0x00 前言
本文代码片段参考v1.21.1版本
0x01 基础知识
k8s基本架构
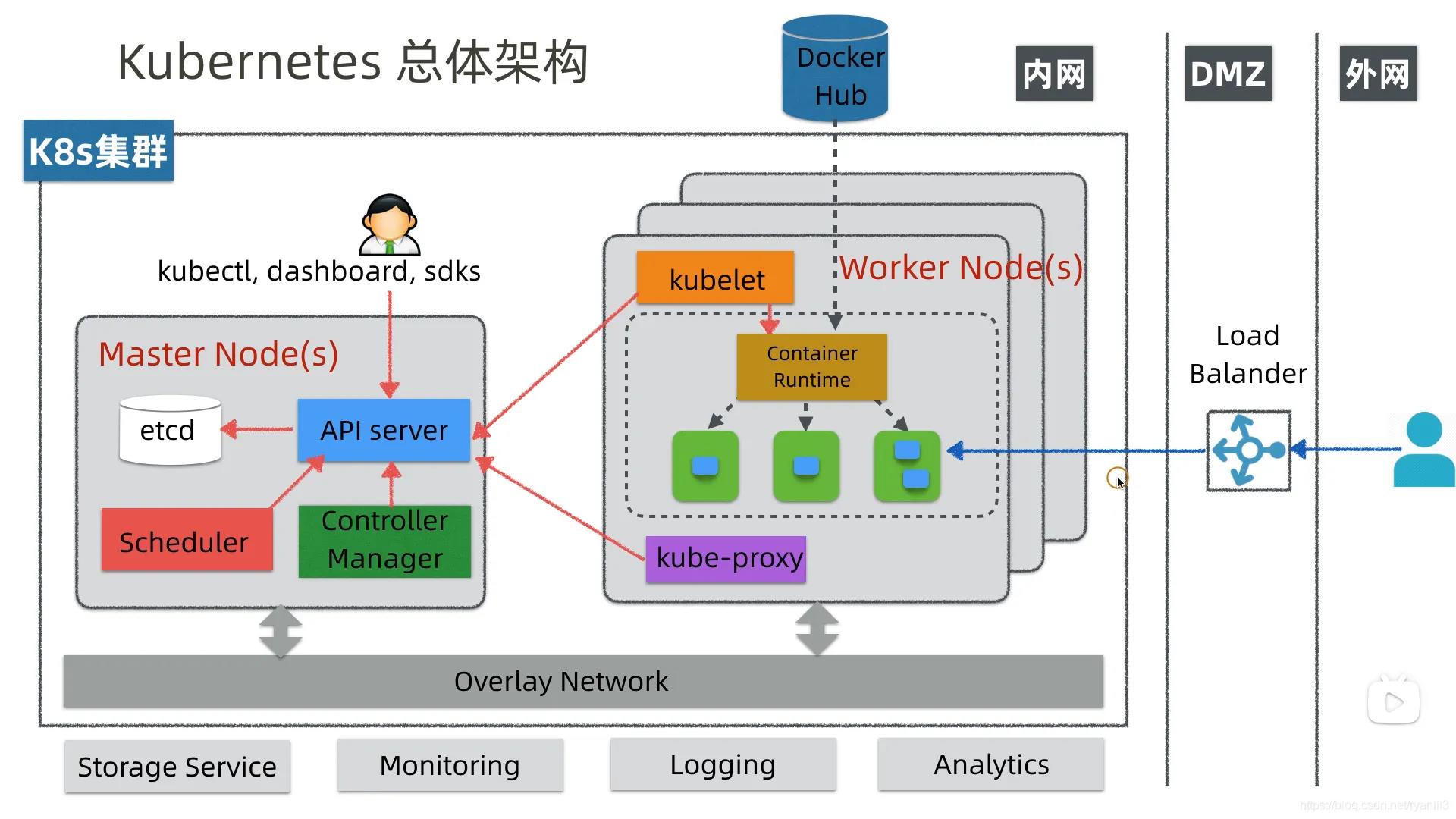
- apiserver:资源操作的唯一入口,接收用户输入的命令,提供认证、授权、API注册和发现等机制,通过标准的RESTFul API,重新封装了对 ETCD 接口调用,提供系统内其他组件调用的代理入口
- scheduler:负责集群资源调度,按照预定的调度策略将Pod调度到相应的node节点上
- controllerManager:负责维护集群的状态,比如程序部署安排、故障检测、自动扩展、滚动更新等
- etcd:负责存储集群中各种资源对象的信息,k/v方式存储,所有的 k8s 集群数据存放在此。此外,各个组件通信都并不是互相调用 API 来完成的,而是把状态写入 ETCD(相当于写入一个消息),其他组件通过监听 ETCD 的状态的的变化(相当于订阅消息),然后做后续的处理,然后再一次把更新的数据写入 ETCD
- kuberctl:命令行配置工具
- node:集群的数据平面,负责为容器提供运行环境
- kubelet:负责维护容器的生命周期,即通过控制docker,来创建/更新/销毁容器,会按固定频率检查节点健康状态并上报给 APIServer,该状态会记录在 Node 对象的 status 中
- kubeProxy:负责提供集群内部的服务发现和负载均衡
- docker(runtime):负责节点上容器的各种操作
Linux VS kubernetes
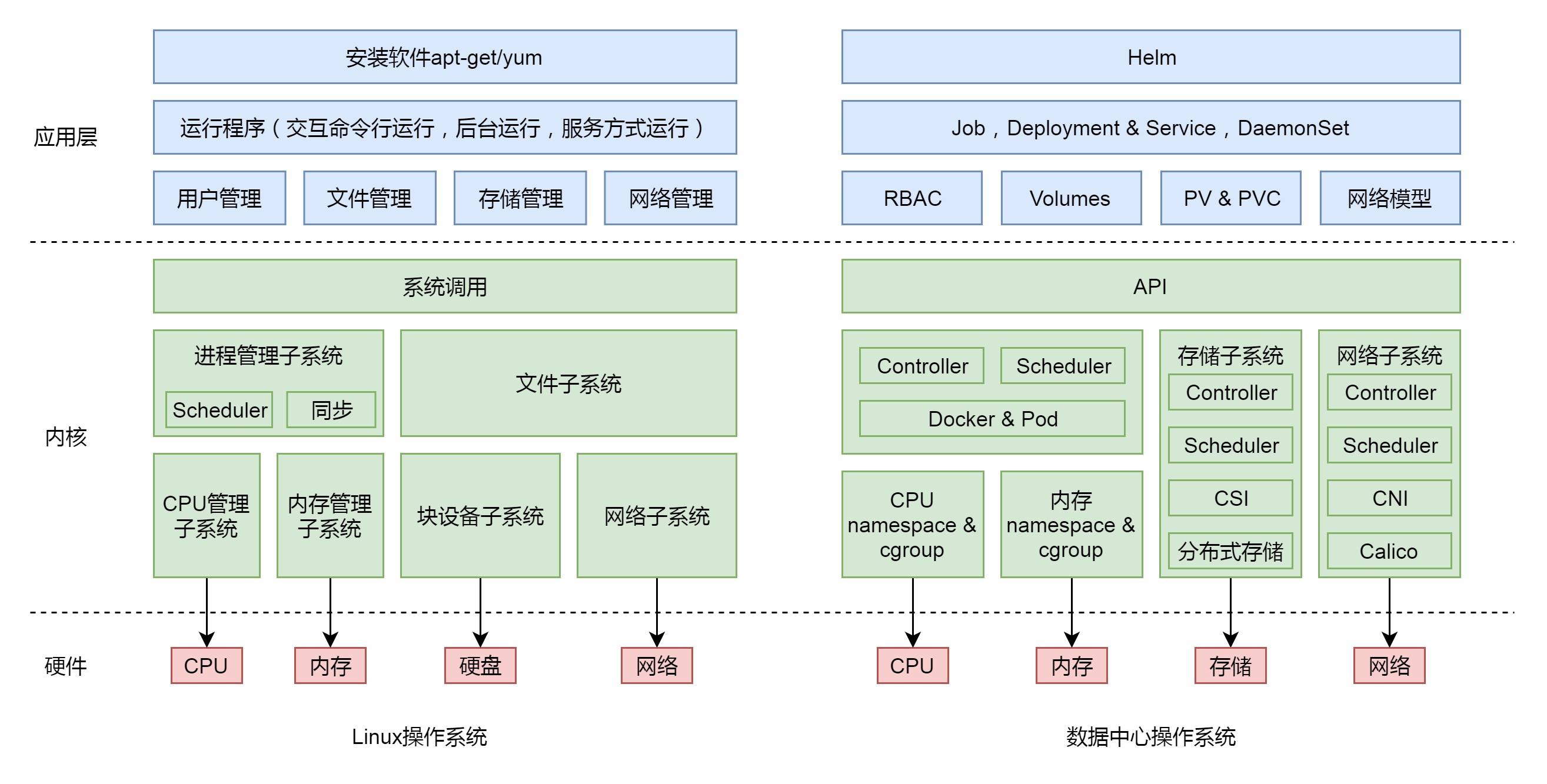
声明式应用管理
Kubernetes 总体设计遵循控制器模式,用户通过 YAML 文件等方式来表达所需要的期望状态也就是终态(无论网络、存储等),然后 Kubernetes 的各种组件就会让整个集群的状态跟用户声明的终态逼近,最终达成两者的完全一致。这个实际状态逐渐向期望状态逼近的过程,就叫做 reconcile(调谐),同样 Operator 和自定义 Controller 也类似此工作方式
声明式应用管理的本质即Infrastructure as Data/Configuration as Data,基础设施的管理不应该耦合于某种编程语言或者配置方式,而应该是纯粹的、格式化的、系统可读的数据,并且这些数据能够完整的表征使用者所期望的系统状态。任何时候对基础设施做操作,最终都等价于对这些数据的增/删/改/查。若想在 Kubernetes 上做任何操作,只需要提交一个 YAML 文件,然后对这个 YAML 文件进行增删改查即可,而无需使用 Kubernetes 项目的 Restful API来完成。此YAML 文件里的内容本质就是 Kubernetes 系统对应的 Data(简单理解就是API对象等同于具有不同类型固定格式的Data)。Kubernetes 本质上其实是一个以数据(Data)来表达系统的设定值、通过控制器(Controller)的动作来让系统维持在设定值的调谐系统
通俗点说,kubernetes的本质是一个数据库,那么相关分类如下:
- 数据模型:Kubernetes 的各种 API 对象与 CRD 机制
- 数据拦截校验和修改机制:Kubernetes Admission Hook
- 数据驱动机制:Kubernetes Controller/Operator
- 数据监听变更与索引机制:Informer 机制
k8s的组件
| 组件 | 作用 | 归属 |
|---|---|---|
| kubectl | ||
| kubelet | ||
| cri-shim | ||
| csi | ||
| cni plugin |
k8s核心组件的实现思路
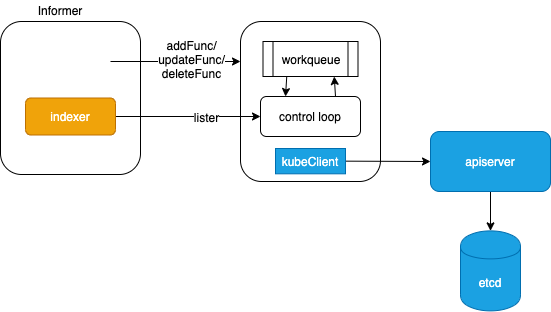
在k8s中,与apiserver 通信的Controller/Scheduler 的业务逻辑可以抽象为如下模型,如图所示:
- 若组件需要与apiserver 交互(通信),k8s抽象了通用Informer 框架(实现在 apiserver 的 访问包client-go)负责apiserver 数据的本地cache及监听。Informer 还会比对资源是否变更(依靠内部的Delta FIFO Queue),只有变更的资源才会触发handler
- 组件都采用control loop 逻辑
- 组件内部维护一个 queue队列,通过注册Informer事件函数保持queue数据的更新,作用相当于队列的生产者,而control loop 作为队列的消费者
- 通过 Informer 提供过的 Lister 拥有遍历数据的能力,将操作结果重新通过kubeclient 写入到apiserver
编排系统的设计
1、资源模型的抽象
- 有哪些种类的资源,如CPU、内存等
- 如何用数据结构表示这些资源
2、资源的调度设计
- 如何描述一个 workload 的资源申请(spec),如该容器需要
4核和12GB~16GB内存 - 如何描述一台 node 当前的资源分配状态,例如已分配/未分配资源量,是否支持超分等
3、调度算法设计:如何根据 workload spec 为它挑选最合适的 node
4、资源的限额(capacity enforcement)
- 如何确保 workload 使用的资源量不超出预设范围(从而不会影响其他 workload)
- 如何确保 workload 和系统/基础服务的限额,使二者互不影响
容器生态系统
- Docker,Kubernetes 等工具来运行一个容器时会调用容器运行时(CRI)比如 containerd,CRI-O
- 通过容器运行时来完成容器的创建、运行、销毁等实际工作
- Docker 使用的是 containerd 作为其运行时;Kubernetes 支持 containerd,CRI-O 等多种容器运行时
- 这些容器运行时都遵循了 OCI 规范,并通过 runc 来实现与操作系统内核交互来完成容器的创建和运行
0x01 review:基础概念
pod
pod 控制器
service
1、
2、NodePort
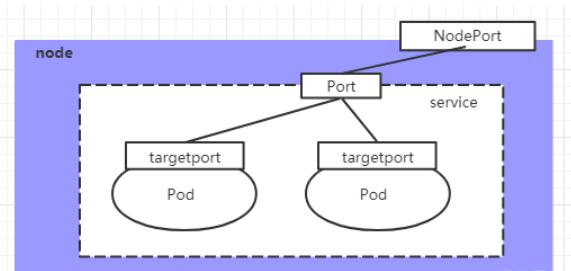
3、Loadbalance
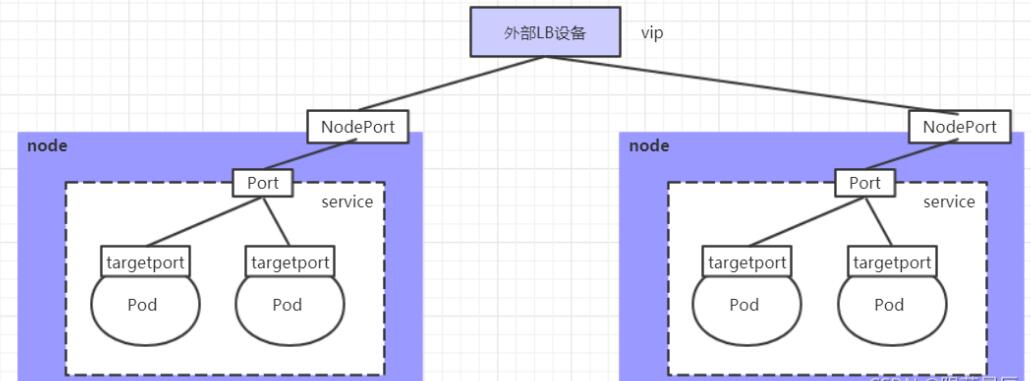
volume
basic flow
通过kubectl创建创建pod时,大概流程如下:
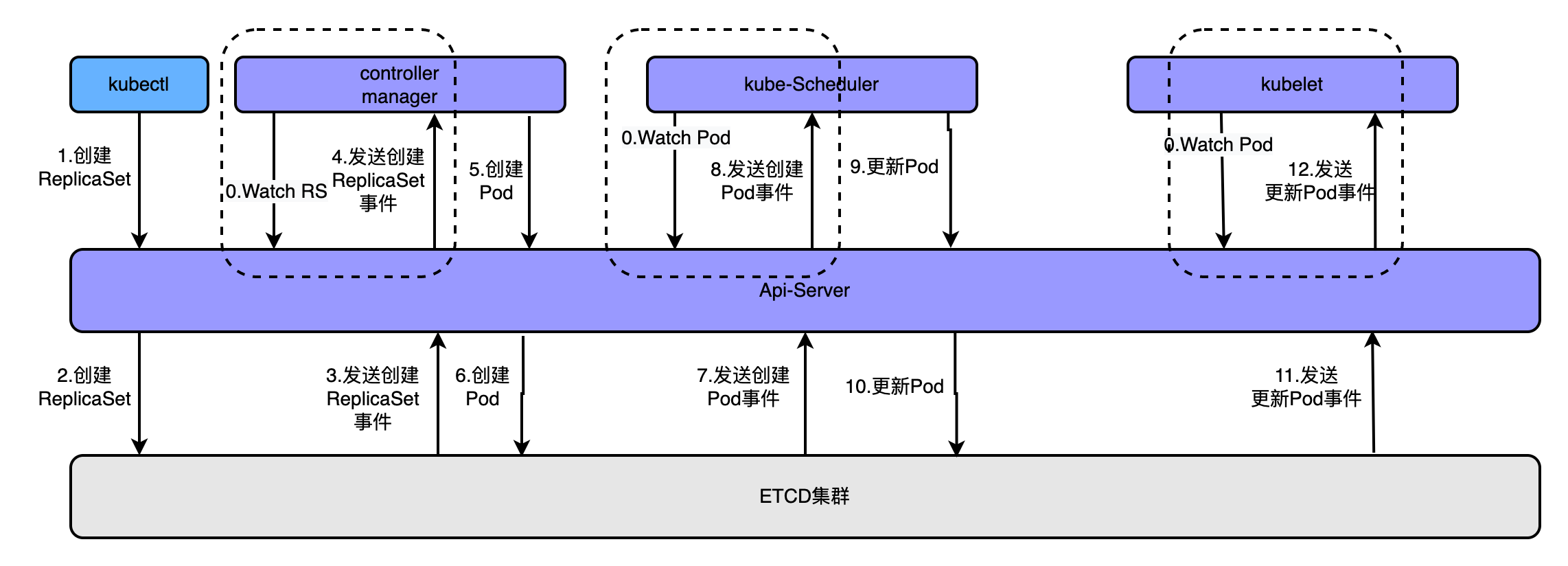
- apiserver接收kubectl的创建资源的请求
- apiserver将创建请求写入ECTD
- apiserver接收到etcd的回调事件
- apiserver将回调事件发送给ControllerManager(实际上是watch-notify机制)
- controllerManager中的ReplicationController处理本次请求,创建RS,然后它会调控RS中的Pod的副本数量处于期望值,比期望值小就新创建Pod,于是它告诉apiserver要创建pod
- apiserver将创建pod的请求写入etcd集群
- apiserver接收etcd的创建pod的回调事件
- apiserver将创建pod的回调事件发送给scheduler模块,由它为pod挑选一个合适的宿主node
- scheduler告诉apiserver,这个pod可以调度到哪个node上
- apiserver将scheduler通知的事件写入etcd
- apiserver接收到etcd的回调,将更新pod的事件发送给对应node上的kubelet进程(同样也是watch机制)
- kubelet通过CRI接口同容器运行时(Docker)交互,维护更新对应的容器
k8s组件的若干细节
1、控制平面(集群)
kube-apiserver:k8s入口(其它控制面组件都没有被设计为可暴露远程服务)。此外,apiserver 与各其他组件通信时都需要提供/验证相应的证书(客户端/服务端),apiserver的核心功能分为网关功能(认证、鉴权、消息转发)以及封装了对ETCD的大部分CRUD、List-watch操作等等,用于提供k8s的资源注册与发现功能。以CRD为例,创建 CRD 是自定义资源的注册过程,而ControllerManager 是收到对资源事件从而作出响应的处理
kube-scheduler:集群默认调度器,调度器通过 kubernetes 的监测(etcd Watch)机制来发现集群中新创建且尚未被调度到 Node 上的 Pod。调度器会保证节点上有足够的资源供其上的所有 Pod 使用
- scheduler会检查节点上所有容器的请求的总和不会超过节点的容量
- scheduler先在集群中找到一个 Pod 的所有可调度节点,然后根据一系列函数对这些可调度节点打分, 选出其中得分最高的 Node 来运行 Pod,然后scheduler将这个调度决定通知给 kube-apiserver
- scheduler在做调度决定时需要考虑的因素包括单独和整体的资源请求(request)、硬件/软件/策略限制(limit)、亲和/反亲和等
kube-scheduler 给一个 pod 做调度选择包含如下两步:
- 过滤阶段:会将所有满足 Pod 调度需求的 Node 选出来,通常情况下,这个 Node 列表包含不止一个 Node。如果这个列表是空的,代表这个 Pod 不可调度
- 打分阶段:调度器会为 Pod 从所有可调度节点中选取一个最合适的 Node。根据当前启用的打分规则,调度器会给每一个可调度节点进行打分
kube-controller-manager:自带的控制器包括 Replicaset Controller、Node Controller、Namespace Controller 和 ServiceAccount Controller等
2、Node节点(集群)
kubelet:对Node的大部分操作都归属kubelet管理,分三类说明如下:
-
针对pod管理:它保证容器(containers)都运行在 Pod 中。即最主要的功能就是保证pod能健康的运行起来。某些情况下,当节点不可达时,API 服务器不能和其上的 kubelet 通信。 删除 Pod 的决定不能传达给 kubelet,直到它重新建立和 API 服务器的连接为止。 与此同时,被计划删除的 Pod 可能会继续在游离的节点上运行。除此之外,还有以下重要功能:
如果某资源(deployment)对每一个容器都定义了一个资源限制(Limit),kubelet 会为与该资源(CPU 的 cpu.cfs_quota_us 以及内存的 memory.limit_in_bytes) 相关的 pod cgroup(Cgroups 的详情可以参考这篇文章) 设定一个上限。
-
kubelet 会为每个 Pod 生成/etc/resolv.conf文件,用于DNS查询,以及单独挂载/etc/hosts
-
kubelet 根据容器配置的策略拉取镜像,如 IfNotPresent 这一策略会使得 kubelet 在镜像已经存在的情况下直接略过拉取镜像的操作。镜像与容器的垃圾回收工作 也是由 kubelet 来完成
-
当调用容器生命周期管理回调时,Kubernetes 管理系统根据回调动作执行其处理程序,exec 在容器内执行,而 httpGet 和 tcpSocket 则是 kubelet 进程执行
针对 Node的功能:
kubelet 监控集群节点的 CPU、内存、磁盘空间和文件系统的 inode 等资源。 当这些资源中的一个或者多个达到特定的消耗水平, kubelet 可以主动地使节点上一个或者多个 Pod 失效,以回收资源防止饥饿。
kubelet 也会 负责创建和更新节点的 .status,以及更新它们对应的 Lease。
针对 apiserver 的功能:
从 apiserver 到 kubelet 的连接用于:
获取 Pod 日志
挂接(通过 kubectl)到运行中的 Pod(kubectl exec)
提供 kubelet 的端口转发功能(kubectl port-forward)
kube-proxy:是每个Node上运行的网络代理,反映了每个Node上 Kubernetes API 中定义的服务(Service),并且支持流量转发(通过iptables实现)功能,包括userspace 代理模式、iptables 规则代理模式以及IPVS 代理模式
它与 CNI
有什么关系呢?
CNI 主要实现一个 overlay network
的网络模型。
那么什么 overlay network?CNI主要解决了什么问题?搞清楚这两个问题,也就明白了 CNI 的作用。
什么是 overlay network?
在已有的宿主机网络上,再通过软件构建一个覆盖在已有宿主机(所有集群结点)网络之上的、可以把所有容器连通在一起的虚拟网络。
主要解决了什么问题?
集群里面的所有容器能够互通,比如 pod A/B 在不同的结点上,可以相互 ping 通
可见, kube-proxy 主要解决 Service 流量转发 到 pod 的问题。
而 CNI 解决的集群容器互通 的问题。
容器运行时(Container Runtime)
你需要在集群中的每个节点上都有一个可以正常工作的 容器运行时, 这样 kubelet 能启动 容器 及其 Pod。
容器运行时接口(CRI)是 kubelet 和容器运行时之间通信的主要协议(grpc)。
目前主要的运行时比如: Docker( 1.24 已经弃用)、 containerd、CRI-O 等。
控制平面层(Master) 中包含的组件:
apiserver: 核心枢纽,是流量进出口,外界也只能通过它才能与 k8s "打交道"。
kube-scheduler: 决定了 pod 调度到哪个节点上。注意调度之后它就不管事了,需要 descheduler。
etcd:存储组件。
controller-manager: 即 k8s 自带的所有 资源 controller 集合。
节点中包含的组件:
kubele: 负责节点上容器相关动作的管理。
kube-proxy: 负责将节点上的流量转发到容器中。
kubeproxy-iptables模式的转发分析
以笔者本机搭建的minikube为例,有如下服务crd-array-watcher,类型为NodePort,那么从CVM上访问telnet $(minikube ip) 32198服务的路径如下:
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos ~]# kubectl get svc -A
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default crd-array-watcher NodePort 10.100.116.139 <none> 8080:32198/TCP 5d18h
在minikube的Node节点上:
# minikube ssh
root@minikube:~# iptables -t nat -L -v -n --line-numbers
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 55 packets, 3300 bytes)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 1297 82043 KUBE-SERVICES all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* kubernetes service portals */
2 65 3953 DOCKER_OUTPUT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.49.1
3 876 52560 DOCKER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
......
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 7175 packets, 431K bytes)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 2273K 136M KUBE-SERVICES all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* kubernetes service portals */
2 241 20129 DOCKER_OUTPUT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.49.1
3 662K 40M DOCKER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.0/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
......
Chain KUBE-SERVICES (2 references)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 0 0 KUBE-SVC-5WLEADX2DETM25TL tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.97.142.21 /* kubearmor/kubearmor-controller-webhook-service cluster IP */ tcp dpt:443
2 36 2682 KUBE-SVC-TCOU7JCQXEZGVUNU udp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.96.0.10 /* kube-system/kube-dns:dns cluster IP */ udp dpt:53
3 0 0 KUBE-SVC-JD5MR3NA4I4DYORP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.96.0.10 /* kube-system/kube-dns:metrics cluster IP */ tcp dpt:9153
......
8 0 0 KUBE-SVC-HW2XM7FRY33HEVYM tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.100.116.139 /* default/crd-array-watcher cluster IP */ tcp dpt:8080
9 0 0 KUBE-SVC-GCRHHKL6ZB4XAFBC tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.103.198.138 /* default/crd-array-watchers cluster IP */ tcp dpt:8080
10 6552 393K KUBE-NODEPORTS all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* kubernetes service nodeports; NOTE: this must be the last rule in this chain */ ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
......
Chain KUBE-SVC-HW2XM7FRY33HEVYM (2 references)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 2 120 KUBE-MARK-MASQ tcp -- * * !10.244.0.0/16 10.100.116.139 /* default/crd-array-watcher cluster IP */ tcp dpt:8080
2 4 240 KUBE-SEP-PLQTWCYKKRRVAV4U all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* default/crd-array-watcher -> 10.244.0.35:8080 */
......
root@minikube:~# iptables -t nat -L KUBE-SVC-HW2XM7FRY33HEVYM -v -n --line-numbers
Chain KUBE-SVC-HW2XM7FRY33HEVYM (2 references)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 2 120 KUBE-MARK-MASQ tcp -- * * !10.244.0.0/16 10.100.116.139 /* default/crd-array-watcher cluster IP */ tcp dpt:8080
2 4 240 KUBE-SEP-PLQTWCYKKRRVAV4U all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* default/crd-array-watcher -> 10.244.0.35:8080 */
root@minikube:~# iptables -t nat -L KUBE-SEP-PLQTWCYKKRRVAV4U -v -n --line-numbers
Chain KUBE-SEP-PLQTWCYKKRRVAV4U (1 references)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 0 0 KUBE-MARK-MASQ all -- * * 10.244.0.35 0.0.0.0/0 /* default/crd-array-watcher */
2 4 240 DNAT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 /* default/crd-array-watcher */ tcp to:10.244.0.35:8080
0x02 API && CRD
K8S 的 API 类型
在kubernetes中可以通过 GET/LIST/PUT/POST/DELETE 等 API 操作,来创建、查询、修改或删除集群中的资源,相应的各 kube-controller 监听到资源变化时,就会执行相应的 reconcile 逻辑,来使 status 与 spec 描述相符,API的类型:
- 标准 API(针对内置资源类型):Namespaced 类型,可以用 namespace 来隔离(如namespaces、pods、services等),格式为
/api/{version}/namespaces/{namespace}/{resource}(如/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods);Un-namespaced 类型为全局的,不能用 namespace 隔离(如nodes、clusterroles等),格式为/api/{version}/{resource}(如/api/v1/nodes) - 扩展 API(apiextension):常见Namespaced 类型,格式为
/apis/{apiGroup}/{apiVersion}/namespaces/{namespace}/{resource}(如/apis/cilium.io/v2/namespaces/kube-system/ciliumnetworkpolicies)
CRD
CRD是扩展 API 的(最主要)声明和使用方式
- CRD:用来声明用户的自定义资源,例如它是 namespace-scope 还是 cluster-scope 的资源、有哪些字段等等,K8s 会自动根据这个定义生成相应的 API
- CRD 是资源类型定义,具体的资源叫 CR
- Operator 框架:本质功能是时刻盯着资源状态,一有变化马上作出反应(即 reconcile 过程)
怎么理解CRD?
K8s 是个数据库,CRD 是一张表,API 是 SQL
1、K8s:数据库,存储引擎为etcd,以及构建在存储引擎之上的一套 API 和语义,允许用户创建、读取、更新和删除数据库中的数据
| 关系型数据库 | Kubernetes | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| DATABASE | cluster | 一套 K8s 集群(或者namespace)就是一个 database |
| TABLE | Kind | 每种资源类型对应一个表,分为内置类型和扩展类型 |
| COLUMN | property | 表里面的列,可以是 string、boolean 等类型 |
| rows | resources | 表中的一个具体 record |
- 内置 Kind:Job、Service、Deployment、Event、NetworkPolicy、Secret、ConfigMap 等等
- 扩展 Kind:各种 CRD,例如 CiliumNetworkPolicy
2、CRD 是一张表,CRD 和内置的 Pod、Service、NetworkPolicy 一样,也是数据库的一张表,参考如下的示例 fruit CRD,有 name/sweet/weight/comment 列,以及 apple/banana 等 entry。所以CRD允许用户创建自己的表,设置自己的列,声明 CRD 就会自动创建 API
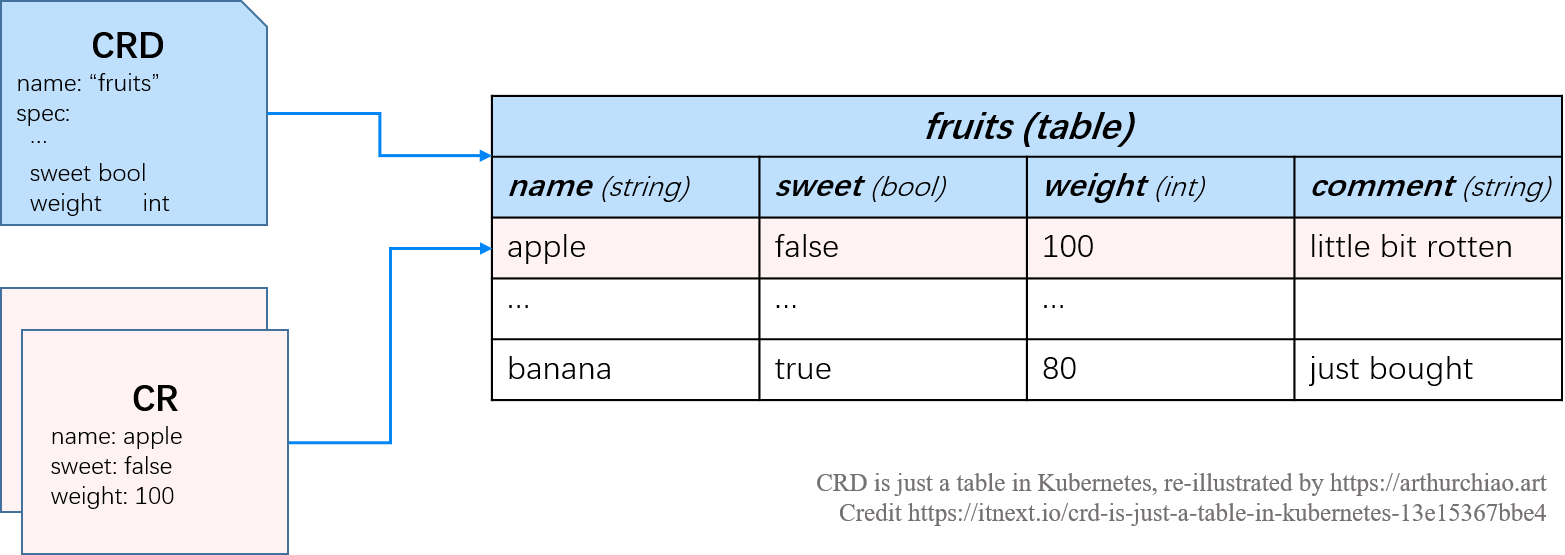
#cat fruit.yaml
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: fruits.example.org # CRD 名字
spec:
conversion:
strategy: None
group: example.org # REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
names:
kind: Fruit
listKind: FruitList
plural: fruits
singular: fruit
scope: Namespaced # Fruit 资源是区分 namespace 的
versions:
- name: v1 # REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
spec:
properties:
comment: # 字段 1,表示备注
type: string
sweet: # 字段 2,表示甜否
type: boolean
weight: # 字段 3,表示重量
type: integer
type: object
type: object
served: true # 启用这个版本的 API(v1)
storage: true
additionalPrinterColumns: # 可选项,配置了这些 printer columns 之后,
- jsonPath: .spec.sweet # 命令行 k get <crd> <cr> 时,能够打印出下面这些字段,
name: sweet # 否则,k8s 默认只打印 CRD 的 NAME 和 AGE
type: boolean
- jsonPath: .spec.weight
name: weight
type: integer
- jsonPath: .spec.comment
name: comment
type: string
#apple-cr.yaml
apiVersion: example.org/v1
kind: Fruit
metadata:
name: apple
spec:
sweet: false
weight: 100
comment: little bit rotten
#cat banana-cr.yaml
apiVersion: example.org/v1
kind: Fruit
metadata:
name: banana
spec:
sweet: true
weight: 80
comment: just bought
3、定义表结构(CRD spec),CRD(CR)描述格式可以是 YAML 或 JSON。CRD 的内容可以简单分为三部分:
常规 k8s metadata:每种 K8s 资源都需要声明的字段,包括 apiVersion/kind/metadata.name 等
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: fruits.example.org # CRD 名字
......
Table-level 信息:例如表的名字,最好用小写,方便以后命令行操作
......
spec:
conversion:
strategy: None
group: example.org # REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
names:
kind: Fruit
listKind: FruitList
plural: fruits
singular: fruit
scope: Namespaced # Fruit 资源是区分 namespace 的
......
Column-level 信息:列名及类型等等,遵循 OpenAPISpecification v3 规范
......
versions:
- name: v1 # REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
spec:
properties:
comment: # 字段 1,表示备注
type: string
sweet: # 字段 2,表示甜否
type: boolean
weight: # 字段 3,表示重量
type: integer
type: object
type: object
served: true # 启用这个版本的 API(v1)
storage: true
additionalPrinterColumns: # 可选项,配置了这些 printer columns 之后,
- jsonPath: .spec.sweet # 命令行 k get <crd> <cr> 时,能够打印出下面这些字段,
name: sweet # 否则,k8s 默认只打印 CRD 的 NAME 和 AGE
type: boolean
- jsonPath: .spec.weight
name: weight
type: integer
- jsonPath: .spec.comment
name: comment
type: string
4、关于CRD的常用操作
#创建 CRD:这一步相当于 `CREATE TABLE fruits ...;`
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos crd1]# kubectl apply -f fruit.yaml
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/fruits.example.org created
#创建 CR:相当于 INSERT INTO fruits values(...);
kubectl create -f apple-cr.yaml
fruit.example.org/apple created
kubectl create -f banana-cr.yaml
fruit.example.org/banana created
#查询 CR:相当于 SELECT * FROM fruits ... ; 或 SELECT * FROM fruits WHERE name='apple';
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos crd1]# kubectl get fruits
NAME SWEET WEIGHT COMMENT
apple false 100 little bit rotten
banana true 80 just bought
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos crd1]# kubectl get fruits apple
NAME SWEET WEIGHT COMMENT
apple false 100 little bit rotten
# 删除 CR:相当于 DELETE FROM fruits WHERE name='apple';
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos crd1]# kubectl delete fruit apple
fruit.example.org "apple" deleted
# 查看文档
kubectl explain fruits
# 标签操作
# 和内置资源类型一样,K8s 支持对 CR 打标签,然后根据标签做过滤:
# 查看所有 frutis
$ kubectl get fruits
NAME SWEET WEIGHT COMMENT
apple false 100 little bit rotten
banana true 80 just bought
# 给 banana 打上一个特殊新标签
$ kubectl label fruits banana tastes-good=true
fruit.example.org/banana labeled
# 按标签筛选 CR
$ kubectl get fruits -l tastes-good=true
NAME SWEET WEIGHT COMMENT
banana true 80 just bought
# 删除 label
$ kubectl label fruits banana tastes-good-
fruit.example.org/banana labeled
5、API 是 SQL
前文说过,通过 kubectl 命令行来执行 CR 的增删查改,它其实只是一个外壳,内部调用的是 Kubernetes 为这个 CRD 自动生成的 API,如下:
kubectl create -v 10 -f apple-cr.yaml
......
I0926 10:50:58.158636 3310786 helper.go:246] "Request Body" body=<
{"apiVersion":"example.org/v1","kind":"Fruit","metadata":{"name":"banana","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"comment":"just bought","sweet":true,"weight":80}}
>
I0926 10:50:58.158696 3310786 round_trippers.go:527] "Request" curlCommand=<
curl -v -XPOST -H "Accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.33.1 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/8adc0f0" 'https://192.168.49.2:8443/apis/example.org/v1/namespaces/default/fruits?fieldManager=kubectl-create&fieldValidation=Strict'
>
I0926 10:50:58.162442 3310786 round_trippers.go:632] "Response" verb="POST" url="https://192.168.49.2:8443/apis/example.org/v1/namespaces/default/fruits?fieldManager=kubectl-create&fieldValidation=Strict" status="201 Created" headers=<
Audit-Id: 5ad37351-24b3-4014-9050-238ed4f34b4e
Cache-Control: no-cache, private
Content-Length: 511
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Fri, 26 Sep 2025 02:50:58 GMT
X-Kubernetes-Pf-Flowschema-Uid: fc02528a-ec6f-4720-b6b4-4bb1129cd230
X-Kubernetes-Pf-Prioritylevel-Uid: ae8d9360-7b04-4f51-8428-ced0722e032e
> milliseconds=3 getConnectionMilliseconds=0 serverProcessingMilliseconds=3
I0926 10:50:58.162513 3310786 helper.go:246] "Response Body" body=<
{"apiVersion":"example.org/v1","kind":"Fruit","metadata":{"creationTimestamp":"2025-09-26T02:50:58Z","generation":1,"managedFields":[{"apiVersion":"example.org/v1","fieldsType":"FieldsV1","fieldsV1":{"f:spec":{".":{},"f:comment":{},"f:sweet":{},"f:weight":{}}},"manager":"kubectl-create","operation":"Update","time":"2025-09-26T02:50:58Z"}],"name":"banana","namespace":"default","resourceVersion":"537732","uid":"e155e0ba-01d1-4b4e-86dc-dfbbe3568ac3"},"spec":{"comment":"just bought","sweet":true,"weight":80}}
>
fruit.example.org/banana created
CRD的适用场景?
0x03 鉴权(RBAC)与认证
authentication(AuthN)
Authorization(AuthZ)
例1:基于Role的pod watch权限配置
1、创建专属 ServiceAccount(客户端 Pod 使用)
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: grpc-lb-client-sa # 服务账户名称
namespace: client-ns # 客户端所在命名空间
2、定义 Role 授予 Endpoints 权限
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: client-ns # 必须与客户端命名空间一致
name: grpc-endpoint-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # 核心 API 组(Endpoints 属于 core/v1)
resources: ["endpoints","pods"] # 资源类型
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] # 必须包含 watch 以实现监听
3、绑定 Role 到 ServiceAccount
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: bind-grpc-endpoint-reader
namespace: client-ns
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: grpc-lb-client-sa # 步骤1创建的 SA
namespace: client-ns
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: grpc-endpoint-reader # 步骤2定义的 Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
4、POD配置,在客户端 Deployment 中指定 ServiceAccount
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx-app
namespace: client-ns
spec:
replicas: 1 #pod副本数量
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-nginx-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-nginx-app
spec:
serviceAccountName: grpc-lb-client-sa # 关键:绑定专属 SA
containers:
- name: nginx
image: hub.x.com/cls/nginx:base
ports:
- containerPort: 80
测试,在pod(my-nginx-app)中访问监控的url,然后增加replicas的值,观察数据输出:
# 使用 SA Token 访问 APIServer
TOKEN=$(cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token)
curl -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
https://kubernetes.default.svc/api/v1/namespaces/client-ns/pods?watch=true
输出如下,这里的type包括如下类型:
| 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ADDED | 表示一个新对象被创建并添加到资源列表中 |
| MODIFIED | 一个已存在的对象被更新或修改 |
| DELETED | 一个已存在的对象被删除 |
| BOOKMARK | 特殊的事件,它不代表资源的变化,而是作为一个书签,用于通知客户端当前资源的最新 ResourceVersion |
| ERROR | 发生错误,watch终止 |
特殊说明下,当启动 Watch 连接时,apiserver 会首先列出所有现有对象,并为每个对象发送一个 ADDED事件,以便客户端初始化其本地状态(这就是 Informer 的 ListAndWatch机制中的 List 部分);此外在 Watch 过程中,如果有一个新的 Pod(或任何你正在 watch 的资源)被创建时会收到一个 ADDED事件
{
"type": "ADDED",
"object": {
"kind": "Pod",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "my-nginx-app-1-65b4996c66-j7jb2",
"generateName": "my-nginx-app-1-65b4996c66-",
"namespace": "client-ns",
"uid": "30b9d400-4881-4220-8915-633e41d60a8a",
"resourceVersion": "549709",
"generation": 1,
"creationTimestamp": "2025-09-26T06:57:45Z",
"labels": {
"app": "my-nginx-app-1",
"pod-template-hash": "65b4996c66"
},
"annotations": {
"kubearmor-policy": "enabled",
"kubearmor-visibility": "process,file,network,capabilities"
},
"ownerReferences": [{
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"name": "my-nginx-app-1-65b4996c66",
"uid": "2ec7fdf6-94bf-4e6d-985f-591c36cf2d10",
"controller": true,
"blockOwnerDeletion": true
}],
"managedFields": [{
"manager": "kube-controller-manager",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2025-09-26T06:57:45Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:metadata": {
"f:generateName": {},
"f:labels": {
".": {},
"f:app": {},
"f:pod-template-hash": {}
},
"f:ownerReferences": {
".": {},
"k:{\"uid\":\"2ec7fdf6-94bf-4e6d-985f-591c36cf2d10\"}": {}
}
},
"f:spec": {
"f:containers": {
"k:{\"name\":\"nginx\"}": {
".": {},
"f:image": {},
"f:imagePullPolicy": {},
"f:name": {},
"f:ports": {
".": {},
"k:{\"containerPort\":80,\"protocol\":\"TCP\"}": {
".": {},
"f:containerPort": {},
"f:protocol": {}
}
},
"f:resources": {},
"f:terminationMessagePath": {},
"f:terminationMessagePolicy": {}
}
},
"f:dnsPolicy": {},
"f:enableServiceLinks": {},
"f:restartPolicy": {},
"f:schedulerName": {},
"f:securityContext": {},
"f:serviceAccount": {},
"f:serviceAccountName": {},
"f:terminationGracePeriodSeconds": {}
}
}
}, {
"manager": "kubelet",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2025-09-26T06:57:46Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:status": {
"f:conditions": {
"k:{\"type\":\"ContainersReady\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:observedGeneration": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"Initialized\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:observedGeneration": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"PodReadyToStartContainers\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:observedGeneration": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"PodScheduled\"}": {
"f:observedGeneration": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"Ready\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:observedGeneration": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
}
},
"f:containerStatuses": {},
"f:hostIP": {},
"f:hostIPs": {},
"f:observedGeneration": {},
"f:phase": {},
"f:podIP": {},
"f:podIPs": {
".": {},
"k:{\"ip\":\"10.244.0.52\"}": {
".": {},
"f:ip": {}
}
},
"f:startTime": {}
}
},
"subresource": "status"
}]
},
"spec": {
"volumes": [{
"name": "kube-api-access-qccwf",
"projected": {
"sources": [{
"serviceAccountToken": {
"expirationSeconds": 3607,
"path": "token"
}
}, {
"configMap": {
"name": "kube-root-ca.crt",
"items": [{
"key": "ca.crt",
"path": "ca.crt"
}]
}
}, {
"downwardAPI": {
"items": [{
"path": "namespace",
"fieldRef": {
"apiVersion": "v1",
"fieldPath": "metadata.namespace"
}
}]
}
}],
"defaultMode": 420
}
}],
"containers": [{
"name": "nginx",
"image": "hub.x.com/cls/nginx:base",
"ports": [{
"containerPort": 80,
"protocol": "TCP"
}],
"resources": {},
"volumeMounts": [{
"name": "kube-api-access-qccwf",
"readOnly": true,
"mountPath": "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"
}],
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
"terminationMessagePolicy": "File",
"imagePullPolicy": "IfNotPresent"
}],
"restartPolicy": "Always",
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
"serviceAccountName": "grpc-lb-client-sa-cluster",
"serviceAccount": "grpc-lb-client-sa-cluster",
"nodeName": "minikube",
"securityContext": {},
"schedulerName": "default-scheduler",
"tolerations": [{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}, {
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}],
"priority": 0,
"enableServiceLinks": true,
"preemptionPolicy": "PreemptLowerPriority"
},
"status": {
"observedGeneration": 1,
"phase": "Running",
"conditions": [{
"type": "PodReadyToStartContainers",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:46Z"
}, {
"type": "Initialized",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:45Z"
}, {
"type": "Ready",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:46Z"
}, {
"type": "ContainersReady",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:46Z"
}, {
"type": "PodScheduled",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:45Z"
}],
"hostIP": "192.168.49.2",
"hostIPs": [{
"ip": "192.168.49.2"
}],
"podIP": "10.244.0.52",
"podIPs": [{
"ip": "10.244.0.52"
}],
"startTime": "2025-09-26T06:57:45Z",
"containerStatuses": [{
"name": "nginx",
"state": {
"running": {
"startedAt": "2025-09-26T06:57:46Z"
}
},
"lastState": {},
"ready": true,
"restartCount": 0,
"image": "hub.x.com/cls/nginx:base",
"imageID": "docker-pullable://hub.x.com/cls/nginx@sha256:2f2cf15feee194648a7efb4bd1d399d37abb5285fa2e31b46596fd8221416552",
"containerID": "docker://9bc2f3cbe013b1933fec7f66e7b91a8ca7893fc3eb0998fe7a94dc5d6ee03750",
"started": true,
"resources": {},
"volumeMounts": [{
"name": "kube-api-access-qccwf",
"mountPath": "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount",
"readOnly": true,
"recursiveReadOnly": "Disabled"
}]
}],
"qosClass": "BestEffort"
}
}
}
例2:基于clusterRole的watch权限配置
1、service account
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: grpc-lb-client-sa-cluster # 服务账户名称
namespace: client-ns # 客户端所在命名空间
2、权限(ClusterRole)
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: client-ns # 必须与客户端命名空间一致
name: grpc-endpoint-reader-cluster
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # 核心 API 组(Endpoints 属于 core/v1)
resources: ["endpoints","pods"] # 资源类型
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] # 必须包含 watch 以实现监听
3、ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: bind-grpc-endpoint-reader-cluster
namespace: client-ns
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: grpc-lb-client-sa-cluster # 步骤1创建的 SA
namespace: client-ns
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: grpc-endpoint-reader-cluster # 步骤2定义的 Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
4、POD配置
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx-app-1
namespace: client-ns
spec:
replicas: 1 #pod副本数量
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-nginx-app-1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-nginx-app-1
spec:
serviceAccountName: grpc-lb-client-sa-cluster # 关键:绑定专属 SA
containers:
- name: nginx
image: hub.x.com/cls/nginx:base
ports:
- containerPort: 80
5、启动POD,进入容器开启watch监听pods事件
TOKEN=$(cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token)
curl -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" https://kubernetes.default.svc/api/v1/pods/?watch=true
输出如下:
{
"type": "ADDED",
"object": {
"kind": "Pod",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "nginx12345-7cd74c867-shlsr",
"generateName": "nginx12345-7cd74c867-",
"namespace": "default", # the other namespace
"uid": "ee5b448d-2538-42ed-a9ad-18ccb126d3a6",
"resourceVersion": "550038",
"generation": 1,
"creationTimestamp": "2025-09-26T07:04:23Z",
"labels": {
"app": "nginx12345",
"pod-template-hash": "7cd74c867"
},
"ownerReferences": [{
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"name": "nginx12345-7cd74c867",
"uid": "cce26a3d-82f5-43be-886e-763339cdd1ec",
"controller": true,
"blockOwnerDeletion": true
}],
"managedFields": [{
"manager": "kube-controller-manager",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2025-09-26T07:04:23Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:metadata": {
"f:generateName": {},
"f:labels": {
".": {},
"f:app": {},
"f:pod-template-hash": {}
},
"f:ownerReferences": {
".": {},
"k:{\"uid\":\"cce26a3d-82f5-43be-886e-763339cdd1ec\"}": {}
}
},
"f:spec": {
"f:containers": {
"k:{\"name\":\"nginx\"}": {
".": {},
"f:image": {},
"f:imagePullPolicy": {},
"f:name": {},
"f:resources": {},
"f:terminationMessagePath": {},
"f:terminationMessagePolicy": {}
}
},
"f:dnsPolicy": {},
"f:enableServiceLinks": {},
"f:restartPolicy": {},
"f:schedulerName": {},
"f:securityContext": {},
"f:terminationGracePeriodSeconds": {}
}
}
}]
},
"spec": {
"volumes": [{
"name": "kube-api-access-4hrxn",
"projected": {
"sources": [{
"serviceAccountToken": {
"expirationSeconds": 3607,
"path": "token"
}
}, {
"configMap": {
"name": "kube-root-ca.crt",
"items": [{
"key": "ca.crt",
"path": "ca.crt"
}]
}
}, {
"downwardAPI": {
"items": [{
"path": "namespace",
"fieldRef": {
"apiVersion": "v1",
"fieldPath": "metadata.namespace"
}
}]
}
}],
"defaultMode": 420
}
}],
"containers": [{
"name": "nginx",
"image": "nginx",
"resources": {},
"volumeMounts": [{
"name": "kube-api-access-4hrxn",
"readOnly": true,
"mountPath": "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"
}],
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
"terminationMessagePolicy": "File",
"imagePullPolicy": "Always"
}],
"restartPolicy": "Always",
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
"serviceAccountName": "default",
"serviceAccount": "default",
"securityContext": {},
"schedulerName": "default-scheduler",
"tolerations": [{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}, {
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}],
"priority": 0,
"enableServiceLinks": true,
"preemptionPolicy": "PreemptLowerPriority"
},
"status": {
"phase": "Pending",
"qosClass": "BestEffort"
}
}
}
例3:基于user account的get权限配置(kubectl)
TODO
0x04 informer机制
从前文已知,在kubernetes是典型的server-client架构中,etcd存储集群的数据信息,apiserver作为统一的操作入口,任何对数据的操作都必须经过apiserver。客户端通过ListAndWatch机制查询apiserver,而informer模块则封装了List-watch
具体的数据流向:
如上图,kubernetes informer的架构中主要包含了Controller、Indexer以及Listener组成,其中Controller的实现又包含了Reflector、DeltaFIFO、以及配套的消费者实现
Controller
type Controller interface {
Run(stopCh <-chan struct{})
HasSynced() bool
LastSyncResourceVersion() string
}
//controller结构体实现了Controller接口
type controller struct {
config Config
reflector *Reflector //包含了Reflector
reflectorMutex sync.RWMutex
clock clock.Clock
}
type Config struct {
Queue //重要:DeltaFIFO
ListerWatcher //重要:ListerWatcher
Process ProcessFunc //重要:从DeltaFIFO Pop调用时,调用的回调
ObjectType runtime.Object //期待处理的资源对象的类型
FullResyncPeriod time.Duration //全量resync的周期
ShouldResync ShouldResyncFunc //delta fifo周期性同步判断时使用
RetryOnError bool
......
}
Reflector
同一类型资源Informer共享一个Reflector,Reflector通过ListAndWatch成员来ListAndWatch apiserver来获取资源的数据,获取时需要基于ResourceVersion(Etcd生成的全局唯一且递增的资源版本号)。通过此序号,客户端可以知道目前与服务端信息同步的状态,每次只取大于等于本地序号的事件,如此保证了事件的全局唯一,并可基于此特性实现断点续传等功能
ListAndwatch包含了两层意思,即List与Watch
- 当Controller重启或Watch中断的情况下,可以调用资源的list API(HTTP短连接)以进行全量更新,如
r.listerWatcher.List方法用于获取资源下的所有对象(如pod)的数据,参数options的ResourceVersion控制获取的位置,如果ResourceVersion为0,则表示获取所有Pod的资源数据,如果ResourceVersion非0,则表示根据资源版本号继续获取 - Watch方式会基于当前的资源版本号监听资源变更(Added/Updated/Deleted)事件,通过在Http请求中设置
watch=true,表示采用Http长连接持续监听apiserver发来的资源变更事件,apiserver在response的HTTP Header中设置Transfer-Encoding的值为chunked,表示采用分块传输编码。每当有事件来临,返回一个WatchEvent
Reflector在获取新的资源数据后,调用Add方法将资源对象的Delta记录存放到本地缓存DeltaFIFO中
type Reflector struct {
name string
expectedTypeName string //被监控的资源的类型名
expectedType reflect.Type // 监控的对象类型
expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind
store Store // 存储,就是Delta_FIFO,这里的Store类型实际是Delta_FIFO的父类
listerWatcher ListerWatcher // 用来进行list&watch的接口对象
backoffManager wait.BackoffManager
resyncPeriod time.Duration //重新同步的周期
ShouldResync func() bool //周期性的判断是否需要重新同步
clock clock.Clock //时钟对象,主要是为了给测试留后门,方便修改时间
......
}
DeltaFIFO
对于Delta_fifo,我们知道它是一个先进先出的队列,队列中具体的元素是Delta。现在我们利用解析Indexer同样的方法来解析Delta_fifo 对于Delta_fifo,我们知道它是一个先进先出的队列,队列中具体的元素是Delta。现在我们利用解析Indexer同样的方法来解析Delta_fifo。
数据结构 如同我前文所说,K8S中运用了大量的接口,实际上,Delta_fifo与threadSafeStore本质上都是实现了Store这个接口。Delta_fifo的结构相对简单些,它结构的示意图如下。其中,
delta_fifo 在队列中核心数据是Delta。Delta包含两部分,一个是类型,另一个是对象(object)。Delta的类型包括:
const ( Added DeltaType = “Added” Updated DeltaType = “Updated” Deleted DeltaType = “Deleted” // Replaced is emitted when we encountered watch errors and had to do a // relist. We don’t know if the replaced object has changed. // // NOTE: Previous versions of DeltaFIFO would use Sync for Replace events // as well. Hence, Replaced is only emitted when the option // EmitDeltaTypeReplaced is true. Replaced DeltaType = “Replaced” // Sync is for synthetic events during a periodic resync. Sync DeltaType = “Sync” ) Delta存放在一个数组里面,名为Deltas。一个Deltas对应一个资源对象,Deltas中的每个Delta蕴含着Event的动作,所以Deltas记录着这个资源对象一系列的变化。最新的对象在数组末尾,最旧的则是数组的第一个元素。 items是一个map,其中的每个key对应着一个Deltas队列。 Queue是一个包含了所有key的数组。 KeyFunc与Indexer提到的KeyFunc一样,默认也是{namespace}/{name}的形式。 Delta_fifo还包含着一个成员叫knownObjects,Delta_fifo可以通过调用它的ListKeys()方法得到底层存储的所有Key,通过GetByKey()得到对应key的对象。在Informer中,这里的底层存储就是Indexer。
- 方法
Delta_fifo比较重要的方法有以下几个
Add\Update\Delete 这几个放在一起是因为他们逻辑相似,大同小异。 作用:向Delta_fifo加入一个Added\Updated\Deleted Delta。 输入:object 返回:无 Add\Update 除了加入的Delta动作类型不一致以外,加入内部逻辑是一样的。而Delete方法在把包含Deleted动作的Delta加入至fifo里之前会检查这个对象的key是否既不存在于indexer缓存,也不存在于队列里,如果是的话则返回错误。 Add\Update\Delete都调用queueActionLocked去执行加入Delta到队列的操作,下面重点介绍这个方法的逻辑。 输入:DeltaType (Added\Updated\Deleted); object 输出:无 内部逻辑: 根据KeyFunc得到object的key 根据key通过items获取旧的Deltas,把新的Delta加到队列后面,形成新的Deltas 对Deltas进行去重操作 如果这个key的Deltas不存在,则queue数组增加一项新的key,加入末尾。 在items新添加新的一项key与新deltas的绑定 Replace 作用:在初始化Delta_fifo时使用。Informer会通过list得到某资源下全部的对象,而Replace方法就可以把这些资源对象一次性装载至队列,并同步至Indexer。 输入:object数组 返回:无 内部逻辑: 根据输入object数组的长度创建一个装载key的set keys(之前在Indexer部分提到的sets.string ) 遍历object数组,获取每个object的key,把key加入到keys这个集合中,同时利用之前提到的queueActionLocked把对象加入Delta到队列,值得一提的是这个DeltaType为Replaced。 通过knownObjects.ListKeys()得到所有本地缓存中所有key 遍历这些key,判断刚才创建的keys集合中有没有本地缓存的key,没有的话从本地缓存中拿到key对应的object,再次利用queueActionLocked把它加入到Delta_fifio中,这里的DeltaType为Deleted。意味着这个对象应该被删除。 Resync 作用:可以同步队列与本地存储 输入:无 输出:无 内部逻辑: 通过knownObjects.ListKeys()得到所有Indexer本地缓存中所有key 遍历这些key,先通过knownObjects.GetByKey(key)得到object,然后调用queueActionLocked新增delta进队列,此时的动作为Sync Pop 作用: 输入:一个自定义的处理函数ProcessFunc,pop时会把出队列的deltas用这个方法处理 输出:某一个deltas 内部逻辑: 死循环执行出队列操作,循环内逻辑如下: 通过queue数组拿到最旧的(下标为0)key,queue指针下移一位 通过items map得到deltas,把它从items map中删除 用ProcessFunc处理这个Deltas 通过上述分析我们能看出来其实Delta_fifo并没有做具体地对资源对象做更新删除等操作,它更多是充当一个缓冲和转存的作用。资源对象的最新本地缓存是在Indexer中的,Indexer与etcd中存储的对象是保持状态一致的。
Informer 启动时都做了什么? 当Informer调用Run方法时,Informer启动,开始工作。Informer初始化的工作包括:
初始化delta_fifo,指定其knownObjects为某一indexer(或指定空indexer) 等待从delta_fifo队列pop,并等待用processer处理 list,把list的结果用delta_fifo.replace方法放进delta_fifo list后进行watch,开始接收event
Informer
Informer是一个抽象概念,SharedInformerFactory
type SharedInformerFactory interface {
internalinterfaces.SharedInformerFactory
ForResource(resource schema.GroupVersionResource) (GenericInformer, error)
WaitForCacheSync(stopCh <-chan struct{}) map[reflect.Type]bool
Admissionregistration() admissionregistration.Interface
Internal() apiserverinternal.Interface
Apps() apps.Interface
Autoscaling() autoscaling.Interface
Batch() batch.Interface
Certificates() certificates.Interface
Coordination() coordination.Interface
Core() core.Interface
Discovery() discovery.Interface
Events() events.Interface
Extensions() extensions.Interface
Flowcontrol() flowcontrol.Interface
Networking() networking.Interface
Node() node.Interface
Policy() policy.Interface
Rbac() rbac.Interface
Scheduling() scheduling.Interface
Storage() storage.Interface
}
Indexer
Indexer 接口是缓存(Store)和索引(Index系列)的高级抽象,实现了 Informer 高效、快速的索引查询功能。结构如下:
Store接口:缓存 Local Store 的抽象cache结构体:Indexer的实现,其中ThreadSafeStore类型的成员cacheStorage也实现了Indexer的所有方法,ThreadSafeStore意义是定义了线程安全的存储接口
type Indexer interface {
// 封装了 缓存 Local Store
Store
// 下面方法 为对索引结构的操作
// Index returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// intersects the set of indexed values of the given object, for
// the named index
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
// IndexKeys returns the storage keys of the stored objects whose
// set of indexed values for the named index includes the given
// indexed value
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
// ListIndexFuncValues returns all the indexed values of the given index
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
// ByIndex returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// for the named index includes the given indexed value
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
// GetIndexer return the indexers
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
//cache 结构体实现了 Indexer 中的所有方法(包含Store的方法)
type cache struct {
// cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cache
// 这是个接口其实 就涵盖了 Indexer 接口 的所有方法
// 因此实现了 ThreadSafeStore 该接口,就相当于实现了 Indexer 接口
cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore
// keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and
// should be deterministic.
// 用于计算 Object 的 key
keyFunc KeyFunc
}
// ThreadSafeStore 接口:表示可以对缓存的操作
type ThreadSafeStore interface {
Add(key string, obj interface{})
Update(key string, obj interface{})
Delete(key string)
Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Replace(map[string]interface{}, string)
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
Resync() error
}
结构体threadSafeMap是接口ThreadSafeStore的实例化,也是缓存(Local Store)的实际数据存储(安全有锁),下面详细描述下基于缓存的索引如何组织:
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
// 相当于缓存的本质,存储着 key-object
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// Indexers Indices 也是map 结构
// 相当于 索引的 结构
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
// 索引值 map: 由索引函数计算所得索引值(indexedValue) => [objKey1, objKey2...]
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indexers maps a name to a IndexFunc
// map 索引类型 => 索引函数
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Indices maps a name to an Index
// map 索引类型 => 索引值 map
type Indices map[string]Index
// k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/sets/string.go
// sets.String 可以理解为 没有重复元素的数组,不过在 go 语言里面是采用 map 形式构建,因为 map 的 key 不能重复
// sets.String is a set of strings, implemented via map[string]struct{} for minimal memory consumption.
type String map[string]Empty
举个例子,用一个 Informer 来监听 Kubernetes 集群中的 Pod 资源,需要建立一个索引,以便能快速根据 Pod 所在的节点名称(nodeName)查找所有运行在该节点上的 Pod,那么上面数据结构的功能如下
sets.String:集合用于存储一组不重复的键,用来存储具有相同索引值(如同一个Node)的所有对象的 Key,通常key为namespace/name组成(如 default/mypod)。所有运行在 node-123节点上的 Pod,它们的 Key 会被收集到一个 sets.String集合中,如下:
sets.String{
"default/pod-1": struct{}{},
"default/pod-2": struct{}{},
"kube-system/pod-abc": struct{}{},
}
Index:将一个索引值(如具体的Node node-123)映射到包含所有具有该索引值的对象 Key 的集合
// Index
map[string]sets.String{
"node-123": sets.String{"default/pod-1": {}, "default/pod-2": {}, "kube-system/pod-abc": {}},
"node-456": sets.String{"default/pod-3": {}},
"node-789": sets.String{}, // 即使没有 Pod 的节点,也可能存在(为空集合)
}
Indexers:类似一个注册表,它定义了可以创建哪些类型的索引以及如何计算这些索引。键是索引类型的名称,值是用来计算对象索引值的函数
//key:索引类型的名字,例如 "byNode"
//value:IndexFunc,一个函数,输入是一个对象,输出是该对象在此索引类型下的所有索引值(一个字符串切片)
//首先需要注册一个索引器,告诉系统如何从 Pod 对象中提取节点名
// 定义一个 IndexFunc
nodeIndexFunc := func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
pod := obj.(*v1.Pod) // 将对象转换为 Pod
return []string{pod.Spec.NodeName}, // 返回这个 Pod 的 nodeName
}
// 注册到 Indexers中
indexers := map[string]IndexFunc{
"byNode": nodeIndexFunc, // 索引类型"byNode"的计算方法 = nodeIndexFunc
}
Indices:这是整个索引的顶层容器。它将每个索引类型(如 byNode)映射到该类型下完整的索引数据(即一个 Index)
//key:索引类型的名字,例如 "byNode"
//value:该索引类型下所有的索引数据
indices := map[string]Index{
// 索引类型 "byNode" 对应的所有索引数据
"byNode": {
// 下面是 Index (map[string]sets.String)
"node-123": sets.String{"default/pod-1": {}, "default/pod-2": {}, "kube-system/pod-abc": {}},
"node-456": sets.String{"default/pod-3": {}},
},
// 未来还可以有其他索引类型,例如 "byNamespace"
// "byNamespace": { ... }
}
现在,假设新增一个 pod-4,它被调度到 node-456,其 Key 为 default/pod-4,那么操作过程如下:
- 计算索引值:系统查看 Indexers,发现注册了一个
byNode索引类型,其计算函数是nodeIndexFunc。于是调用nodeIndexFunc(pod-4),得到索引值["node-456"] - 更新索引:系统找到 Indices中
byNode这个索引类型对应的 Index,然后在这个 Index中,找到键为node-456的集合(一个sets.String) - 将新 Pod 的 Key
default/pod-4添加到这个集合中 - 最终状态:更新后,
indices["byNode"]["node-456"]这个集合现在就包含了default/pod-3和default/pod-4
查询时的过程如下,假设需要获取所有在 node-456上的 Pod,过程如下:
- 通过 Indices找到
byNode索引 - 通过 Index找到
node-456这个键对应的sets.String(即{"default/pod-3", "default/pod-4"}) - 最后根据这些 Key,从底层存储的
map[string]interface{}中取出完整的 Pod 对象