 是x/core/ Router的实例化
type route struct {
nodes []*chain.Node // Node is interface
options RouteOptions
}
// Chain的实例化实现:包含了多个Hop
type Chain struct {
name string
hops []hop.Hop
marker selector.Marker
metadata metadata.Metadata
logger logger.Logger
}
Chain的几个重要方法如下:AddHop和Route,前者用于构建隧道路径上的某一跳hops,后者用于把这些hops打通
func (c *Chain) AddHop(hop hop.Hop) {
c.hops = append(c.hops, hop)
}
Chain.Route方法:
// 根据c.hops构建rt
func (c *Chain) Route(ctx context.Context, network, address string, opts ...chain.RouteOption) chain.Route {
if c == nil || len(c.hops) == 0 {
return nil
}
var options chain.RouteOptions
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
rt := NewRoute(ChainRouteOption(c))
//根据host构建最终的rt结构 (nodes []*chain.Node)
for _, h := range c.hops {
node := h.Select(ctx,
hop.NetworkSelectOption(network),
hop.AddrSelectOption(address),
hop.HostSelectOption(options.Host),
)
if node == nil {
return rt
}
if node.Options().Transport.Multiplex() {
tr := node.Options().Transport.Copy()
tr.Options().Route = rt
node = node.Copy()
node.Options().Transport = tr
rt = NewRoute()
}
rt.addNode(node)
}
return rt
}
0x03 实例化分析:一个例子
以 多级转发链 为例,看下代码的数据运转流程:
gost -L :8080 -F http://192.168.1.1:8080 -F socks5://192.168.1.2:1080