0x00 前言
本文代码基于 v4.11.6 版本
Linux一切皆文件,如常规文件、目录、目录中的.和..、以及软/硬连接、socket、管道等,这些都属于文件
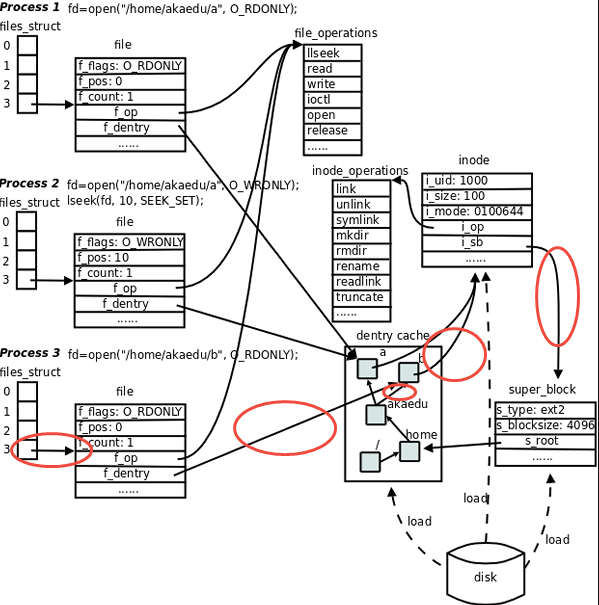
用户进程在能够读 / 写一个文件之前必须要先 open 这个文件。对文件的读 / 写从概念上说是一种进程与文件系统之间的一种有连接通信,所谓打开文件实质上就是在进程与文件之间建立起链接。在文件系统的处理中,每当一个进程重复打开同一个文件时就建立起一个由 struct file 结构代表的独立的上下文。通常一个 file 结构,即一个读 / 写文件的上下文,都由一个打开文件号(fd)加以标识。从 VFS 的层面来看,open 操作的实质就是根据参数指定的路径去获取一个该文件系统(比如 ext4)的 inode(硬盘上),然后触发 VFS 一系列机制(如生成 dentry、加载 inode 到内存 inode 以及将 dentry 指向内存 inode 等等),然后去填充 VFS 层的 struct file 结构体,这样就可以让上层使用了
用户态程序调用 open 函数时,会产生一个中断号为 5 的中断请求,其值以该宏 __NR__open 进行标示,而后该进程上下文将会被切换到内核空间,待内核相关操作完成后,就会从内核返回至用户态,此时还需要一次进程上下文切换,本文就以内核视角追踪下 open 的内核调用过程
0x01 ftrace open 系统调用
内核调用链如下(简化)
1) open1-3789488 | | __x64_sys_openat() {
1) open1-3789488 | | do_sys_openat2() {
1) open1-3789488 | | do_filp_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | path_openat() {
1) open1-3789488 | | lookup_open.isra.0() {
1) open1-3789488 | | do_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | may_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | vfs_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | do_dentry_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | security_file_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | selinux_file_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | bpf_lsm_file_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | ext4_file_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | | dquot_file_open() {
1) open1-3789488 | 0.172 us | generic_file_open();
完整的函数调用链 可见
0x02 VFS的若干细节(文件系统缓存、挂载等)
VFS的hash表:dentry cache(dcache)
一个 struct dentry 结构代表文件系统中的一个目录或文件,VFS dentry 结构的意义,即需要建立文件名 filename 到 inode 的映射关系,目的为了提高系统调用在操作、查找目录/文件操作场景下的效率,且 dentry 是仅存在于内存的数据结构,所以内核使用了 dentry_hashtable(dentry 树)来管理整个系统的目录树结构。在 Linux 可通过下面方式查看 dentry cache 的指标:
[root@VM-X-X-tencentos ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/dentry-state
1212279 1174785 45 0 598756 0
在内核中,dentry-state记录在dentry_stat_t结构体中,在使用内核提供的inotify机制监控时,特别要注意nr_negative对调用inotify性能的影响(某个指定的目录下面存在海量的negative dentry时),参考Negative dentries, 20 years later
struct dentry_stat_t {
long nr_dentry;
long nr_unused;
long age_limit; /* age in seconds */
long want_pages; /* pages requested by system */
long nr_negative; /* # of unused negative dentries */
long dummy; /* Reserved for future use */
};
前文已经描述过 dentry_hashtable 数据结构的意义,即为了提高目录查找效率,内核使用 dentry_hashtable 对 dentry 进行管理,在 open 等系统调用进行路径查找时,用于快速定位某个目录 dentry 下面的子 dentry(哈希表的搜索效率显然更好)
dentry_hashtable用来保存对应一个dentry的hlist_bl_node,使用拉链法来解决哈希冲突。它的好处是能根据路径分量(component)名称的hash值,快速定位到对应的hlist_bl_node,最后通过hlist_bl_node(container_of)获得对应的dentry
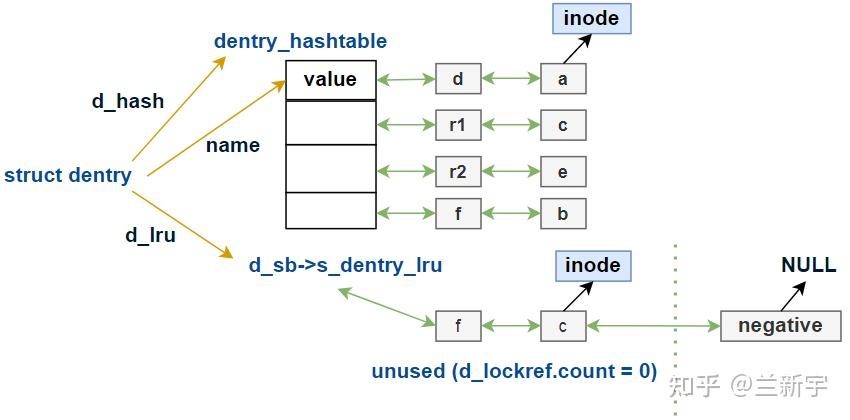
1、dentry 及 dentry_hashtable 的结构(搜索 && 回收)
对 dentry 而言,对于加速搜索关联了两个关键数据结构 d_hash 及 d_lru,dentry 回收关联的重要成员是 d_lockref,d_lockref 内嵌一个自旋锁(spinlock_t),用于保护 dentry 结构的并发修改
struct dentry {
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; //hashtable 的节点
strcut list_head d_lru; //LRU 链上的节点
}
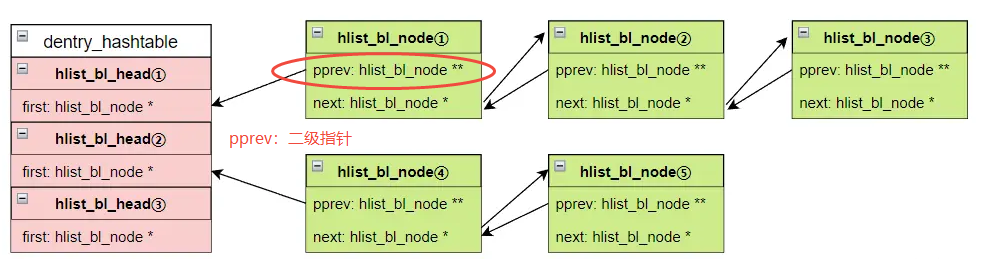
dentry_hashtable是一个指向hlist_bl_head的指针的数组。通过name的hash值,调用d_hash()即可获取dentry_hashtable中对应的hlist_bl_head(即拉链的头),由于dentry cache中每一项的内容是一个路径到inode的映射关系(海量),通过hashtable来管理是非常高效的,在dentry cache这个hashtable中,是通过类型为qstr的name来充当key值,进而计算出hash表的索引(value),即value 是 struct dentry本身
dentry cache 使用拉链法来解决hash碰撞问题,若某两个qstrname相同的,其对应的parent dentry肯定不同(同一目录下不可能有两个同名的文件),所以具有唯一性
//dentry hashtable定义
static struct hlist_bl_head *dentry_hashtable __read_mostly;
// hlist_bl_head的头
struct hlist_bl_head {
struct hlist_bl_node *first;
};
// 链表的节点(双向链表)
struct hlist_bl_node {
struct hlist_bl_node *next, **pprev;
};
// 调用d_hash
// d_hash(dentry->d_name.hash);
static inline struct hlist_bl_head *d_hash(unsigned int hash)
{
return dentry_hashtable + (hash >> (32 - d_hash_shift));
}
如上,结构体hlist_bl_node类似一个双向链表,采用的是头插法(hlist_bl_add_head()),前文已经介绍过此类内核链表实现。pprev这个二级指针,指向的不是前面节点,而是指向前面节点的next指针的存储地址(如果是头节点,pprev会指向hlist_bl_head的first的存储地址)。这样的好处是从链表中移除自身的时候,只需要将next->pprev = pprev即可,关联内核函数为__hlist_bl_del(),对pprev解引用操作即(*pprev)这个值为当前链表节点hlist_bl_node的地址,下面介绍关于dentry_hashtable的几类典型操作:
- 判断节点是否在链表中,只需要判断
pprev是否为NULL(hlist_bl_unhashed()) dentry_hashtable的初始化:通过alloc_large_system_hash()分配一个容量是2的整数次幂的内存块,即一个指针数组hlist_bl_node中并没有dentry相关信息,那么查询dentry_hashtable,如何通过hlist_bl_node指针获取对应的dentry呢?dentry里有一个对象(非指针成员)struct hlist_bl_node d_hash,所以可以用hlist_bl_node指针,通过container_of()机制获得对应的dentry- 链表遍历:
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(),链表里面包含了冲突节点 - 如何区分是否是目标dentry?
dentry_hashtable是采用拉链法解决冲突的。由于是根据路径分量名称+父parent dentry指针地址来做hash的,所以如何找到需要的节点?- 当hash相同,路径分量名称不同,比较一下路径分量名称的字符串
- 当hash相同,路径分量名称相同,通过
hlist_bl_node获取对应的dentry,判断一下dentry->d_parent是否是它的parent即可。因为同一目录下不可能有两个同名的文件,所以名称相同的,parent肯定不同
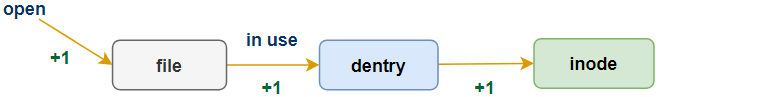
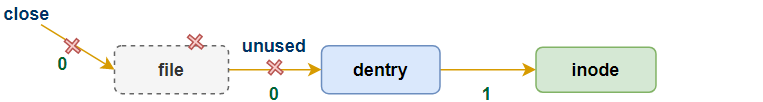
回顾下struct dentry结构的d_lockref.count成员,该字段表示此dentry的引用计数,若其值不为0,说明还有进程在引用它(如通过open),此时dentry处于in use状态;而当其引用计数变为0,表明不再被使用(如文件被close了),则将切换到unused的状态,但此时其指向的内存inode依然有效,因为这些inode对应的文件之后还可能被用到。当内存紧张时,被标记为unused dentry所占据的内存是可以被回收的(参考dentry-state),根据局部性原理,应选择最近未被使用的dentry作为回收的对象。同page cache类似,通过slab cache分配得到的dentry在进入unused状态后,会通过LRU链表的形式被管理,最新加入的unused dentry被放在链表的头部,启动内存shrink的操作时,链表尾部的dentry将被率先回收,过程如下图:
in-use状态:
unused状态:
negative-dentry:

static void d_lru_add(struct dentry *dentry)
{
dentry->d_flags |= DCACHE_LRU_LIST;
this_cpu_inc(nr_dentry_unused);
if (d_is_negative(dentry))
this_cpu_inc(nr_dentry_negative);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_lru_add(&dentry->d_sb->s_dentry_lru, &dentry->d_lru));
}
此外,如果尝试访问(如open)一个磁盘路径,但最后发现此路径对应的文件在磁盘上是不存在的,此时该路径对应的dentry会以negative entry的形式记录在dcache里,这样下次在试图访问这个不存在的路径时,可以立即返回错误(失败的案例同样有价值),如上面描述的dentry-state中的nr_negative字段
struct dentry {
......
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount
* keep separate from RCU lookup area if
* possible!
*/
......
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v6.12.6/source/include/linux/lockref.h#L25
struct lockref {
union {
#if USE_CMPXCHG_LOCKREF
aligned_u64 lock_count;
#endif
struct {
spinlock_t lock;
int count;
};
};
};
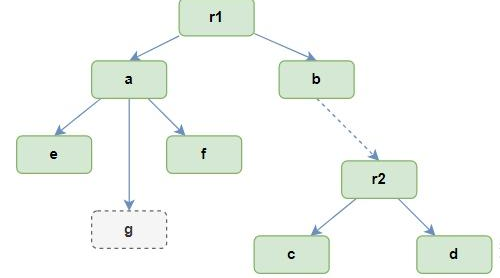
假设现在一个目录树的结构如下,挂载了2个文件系统,挂载点分别是r1和r2(后者对应目录b)。其中目录a下的文件g未被使用到,所以不存在于dcache中。经过hash运算后,其在dcache中的组织结构可能是这样的:
2、dentry_hashtable 的创建过程
在文件系统初始化时,调用 vfs_caches_init->dcache_init 为 dcache 进行初始化,先创建一个 dentry 的 slab,用于后续 dentry 对象的分配,同时还初始化了 dentry_hashtable 这个用于管理 dentry 的全局 hashtable
static struct hlist_head *C __read_mostly;
static void __init dcache_init(void)
{
dentry_cache = KMEM_CACHE_USERCOPY(dentry,
SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT|SLAB_PANIC|SLAB_MEM_SPREAD|SLAB_ACCOUNT,
d_iname);
/* Hash may have been set up in dcache_init_early */
if (!hashdist)
return;
//dentry_hashtable 初始化
dentry_hashtable =
alloc_large_system_hash("Dentry cache",
sizeof(struct hlist_bl_head),
dhash_entries, // bucket size
13,
HASH_ZERO,
&d_hash_shift,
NULL,
0,
0);
d_hash_shift = 32 - d_hash_shift;
}
3、基于dentry-hashtable的 RCU-walk 和 REF-walk 查找机制
RCU-walk 和 REF-walk 是路径查找(Path Lookup)中两种核心的并发控制机制,分别针对高频读取和写操作场景优化,简单介绍下此二种机制:
一、RCU-walk:无锁路径查找,设计目标是在无写入干扰的场景下,避免所有内存写操作(无锁、无引用计数增减),通过 RCU(Read-Copy-Update)和序列锁(Seqlock)保证数据一致性,相关实现原理如下:
- 无锁遍历
- 使用
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu()遍历 dentry 哈希链表(bucket),不获取任何锁 - 依赖 RCU 宽限期(Grace Period)确保被释放的 dentry 不会被访问
- 使用
- seqlock验证一致性
- 通过
raw_seqcount_begin()读取 dentry 的序列号d_seq - 关键操作后调用
read_seqcount_retry()检测序列号是否变化
- 通过
- 快速回退机制,若遇到以下情况,立即切换到 REF-walk:
- Dentries 不在缓存中(如冷数据)
- 检测到并发修改(序列号变化频繁)
- 路径包含符号链接或挂载点等
// seqlock 验证模式
seq = raw_seqcount_begin(&dentry->d_seq);
// 读取 dentry 字段
if (read_seqcount_retry(&dentry->d_seq, seq))
goto retry; // 序列号变化则重试
二、REF-walk:基于引用计数的安全路径查找,设计目标是处理高频写入或复杂路径(如符号链接、权限校验),通过引用计数和锁保证强一致性,相关实现原理如下:
- 引用计数保护
- 对每个 dentry 和 vfsmount 调用
dget()/mntget()增加引用计数,防止并发释放 - 退出时通过
dput()/mntput()减少计数
- 对每个 dentry 和 vfsmount 调用
- 锁机制同步
- 自旋锁:保护 dentry 哈希桶(
dentry->d_lock) - 读写信号量:处理 inode 数据更新(
inode->i_rwsem)
- 自旋锁:保护 dentry 哈希桶(
- 安全处理复杂路径
- 解析符号链接时递归调用
link_path_walk() - 挂载点检查:通过
__lookup_mnt()验证 vfsmount 有效性
- 解析符号链接时递归调用
4、dentry cache的操作(TODO)
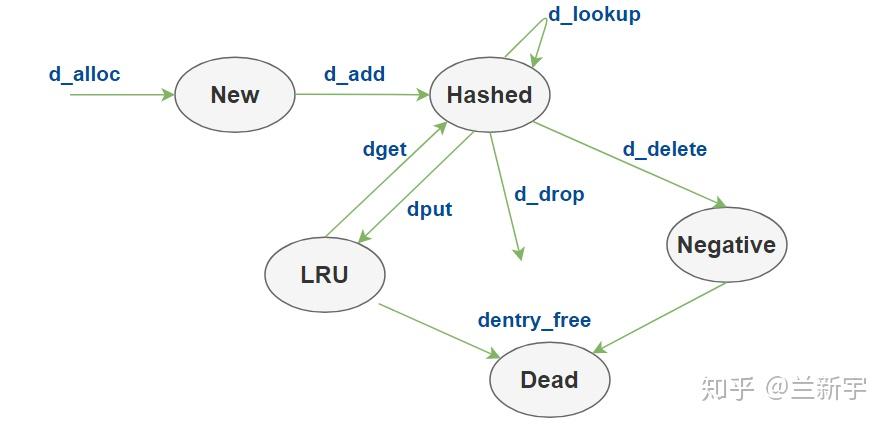
当创建一个新的dentry时,d_alloc()会为其申请内存空间,而后通过d_add函数将这个新的dentry和对应的inode关联起来,并插入dcache的hash表中;对dentry的使用以dget和dput来实现引用计数dentry->d_lockref.count的加减,当引用计数变为0时,加入LRU链表,再次被使用后,从LRU链表移除。最后d_drop函数直接将一个dentry从hashtable中移除(如dentry失效时),而d_delete的目标则是归还inode,并将一个dentry置于negative状态,在内核4.11.6版本中,在vfs_unlink、vfs_rmdir等操作成功前的最后都会调用d_delete
4、dentry cache查找算法的rcu VS ref的设计思路(有趣)
前面简单描述了rcu-walk与ref-walk的场景,关于dcache的查找中,查找dcache的核心函数是link_path_walk,在路径的遍历中,每一层目录/文件都被视为一个component(分量/组件),由于component的查询和判定主要依靠hash表的比对,不需要修改dentry的内容,本质上这是一个读的过程,但考虑到并行的需要,需要对途径的dentry的引用计数加1,而后再减1,由于涉及到reference count值的更新,所以这种方式被称为ref-walk
link_path_walk这个核心路径查找的函数(link_path_walk的 for自顶而下循环 + walk_component逐级分量处理)遵循如下原则:
- 分层处理:路径分量逐级解析
- 缓存优先:每级优先查询 dcache
- 动态扩展:未命中时触发文件系统的 lookup 操作
- 树形构建:新 dentry 加入 dcache 形成dentry树结构
这里以路径/a/b/c中的分量 b为例,假设路径分量b在dentry cache中不存在,但是目录(分量)存在,在walk_component函数的主要工作流程如下:
/*step 1:RCU-walk 模式优先尝试
目标:无锁快速查找
操作:在父目录(a/)的 dcache 中 RCU 查找 b,检查 dentry 有效性(d_seq验证)
结果:命中->返回 dentry(继续下一分量);未命中/无效 -> 返回 -ECHILD
*/
dentry = lookup_fast(nd, flags | LOOKUP_RCU);
/*step 2:回退到 ref-walk 模式
目标:带锁的可靠查找
操作:获取父 inode 锁(inode->i_rwsem);重试 dcache 查找(__d_lookup)
结果:命中 -> 返回 dentry;未命中 -> 进入慢速路径
*/
// RCU失败后回退
dentry = lookup_fast(nd, flags); // 去掉LOOKUP_RCU
/* step3:触发文件系统 lookup
目标:访问存储设备
操作:分配新 dentry:d_alloc(parent, name)
调用文件系统方法:ext4_lookup(dir, dentry, flags)
文件系统从磁盘读取目录项:
1. 存在->关联 inode:d_add(dentry, inode)
2. 不存在 -> 返回 NULL
结果:成功 ->新 dentry 加入 dcache;失败->返回错误(如 ENOENT)
*/
dentry = lookup_slow(nd);
// -> __lookup_slow()
// -> dir->i_op->lookup()
/*
step 4:继续下一分量
// walk_component() 成功后
*/
nd->path.dentry = dentry; // 更新当前路径
return next_component; // 处理下一分量(如 c)
| 步骤 | component | 模式 | 关键操作 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a |
RCU-walk | 在dcache中,使用根目录/ + a 查询 /a是否存在 |
命中dcache(缓存),进入下一分量 |
| 2 | b |
RCU-walk | 在dcache中,使用 a/+b 查询 a/b 是否存在(RCU) |
未命中 -> 回退 ref-walk |
| 3 | b |
ref-walk | 在dcache中,使用 a/+b 查询 a/b 是否存在(ref) |
仍然未命中 |
| 4 | b |
ref-walk | 调用 ext4_lookup() 函数读磁盘 |
找到 inode,创建 dentry |
| 5 | c |
…… | …… | …… |
在ref-walk查找过程中(关联内核函数d_lookup),路径可能会被运行在其他CPU上的线程重命名(如从/a/b更改为/a/c/b),如何检测呢?既然没法防止这种情况的发生,只能通过seqlock检测,如果确实被更改了,就放弃之前的查找结果,再次尝试。因为这个锁主要用来处理重命名的问题,在代码中被称为rename_lock,从代码也可以看出,实际上d_lookup并未占用rename_lock,它仅仅是需要检测在lookup期间,是否有其他线程持有了rename_lock并执行了重命名操作
// d_lookup的循环中,会存在无尽循环的可能吗?
struct dentry *d_lookup(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&rename_lock);
dentry = __d_lookup(parent, name);
if (dentry)
break;
} while (read_seqretry(&rename_lock, seq));
...
}
而真正对rename_lock锁的获取,即这个seqlock的writer,在调用d_move函数的过程中,会试图持有该锁
//在 d_lookup执行期间,d_move可以获取 rename_lock
void d_move(struct dentry *dentry, struct dentry *target)
{
write_seqlock(&rename_lock);
__d_move(dentry, target, false);
write_sequnlock(&rename_lock);
}
由于dentry(dcache)查找是个高频操作(open/stat等),而ref-walk机制需要持有所操作dentry的spinlock(d_lock),开销偏大,频繁地加减reference count可能造成cacheline的刷新。内核实现了更快的rcu-walk查找模式,在代码上二者有何种差异呢?
- rcu-walk:
__d_lookup_rcu()实现,内核优先调用,仅在dcache中进行查找,不涉及到文件系统层面,凸显一个快速 - ref-walk:
__d_lookup()实现,回退到ref-walk
关于dentry hash比对的环节,两者的逻辑是比较相似的,但rcu-walk没有使用dentry的spinlock,也没有更改dentry的引用计数,而是以一个seqcount(d_seq)来替代(只进行sequence的判断),其所要对抗的,也是__d_move()一类的操作
不过rcu-walk同样会在并发修改的场景下失败,当然失败的后果是可接受的,可以通过 unlazy_walk() 去除LOOKUP_RCU标志位,fall back到ref-walk的方式继续查找。那么如果ref-walk模式也失败的话,说明要找的dentry不在dcache中,这时就只能调用inode的lookup,老老实实地从磁盘文件系统中查找,后文介绍open系统调用实现时会详细介绍上述过程
后文将会从代码角度分析下RCU-walk与ref-walk实现的细节区别,以及ref-walk对路径查找的意义
inode cache
只要在内存中建立了一个dentry,那么其指向的inode也会在内存中缓存,这就构成了inode cache(icache),icache的每一项内容都是一个已挂载的文件系统中的文件inode,在系统查看如下:
[root@VM-x-x-tencentos /]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inode-state
79177 5809 0 0 0 0 0
VFS的挂载(mount tree)基础
open系统调用的路径分量解析中也会涉及到对挂载的处理,这里简单回顾下。挂载是指将一个文件系统,挂载到全局文件系统树上。除根文件系统外,挂载点要求是一个已存在的文件系统的目录。根文件系统rootfs,会在系统启动的时候创建,挂载到/,也是全局文件系统树的根节点。当一个目录被文件系统挂载时,原来目录中包含的其他子目录或文件会被隐藏。以后进入该目录时,将会通过VFS切换到新挂载的文件系统所在的根目录,看到的是该文件系统的根目录下的内容
1、VFS挂载的四大对象及两张hashtable
mount:对应一次文件系统的挂载。记录了挂载点的dentry、vfsmount以及文件系统在文件系统树上的父节点mount。也记录了代表它自身的hlist_node,与dentry类似,也是可以用hlist_node的指针,通过container_of获取到对应的mountpoint()vfsmount:记录了一个文件系统的super_block和根目录的dentrymountpoint:记录一个挂载点的dentry和代表它自身的hlist_node,可以用hlist_node的指针,通过container_of获取到对应的mountpoint()mnt_namespace:记录了某个独立的挂载空间
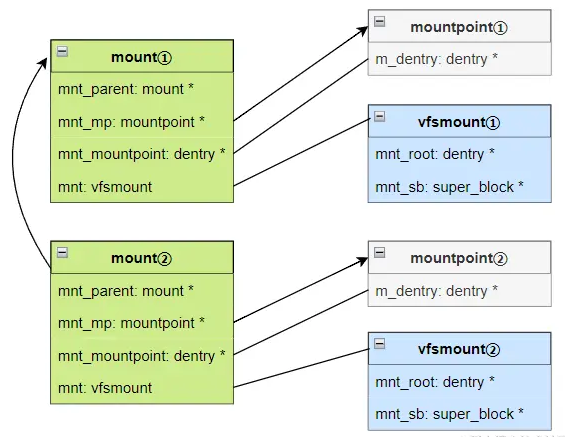
对象之间的关系如下:
mount持有指向mountpoint的指针。它的mnt_mountpoint和mountpoint的m_dentry是指向同一个dentry。该dentry对应的是挂载目录mount持有的是vfsmount的对象(非指针)。当持有指向该vfsmount的指针时,可以通过container_of获得该mount了,关联函数为real_mount()
此外,VFS挂载涉及两张(hashtable)表用来加速查找,两张表的结构设计和dentry_hashtable是一样的
mount_hashtable:通过父mount的vfsmount和挂载点的dentry,生成hash值,通过该表获得mount。关联函数为__lookup_mnt()mountpoint_hashtable:通过挂载点的dentry,生成hash值,通过该表获得mountpoint。关联函数为lookup_mountpoint()
2、mountpoint与mount的关系
前面介绍了struct mount(挂载实例)表示一个具体的文件系统挂载实例,包含挂载的文件系统信息(vfsmount)、父挂载点信息、挂载点位置信息和子挂载点链表
struct mount{
......
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp; //指向对应的 mountpoint
struct hlist_node mnt_mp_list; //链接到 mountpoint 的 m_list
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; // 挂载点dentry
struct vfsmount mnt; // vfsmount结构
......
}
struct mountpoint(挂载点位置)表示一个目录被用作挂载点的信息,包含被挂载的目录项(dentry)、引用计数以及挂载到该位置的所有 mount 结构链表
struct mountpoint {
......
struct hlist_head m_list; // 所有挂载到此位置的 mount 结构(链表)
struct dentry *m_dentry; // 被挂载的目录
......
}
需要特别注意的是mount->mnt_mountpoint与mountpoint->m_dentry的区别以及特殊挂载模式下二者的关系
二者的关系如下:
struct mountpoint struct mount
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ │ │
│ m_dentry ──────┼───────────>│ mnt_mountpoint │
│ │ │ │
│ m_list ────────┼───────────>│ mnt_mp_list │
│ │ │ │
│ m_count │ │ mnt_mp ─────────┼─────────┐
│ │ │ │ │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ │
│
|
struct mountpoint
举例来说,一个 mountpoint 可以对应多个 mount 结构(当同一个目录被多次挂载时),此时mount结构被链表形式组织。如下面的例子
// 同一个目录被多次挂载
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/point
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/point # 再次挂载到同一目录
在这种情况下,只有一个 mountpoint结构对应 /mnt/point目录,有两个 mount结构分别对应 /dev/sda1和 /dev/sda2的挂载,两个 mount结构都通过 mnt_mp_list链接到同一个 mountpoint的 m_list,而mountpoint结构的m_dentry成员指向dentry /mnt/point。
mountpoint->m_count记录有多少个 mount 结构使用此挂载点,当最后一个 mount 卸载时,mountpoint 被释放
TODO
VFS mount tree的构造过程
本小节描述下mount树的构造的典型场景,回顾下基础结构path、mountpoint、mount与vfsmount:
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_hash; // 哈希表链表节点
struct mount *mnt_parent; // 父挂载点
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; // 挂载点dentry
struct vfsmount mnt; // vfsmount结构
struct list_head mnt_mounts; // 子挂载点链表头
struct list_head mnt_child; // 兄弟挂载点链表节点
struct list_head mnt_instance; // 超级块实例链表
// ... 其他成员
};
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
int mnt_flags;
};
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry;
};
struct mountpoint {
struct hlist_node m_hash;
struct dentry *m_dentry;
struct hlist_head m_list;
int m_count;
};
1、树状结构的形成过程
当执行mount挂载操作时,内核调用 do_add_mount函数,注意传入的path参数(标记唯一的路径)
//将一个新的挂载点(newmnt)添加到指定的路径(path)上
static int do_add_mount(struct mount *newmnt, struct path *path, int mnt_flags)
{
struct mountpoint *mp;
struct mount *parent;
int err;
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_INTERNAL_FLAGS;
// 1. 锁定挂载点,防止并发修改
mp = lock_mount(path);
if (IS_ERR(mp))
return PTR_ERR(mp);
// 2. 获取父挂载点
parent = (path->mnt);
err = -EINVAL;
// 3. 检查父挂载点是否有效
if (unlikely(!check_mnt(parent))) {
/* that's acceptable only for automounts done in private ns */
if (!(mnt_flags & MNT_SHRINKABLE))
goto unlock;
/* ... and for those we'd better have mountpoint still alive */
if (!parent->mnt_ns)
goto unlock;
}
/* Refuse the same filesystem on the same mount point */
// 4. 防止同一文件系统挂载到同一位置(避免同一文件系统重复挂载)
err = -EBUSY;
if (path->mnt->mnt_sb == newmnt->mnt.mnt_sb &&
path->mnt->mnt_root == path->dentry)
goto unlock;
err = -EINVAL;
// 5. 检查新挂载点的根目录不是符号链接
if (d_is_symlink(newmnt->mnt.mnt_root))
goto unlock;
// 6. 设置标志并嫁接挂载点
newmnt->mnt.mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
err = graft_tree(newmnt, parent, mp);
unlock:
unlock_mount(mp);
return err;
}
继续,graft_tree函数主要作用是验证挂载参数,然后调用 attach_recursive_mnt进行实际挂载
static int graft_tree(struct mount *mnt, struct mount *p, struct mountpoint *mp)
{
// 1. 检查文件系统是否允许用户挂载
if (mnt->mnt.mnt_sb->s_flags & MS_NOUSER)
return -EINVAL;
// 2. 检查目录类型匹配(挂载点目录类型必须与文件系统根目录类型一致)
if (d_is_dir(mp->m_dentry) != d_is_dir(mnt->mnt.mnt_root))
return -ENOTDIR;
// 3. 递归附加挂载点
return attach_recursive_mnt(mnt, p, mp, NULL);
}
attach_recursive_mnt的作用是递归地将源挂载点附加到目标位置,处理共享挂载传播,在attach_recursive_mnt中主要考虑parent_path为NULL的场景
static int attach_recursive_mnt(struct mount *source_mnt,
struct mount *dest_mnt, struct mountpoint *dest_mp,
struct path *parent_path)
{
HLIST_HEAD(tree_list);
struct mnt_namespace *ns = dest_mnt->mnt_ns;
struct mountpoint *smp;
struct mount *child, *p;
int err;
//1. 预分配挂载点(用于嵌套挂载)
smp = get_mountpoint(source_mnt->mnt.mnt_root);
if (IS_ERR(smp))
return PTR_ERR(smp);
// 2. 检查挂载命名空间容量
if (!parent_path) {
err = count_mounts(ns, source_mnt);
if (err)
goto out;
}
//3. 处理共享挂载传播
if (IS_MNT_SHARED(dest_mnt)) {
// 3.1 分配组ID
err = invent_group_ids(source_mnt, true);
if (err)
goto out;
//3.2 传播挂载到对等组
err = propagate_mnt(dest_mnt, dest_mp, source_mnt, &tree_list);
lock_mount_hash();
if (err)
goto out_cleanup_ids;
//3.3 设置共享标志
for (p = source_mnt; p; p = next_mnt(p, source_mnt))
set_mnt_shared(p);
} else {
lock_mount_hash(); // 非共享挂载直接加锁
}
//4. 实际挂载操作
if (parent_path) {
// 移动挂载点的情况
detach_mnt(source_mnt, parent_path);
attach_mnt(source_mnt, dest_mnt, dest_mp);
touch_mnt_namespace(source_mnt->mnt_ns);
} else {
// 新挂载的情况
mnt_set_mountpoint(dest_mnt, dest_mp, source_mnt);
commit_tree(source_mnt);
}
//5. 处理传播的挂载点
hlist_for_each_entry_safe(child, n, &tree_list, mnt_hash) {
hlist_del_init(&child->mnt_hash);
struct mount *q = __lookup_mnt(&child->mnt_parent->mnt,
child->mnt_mountpoint);
if (q)
mnt_change_mountpoint(child, smp, q);
commit_tree(child);
}
//6. 清理资源
put_mountpoint(smp);
unlock_mount_hash();
return 0;
// 错误处理路径
out_cleanup_ids:
// 清理传播的挂载点
while (!hlist_empty(&tree_list)) {
child = hlist_entry(tree_list.first, struct mount, mnt_hash);
umount_tree(child, UMOUNT_SYNC);
}
unlock_mount_hash();
cleanup_group_ids(source_mnt, NULL);
out:
ns->pending_mounts = 0;
put_mountpoint(smp);
return err;
}
这里主要看下处理实际挂载的两个函数mnt_set_mountpoint以及commit_tree:
//mnt_set_mountpoint:建立挂载点之间的父子关系
void mnt_set_mountpoint(struct mount *mnt,
struct mountpoint *mp, struct mount *child_mnt)
{
//1. 增加引用计数(引用计数管理,防止挂载点被意外释放)
mp->m_count++;
mnt_add_count(mnt, 1);
//2. 建立父子关系
child_mnt->mnt_mountpoint = dget(mp->m_dentry);
child_mnt->mnt_parent = mnt; //核心:mount树的父子关系
child_mnt->mnt_mp = mp;
//3. 添加到挂载点链表(将子挂载点添加到父挂载点的管理链表)
hlist_add_head(&child_mnt->mnt_mp_list, &mp->m_list);
}
//commit_tree:将挂载点正式提交到挂载命名空间
static void commit_tree(struct mount *mnt)
{
struct mount *parent = mnt->mnt_parent;
struct mount *m;
LIST_HEAD(head);
struct mnt_namespace *n = parent->mnt_ns;
BUG_ON(parent == mnt); // 防止自引用
//1. 准备挂载点链表
list_add_tail(&head, &mnt->mnt_list);
list_for_each_entry(m, &head, mnt_list)
m->mnt_ns = n; // 设置命名空间
//2. 添加到命名空间链表(维护命名空间内的挂载点链表)
list_splice(&head, n->list.prev);
//3. 更新命名空间统计
n->mounts += n->pending_mounts;
n->pending_mounts = 0;
//4. 附加到全局数据结构,通过 __attach_mnt注册到全局哈希表
__attach_mnt(mnt, parent);
//5. 更新命名空间时间戳
touch_mnt_namespace(n);
}
attach_mnt负责将新的mount结构注册到全局hash表
static void attach_mnt(struct mount *mnt, struct mount *parent,
struct mountpoint *mp)
{
// 添加到父挂载点的哈希表
mnt->mnt_parent = parent;
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mp->m_dentry;
// 将新挂载点插入到哈希表链表头部(LIFO顺序)
hlist_add_head_rcu(&mnt->mnt_hash,
m_hash(&parent->mnt, mp->m_dentry));
// 添加到挂载点实例链表
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &mnt->mnt.mnt_sb->s_mounts);
}
TODO
VFS挂载的若干细节
2、VFS某个dentry挂载之后的变化
3、VFS的重复挂载
VFS的挂载机制支持在一个挂载点上,先后挂载多个的文件系统的情况(此外,若挂载的文件系统类型相同,文件系统所在磁盘分区不同,也是可以的)。如在binderfs上,先挂载ext2文件系统,再挂载ext4系统,最后再挂载Binder文件系统。这时候只有最后挂载的Binder文件系统是生效的。它们的挂载关联如下图

因为重复挂载的缘故,为了找到最后挂载的Binder文件系统的mount,需要轮询调用__lookup_mnt(),即一边轮询调用__lookup_mnt(),一边更新path,直到__lookup_mnt()返回的mount*为NULL时,说明此时是该dentry上生效的文件系统类型
在下文可以看到,路径查找过程中,在follow_mount*函数中,当遇到当前路径分量是一个挂载点时,会调用__lookup_mnt函数来查询挂载节点struct mount结构
static inline struct hlist_head *m_hash(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry)
{
unsigned long tmp = ((unsigned long)mnt / L1_CACHE_BYTES);
tmp += ((unsigned long)dentry / L1_CACHE_BYTES);
tmp = tmp + (tmp >> m_hash_shift);
return &mount_hashtable[tmp & m_hash_mask];
}
struct mount *__lookup_mnt(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry)
{
//通过父mount的vfsmount和在父文件系统的挂载点的dentry,获得hlist_head
struct hlist_head *head = m_hash(mnt, dentry);
struct mount *p;
//遍历hlist_node链表,找到对应的mount
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, mnt_hash)
if (&p->mnt_parent->mnt == mnt && p->mnt_mountpoint == dentry)
return p;
return NULL;
}
#define hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = hlist_entry_safe (rcu_dereference_raw(hlist_first_rcu(head)),\
typeof(*(pos)), member); \
pos; \
pos = hlist_entry_safe(rcu_dereference_raw(hlist_next_rcu(\
&(pos)->member)), typeof(*(pos)), member))
通常在重复挂载的场景下,要通过循环来寻找到最终dentry上挂载的最终的文件系统,大致的代码如下:
//循环调用的示例代码
void lookup_for_realmount(struct path *path) {
......
struct vfsmount *mnt = path->mnt;
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry;
while (1) {
if (flags & DCACHE_MOUNTED) {
//通过父mount的vfsmount和挂载点的dentry,获取对应的mount
struct mount *mounted = __lookup_mnt(path->mnt, dentry);
//mounted不为NULL,表示不是最后一个挂载在该挂载点的文件系统
if (mounted) {
//更新path
path->mnt = &mounted->mnt;
//更新path里的dentry
dentry = path->dentry = mounted->mnt.mnt_root;
flags = dentry->d_flags;
//继续查找
continue;
}
......
//return的时候,path里记录的就是最后一个挂载在该挂载点的文件系统的vfsmount
//和文件系统根目录"/"的dentry。这也意味着已经切换到了该文件系统
return;
}
return;
}
}
struct path是一个<vfsmount,dentry>二元组,path中的vfsmount记录的是当前所在文件系统的根目录信息,而dentry是当前路径行走所在的分量
TODO
0x03 基础知识
一个进程需要读/写一个文件,必须先通过 filename 建立和文件 inode 之间的通道,方式是通过 open() 函数,该函数的参数是文件所在的路径名 pathname,如何根据 pathname 找到对应的 inode?这就要依靠 dentry 结构了
系统调用
int open (const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
int openat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
- 参数
pathname:文件路径,可以是相对路径或绝对路径(以/开头) - 参数
dirfd: 是打开一个目录后得到的文件描述符,作为相对路径的基准目录。如果文件路径是相对路径,那么在函数openat中解释为相对文件描述符dirfd引用的目录,open函数中解释为相对调用进程的当前工作目录。如果文件路径是绝对路径,openat会忽略参数dirfd - 参数
flags:必须包含一种访问模式:O_RDONLY/O_ WRONLY/O_RDWR,flags可以包含多个文件创建标志和文件状态标志,区别是文件创建标志只影响打开操作, 文件状态标志影响后面的读写操作
文件创建标志
O_CLOEXEC:开启 close-on-exc标志,使用系统调用execve()装载程序的时候关闭文件CREAT:如果文件不存在,创建文件ODIRECTORY:参数pathname必须是一个日录EXCL:通常和标志位CREAT联合使用,用来创建文件。如果文件已经存在,那么open()失败,返回错误号EEXISTNOFOLLOW:不允许参数pathname是符号链接(最后一个分量不能是符号链接,其他分量可以是符号链接)。如果参数pathname是符号链接,那么打开失败,返回错误号ELOOPO_TMPFILE:创建没有名字的临时普通文件,参数pathname指定目录关闭文件的时候,自动删除文件O_TRUNC:如果文件已经存在,是普通文件并且访问模式允许写,那么把文件截断到长度为0
文件状态标志
APPEND:使用追加模式打开文件,每次调用write写文件的时候写到文件的末尾O_ASYNC:启用信号驱动的输入输出,当输入或输出可用的时候,发送信号通知进程,默认的信号是SIGIOO_DIRECT:直接读写存储设备,不使用内核的页缓存。虽然会降低读写速度,但是在某些情况下有用处,例如应用程序使用自己的缓冲区,不需要使用内核的页缓存文件DSYNC:调用write写文件时,把数据和检索数据所需要的元数据写回到存储设备LARGEFILE:允许打开长度超过4GB的大文件(64位内核会强制设置)NOATIME:调用read读文件时,不要更新文件的访问时间O_NONBLOCK:使用非阻塞模式打开文件,open和以后的操作不会导致调用进程阻塞PATH:获得文件描述符有两个用处,指示在目录树中的位置以及执行文件描述符层次的操作。不会真正打开文件,不能执行读操作和写操作O_SYNC:调用write写文件时,把数据和相关的元数据写回到存储设备
mode参数
mode 指定创建新文件时的文件模式,当参数 flags 指定标志位 O_CREAT 或 O_TMPFILE 的时候,必须指定参数 mode,其他情况下忽略参数 mode,组合如下:
S_IRWXU:0700,用户(文件拥有者)有读、写和执行权限S_IRUSR:00400,用户有读权限S_IWUSR:00200,用户有写权限S_IXUSR:00100,用户有执行权限S_IRWXG:00070,文件拥有者所在组的其他用户有读、写和执行权限S_IRGRP:00040,文件拥有者所在组的其他用户有读权限S_IWGRP:00020,文件拥有者所在组的其他用户有写权限S_IXGRP:0010,文件拥有者所在组的其他用户有执行权限S_IRWXO:0007,其他组的用户有读、写和执行权限S_IROTH:0004,其他组的用户有读权限S_IWOTH:00002,其他组的用户有写权限S_IXOTH:00001,其他组的用户有执行权限
AT_FDCWD
AT_FDCWD表明当 filename 为相对路径的情况下,将当前进程的工作目录设置为起始路径
flags && mode 解析
flags:控制打开一个文件mode:新建文件的权限
build_open_flags函数将open的参数转换为内核结构open_flags:
struct open_flags {
int open_flag;
umode_t mode;
int acc_mode;
int intent;
int lookup_flags;
};
static inline int build_open_flags(int flags, umode_t mode, struct open_flags *op)
{
int lookup_flags = 0;
//O_CREAT 或者 `__O_TMPFILE*` 设置了,acc_mode 才有效。
int acc_mode;
// Clear out all open flags we don't know about so that we don't report
// them in fcntl(F_GETFD) or similar interfaces.
// 只保留当前内核支持且已被设置的标志,防止用户空间乱设置不支持的标志
flags &= VALID_OPEN_FLAGS;
if (flags & (O_CREAT | __O_TMPFILE))
op->mode = (mode & S_IALLUGO) | S_IFREG;
else
//如果 O_CREAT | __O_TMPFILE 标志都没有设置,那么忽略 mode
op->mode = 0;
// Must never be set by userspace
flags &= ~FMODE_NONOTIFY & ~O_CLOEXEC;
// O_SYNC is implemented as __O_SYNC|O_DSYNC. As many places only
// check for O_DSYNC if the need any syncing at all we enforce it's
// always set instead of having to deal with possibly weird behaviour
// for malicious applications setting only __O_SYNC.
if (flags & __O_SYNC)
flags |= O_DSYNC;
//如果是创建一个没有名字的临时文件,参数 pathname 用来表示一个目录,
//会在该目录的文件系统中创建一个没有名字的 iNode
if (flags & __O_TMPFILE) {
if ((flags & O_TMPFILE_MASK) != O_TMPFILE)
return -EINVAL;
acc_mode = MAY_OPEN | ACC_MODE(flags);
if (!(acc_mode & MAY_WRITE))
return -EINVAL;
} else if (flags & O_PATH) {
// If we have O_PATH in the open flag. Then we
// cannot have anything other than the below set of flags
// 如果设置了 O_PATH 标志,那么 flags 只能设置以下 3 个标志
flags &= O_DIRECTORY | O_NOFOLLOW | O_PATH;
acc_mode = 0;
} else {
acc_mode = MAY_OPEN | ACC_MODE(flags);
}
op->open_flag = flags;
// O_TRUNC implies we need access checks for write permissions
// 如果设置了,那么写之前可能需要清空内容
if (flags & O_TRUNC)
acc_mode |= MAY_WRITE;
// Allow the LSM permission hook to distinguish append
// access from general write access.
// 让 LSM 有能力区分 追加访问和普通访问
if (flags & O_APPEND)
acc_mode |= MAY_APPEND;
op->acc_mode = acc_mode;
//设置意图,如果没有设置 O_PATH,表示此次调用有打开文件的意图
op->intent = flags & O_PATH ? 0 : LOOKUP_OPEN;
if (flags & O_CREAT) {
//是否有创建文件的意图
op->intent |= LOOKUP_CREATE;
if (flags & O_EXCL)
op->intent |= LOOKUP_EXCL;
}
//判断查找的目标是否是目录
if (flags & O_DIRECTORY)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
//判断当发现符号链接时是否继续跟下去
if (!(flags & O_NOFOLLOW))
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW; //查找标志设置了 LOOKUP_FOLLOW 表示会继续跟下去
//设置查找标志,lookup_flags 在路径查找时会用到
op->lookup_flags = lookup_flags;
return 0;
}
chroot
chroot 改变当前进程所在的内核空间 current->root 的全局变量, 之后该进程所有的文件系统操作的路径,都以新的 path 作为根目录。关联open*系统调用中的set_fs_root函数的处理过程
nameidata/path/vfsmount 结构
nameidata,nameidata 用来存储遍历路径的中间结果(临时性存放),在路径搜索时常用到。这个结构体在路径查找中非常重要,它记录了查找信息、保存了查找起始路径。在路径 /a/b/c/d 的每一个分量的查找中,它会保存当前的结果。对于一般路径名查找,在查找结束时,它会包含查询结果的信息;对于父路径名查找,在查找结束时,它会包含最后一个分量所在目录的信息。最重要的成员是 nameidata.path(记住在 VFS 中只有 path 才能唯一标识一个路径)
如open()、mkdir()、rename()等系统调用,可以使用文件的路径名作为参数,VFS将解析路径名并把它拆分成一个文件序列(分量),除了最后一个文件之外,所有的文件都必须是目录。为了识别目录文件,VFS将沿着路径逐层查找,并且使用nameidata边查找边缓存
last:存储需要解析的文件路径的分量,不仅包字符串,还包含长度和散列值path:存储解析得到的挂载描述符和目录项inode:存储目录项对应的索引节点(path.dentry.d_inode)
1、path 会保存已经成功解析到的信息,last 用来存放当前需要解析的信息,如果 last 解析成功那么就会更新 path
2、如果文件路径的分量是一个符号链接,那么接下来需要解析符号链接的目标,那么stack用来保存文件路径还未被解析的部分,depth 表示深度。假设目录b是符号链接(目标是 e/f),解析文件路径 a/b/c/d,那么解析到 b,发现 b 是符号链接,接下来要解析符号链接 b 的目标 e/f,需要把文件路径中没有解析的部分 c/d 保存到stack中,等解析完符号链接后继续解析
3、nameidata中inode与link_inode成员的作用是什么?
TODO
struct nameidata {
struct path path; //path 保存当前搜索到的路径(包含了 vfsmount 及在该 mount 下的 dentry)
struct qstr last; //last 保存当前子路径名及其散列值
struct path root; //root 用来保存根目录的path信息
struct inode *inode; // path.dentry.d_inode
// inode 指向当前找到的目录项的 inode 结构
unsigned int flags; //flags 是一些和查找(lookup)相关的标志位
unsigned seq, m_seq;
int last_type; //last_type 表示当前节点类型
unsigned depth; // depth 用来记录在解析符号链接过程中的递归深度
int total_link_count;
struct saved {
struct path link;
struct delayed_call done;
const char *name;
unsigned seq;
} *stack, internal[EMBEDDED_LEVELS];
struct filename *name;
struct nameidata *saved; // 保存上一个 nameidata 的指针
struct inode *link_inode;
unsigned root_seq;
int dfd;
};
//set_nameidata
static void set_nameidata(struct nameidata *p, int dfd, struct filename *name)
{
struct nameidata *old = current->nameidata;
p->stack = p->internal;
p->dfd = dfd;
p->name = name;
p->total_link_count = old ? old->total_link_count : 0;
p->saved = old;
}
last_type的五种类型:
LAST_NORM:最后一个分量是普通文件名LAST_ROOT:最后一个分量是/(即整个路径名为/)LAST_DOT:最后一个分量是.LAST_DOTDOT:最后一个分量是..LAST_BIND:最后一个分量是链接到特殊文件系统的符号链接
VFS中的目录查找
在路径名查找时,要考虑如下场景:
- 当遍历路径时遇到一个目录项(dentry),内核需要判断这个 dentry 是否是一个挂载点
- 如果这个dentry是一个挂载点(合法的已经挂载了文件系统的挂载点),那么至少有两个dentry结构,第一个dentry结构对应于原文件系统的目录,第二个dentry结构对应于新挂载点文件系统的
/目录节点 - 当前的分量dentry(如普通分量或者
..),需要检查其是否为挂载点、或者是symlink,所以在代码中可以看到*follow_mount*、*_link*等相关的函数
TODO
VFS 的 path walk:简单介绍
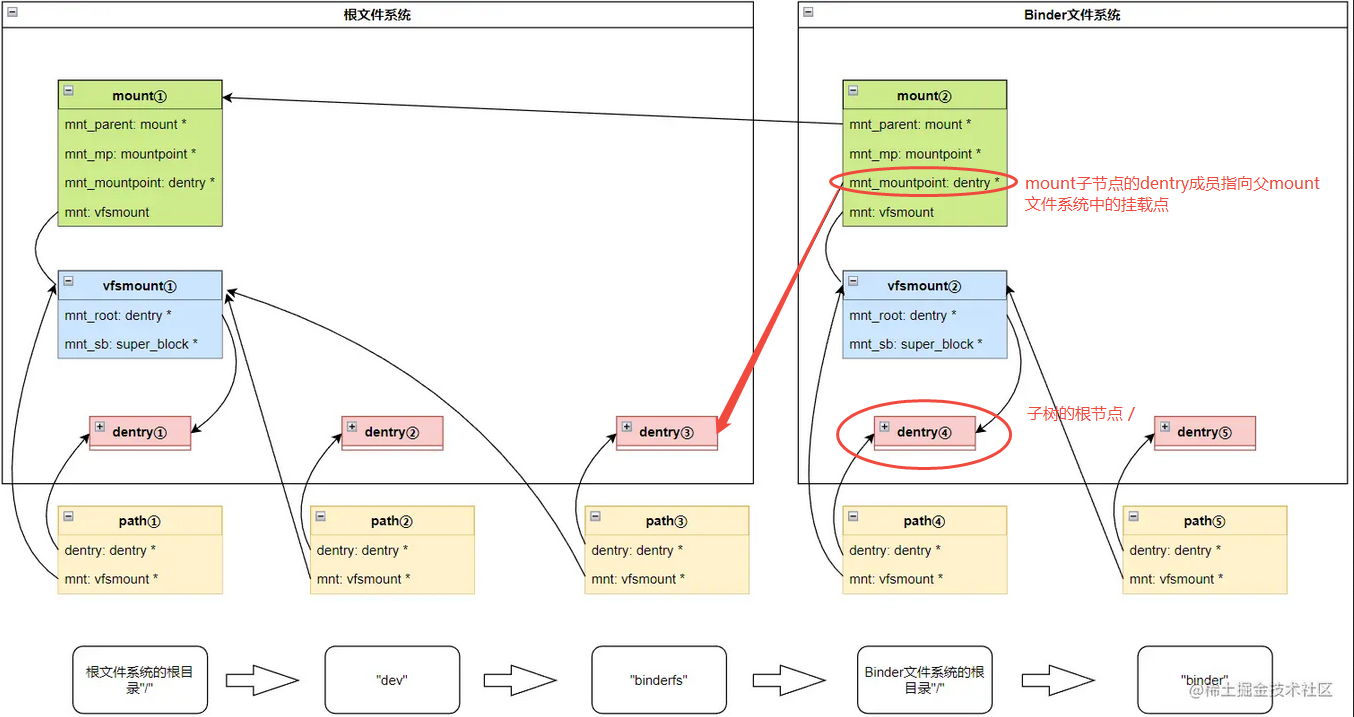
VFS的path walk是open()的内核调用的核心设计,这里以访问/dev/binderfs/binder为例,/是根文件系统rootfs的根目录,dev是根文件系统的根目录下的一个普通目录,非挂载点,binderfs根文件系统下的位于/dev里的目录,同时也是Binder文件系统的挂载点,binder是Binder文件系统的挂载点下的一个代表binder设备的文件,下面是vfs的path walk过程(自上而下的过程):
- walk path起点是在根文件系统
rootfs的根目录。所以一开始,path1记录的是根文件系统的vfsmount1和代表根文件系统根目录/的dentry1 - 进入到
dev分量时,path2记录的dentry将是代表路径分量dev的dentry,由于此时分量仍属于根文件系统,所以记录的vfsmount仍是vfsmount1 - 当进入到
binderfs时,path3记录的dentry将是代表分量binderfs的dentry,由于还是在根文件系统,所以记录的vfsmount仍是vfsmount1。但是检查dentry时,发现其DCACHE_MOUNTED的flag,即表示它是一个挂载点。这时就要利用path里的信息,即父mount1的vfsmount1和挂载点的dentry,从mount_hashtable获得Binder文件系统的mount2(关联内核函数是__lookup_mnt()),最终获得vfsmount2里的dentry4,成功切换到Binder文件系统的根目录(Binder文件系统的根目录在访问的路径上是看不出来的,因为VFS屏蔽了用户的感知) - 在整个VFS的路径行走中,需要先进入根文件系统,最后再进入Binder文件系统,注意
dentry3和dentry4是有区别的,dentry3是由根文件系统创建,而dentry4是由Binder文件系统,在挂载的时候创建的
RCU lock
RCU(Read-copy_update)是一种数据同步机制,允许读写同时进行。读操作不存在睡眠、阻塞、轮询,不会形成死锁,相比读写锁效率更高。写操作时先拷贝一个副本,在副本上进行修改、发布,并在合适时间释放原来的旧数据
0x04 内核实现走读:open
open的内核调用链(主要)
TODO
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(openat, int, dfd,...)
|- do_sys_open()
|- do_sys_openat2()
|- do_filp_open() //初始化结构体nameidata的实例,并将open()相关参数保存在nameidata的实例中
|- path_openat()
|- path_init() //获取根文件系统的vfsmount、根目录的dentry,并保存在nameidata中
|- link_path_walk() //路径行走:逐个解析文件路径分量(除了最后一个分量),获取对应的dentry、inode
|- walk_component()
|- lookup_fast()
|- __d_lookup_rcu() //实现了rcu-walk
|- d_hash() //根据hash值,从dentry_hashtable中获取对应的hlist_bl_head
|- hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu() //遍历链表hlist_bl_head,寻找对应的dentry
|- __d_lookup() //实现了ref-walk
|- lookup_slow() //在lookup_fast()中没有找到dentry,会获取父dentry对应的inode,通过inode->i_op->lookup去查找、创建
|- __lookup_slow()
|- d_alloc_parallel() //创建一个新的dentry,并用in_lookup_hashtable检测、处理并发的创建操作
|- inode->i_op->lookup // 通过父dentry的inode去查找对应的dentry:通过其文件系统,获取信息及创建对应的dentry
|- step_into() //处理dentry是一个链接或者挂载点的情况
|- handle_mounts() //处理一个挂载点的情况,获取最后一个挂载在挂载点的文件系统信息
|- __follow_mount_rcu() //轮询调用__lookup_mnt(),处理重复挂载(查找标记有LOOKUP_RCU时调用)
|- __lookup_mnt() //寻找挂载点
|- traverse_mounts() //作用与__follow_mount_rcu()类似
|- pick_link() //处理是一个链接的情况,获取对应的真实路径
|- do_last() //分析最后的路径分量,部分代码与link_path_walk()类似
|- lookup_fast()
|- step_into()
|- do_open() //根据最后路径分量的inode,调用binder设备的binder_open()
|- vfs_open()
|- do_dentry_open() //将最后的路径分量对应的inode,将inode支持的file_operations,保存在file中
//最后调用file中的file_operations里的open函数指针,最终会调用binder_open()
|- binder_open() //打开binder设备,进行相关初始化
系统调用入口
open系统调用如下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(open, const char __user *, filename, int, flags, umode_t, mode)
{
//64位机器下,force_o_largefile 将展开为 true 并且 O_LARGEFILE 标志将被添加到 open 系统调用的 flags 参数中
if (force_o_largefile())
flags |= O_LARGEFILE;
return do_sys_open(AT_FDCWD, filename, flags, mode);
}
do_sys_open主要流程如下:
- 检查&&解析传入的
flags与mode - 复制文件名到内核空间,调用
getname(filename)从用户空间复制文件名,避免直接访问用户内存引发安全问题 - 分配文件描述符fd,调用
get_unused_fd_flags(flags)从当前进程的文件描述符表files_struct->fdt中分配空闲的 fd。若分配失败,返回EMFILE错误 - 打开文件对象
struct file,调用do_filp_open(dfd, tmp, &op)执行路径解析和文件打开操作 - 关联 fd 与 file 对象,若
do_filp_open成功,通过fd_install(fd, f)将struct file指针存入进程的 fd 数组,完成映射
long do_sys_open(int dfd, const char __user *filename, int flags, umode_t mode)
{
struct open_flags op;
//检查、解析传入标志位
int fd = build_open_flags(flags, mode, &op);
struct filename *tmp;
if (fd)
return fd;
// 将用户空间的路径名复制到内核空间
tmp = getname(filename);
if (IS_ERR(tmp))
return PTR_ERR(tmp);
// 获取一个空闲的文件描述符
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
if (fd>= 0) {
// 调用 do_filp_open() 函数打开文件,返回打开文件的 struct file 结构
struct file *f = do_filp_open(dfd, tmp, &op);
if (IS_ERR(f)) {
//若传参有误,则 do_filp_open 执行失败,并使用 put_unused_fd 释放文件描述符
put_unused_fd(fd);
fd = PTR_ERR(f);
} else {
// 通知 fsnotify 机制
fsnotify_open(f);
// 调用 fd_install() 函数把文件描述符 fd 与 file 结构关联起来
// 即将struct file *f加入到fd索引位置处的数组中
// 如果后续过程中,有对该文件描述符的操作的话,就会通过查找该数组得到对应的文件结构,而后在进行相关操作
fd_install(fd, f);
}
}
//释放已分配的 filename 结构体
putname(tmp);
// 返回文件描述符,也就是 open() 系统调用的返回值
return fd;
}
void fd_install(unsigned int fd, struct file *file)
{
__fd_install(current->files, fd, file);
}
可以看到,open 系统调用的目的就是建立新建 fd 与 struct file 的绑定关系,但是实际上,间接建立的 VFS 内存映射关系可能如下图(假设路径 b 文件并不在 dcache 中)
getname:复制路径名到内核
__getname 用于在内核缓冲区专用队列里申请一块内存用来放置路径名,作用如下:
TODO
0x05 核心查找:do_filp_open->path_openat实现
do_filp_open,主要流程如下:
- 初始化路径查找上下文,通过
path_openat->path_init(dfd, pathname, flags, &nd)初始化struct nameidata nd,确定起始目录(当前目录AT_FDCWD或根目录) - 逐级遍历路径分量,通过
link_path_walk(pathname, &nd)解析每一级路径:- 查找目录项(dentry)并检查权限
- 处理挂载点:若当前 dentry 是挂载点(
d_mountpoint标志),切换到新文件系统的根目录(vfsmount->mnt_root) - 解析符号链接(symbol link):递归处理链接目标路径
- 处理最终路径分量,通过
do_last(&nd, file, ...)处理最后一个路径分量,大致流程为:- 若文件不存在且指定
O_CREAT,则创建新文件 - 检查访问权限(
may_open()) - 调用
vfs_open(&path, file)执行实际文件系统的打开操作
- 若文件不存在且指定
/*
参数 dfd:相对路径的基准目录对应的文件描述符
参数 pathname:指向文件完整路径
参数 op:查找标志
*/
struct file *do_filp_open(int dfd, struct filename *pathname,
const struct open_flags *op)
{
struct nameidata nd;
int flags = op->lookup_flags;
struct file *filp;
// 将 pathname 保存到 nameidata 里
set_nameidata(&nd, dfd, pathname);
// 调用 path_openat,此时是 flags 是带了 LOOKUP_RCU flag
//RCU 模式(首先尝试RCU快速路径)
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)))
//正常模式(回退到慢速路径)
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)))
//NFS模式,这里不讨论
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_REVAL);
restore_nameidata();
return filp;
}
函数 do_filp_open 三次调用函数 path_openat以解析文件路径的目的是什么?简单说明下
- 第一次解析传入标志
LOOKUP_RCU,该模式LOOKUP_RCU即rcu-walk方式,在 dcache 哈希表中根据{父目录, 名称}查找目录的过程中,使用 RCU机制保护dcache桶上的链表,使用序列号保护目录,其他处理器可以并行地修改目录, RCU 查找方式速度最快 - 如果在第一次解析的过程中发现其他处理器修改了正在查找的目录(问题:内核如何发现?),返回错误号
-ECHILD,那么第二次使用引用查找(ref-walk)即REF 方式,在dcache中根据{父目录, 名称}查找目录的过程中,使用 RCU 保护散列桶的链表,使用自旋锁保护目录,并且把目录的引用计数加1,引用查找方式速度较慢 - 网络文件系统的文件在网络的服务器上,本地上次查询得到的信息可能过期,和服务器的当前状态不一致。如果第二次解析发现信息过期,返回错误号
-ESTALE,那么第三次解析传入标志LOOKUP_REVAL,表示需要重新确认信息是否有效
do_filp_open->path_openat(open调用的核心)
path_openat,在 path_openat 中,先调用 get_empty_filp 方法分配一个空的 struct file 实例,再调用 path_init、link_path_walk、do_last 等方法执行后续的 open 操作,如果都成功了,则返回 struct file 给上层
open系统调用涉及到目录的从顶至底的查找过程的核心代码就浓缩为下面这段:
link_path_walk--->do_last:完成某个指定路径,如/a/b/c/d/e的分量解析,直至do_last完成最后一个分量(e)的处理- 如果在
link_path_walk每个分量解析过程中出现了symlink或者挂载点,那么就(TODO) - 如果
/a/b/c/d/e是一个符号链接,那么将/a/b/c/d/e转为实际路径后,继续循环处理;否则解析完成
while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) &&
(error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) {
nd->flags &= ~(LOOKUP_OPEN|LOOKUP_CREATE|LOOKUP_EXCL);
s = trailing_symlink(nd);
......
}
path_openat的主要功能是尝试寻找一个与路径相符合的 dentry 目录数据结构,核心方法是 path_init、link_path_walk、do_last,其中 path_init 和 link_path_walk 通常合在一起调用,作用是 可以根据给定的文件路径名称在内存中找到或者建立代表着目标文件或者目录的 dentry 结构和 inode 结构
注意while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) && (error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) 这里的循环的作用是什么?通过后续的trailing_symlink字面意思不难看出,是为了递归处理路径解析过程中可能存在的末尾符号链接(trailing symlink)
此外,这里阅读代码要区别flags带不带LOOKUP_RCU,即快速/慢速查找模式
static struct file *path_openat(struct nameidata *nd,
const struct open_flags *op, unsigned flags)
{
const char *s;
struct file *file;
int opened = 0;
int error;
file = get_empty_filp();
if (IS_ERR(file))
return file;
file->f_flags = op->open_flag;
......
if (unlikely(file->f_flags & O_PATH)) {
error = do_o_path(nd, flags, file);
if (!error)
opened |= FILE_OPENED;
goto out2;
}
// 路径初始化,确定查找的起始目录,初始化结构体 nameidata 的成员 path
// 调用 path_init() 设置 nameidata 的 path 结构体
// 对于常规文件来说,如 /data/test/testfile,设置 path 结构体指向根目录 /
// 即设置 path.mnt/path.dentry 指向根目录 /
// 为后续的目录解析做准备
// path_init() 的返回值即指向 open file 的完整路径名字串开头
s = path_init(nd, flags);
if (IS_ERR(s)) {
put_filp(file);
return ERR_CAST(s);
}
// 核心方法 link_path_walk && do_last
// 调用函数 link_path_walk 解析文件路径的每个分量,最后一个分量除外
// 调用函数 do_last,解析文件路径的最后一个分量,并且打开文件
while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) &&
(error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) {
nd->flags &= ~(LOOKUP_OPEN|LOOKUP_CREATE|LOOKUP_EXCL);
// 如果最后一个分量是符号链接,调用 trailing_symlink 函数进行处理
// 读取符号链接文件的数据,新的文件路径是符号链接链接文件的数据,然后继续 while
// 循环,解析新的文件路径
s = trailing_symlink(nd);
if (IS_ERR(s)) {
error = PTR_ERR(s);
break;
}
}
// 结束查找,释放解析文件路径的过程中保存的目录项和挂载描述符
terminate_walk(nd);
out2:
if (!(opened & FILE_OPENED)) {
BUG_ON(!error);
put_filp(file);
}
if (unlikely(error)) {
if (error == -EOPENSTALE) {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
error = -ECHILD;
else
error = -ESTALE;
}
file = ERR_PTR(error);
}
return file;
}
这里稍微整理一下while(....)中的实现过程和部分关键代码,对于路径 /a/b/c/d/e的处理,在进入 do_last之前,路径中除最后一个分量外的所有目录分量(a、b、c、d)都已经成功解析,并且它们的 dentry 通常已经存在于 dcache 中,最后一个分量(e)的处理在 do_last中完成
1、目录分量缓存机制,在路径解析过程中遵循如下规则:
- 缓存优先:每个目录分量首先通过
lookup_fast尝试从 dcache 获取 - 缓存未命中:如果未命中缓存dcache,通过
lookup_slow和文件系统查找 - 缓存填充:新找到的目录分量通过
d_add加入dcache(d_alloc_parallel) - 路径更新:
path_to_nameidata更新当前路径
TODO
path_openat->path_init
path_init 方法主要是用来初始化 struct nameidata 实例中的 path、root、inode 等字段。当 path_init 函数执行成功后,就会在 nameidata 结构体的成员 nd->path.dentry 中指向搜索路径的起点,接下来就使用 link_path_walk 函数顺着路径进行搜索
TODO:path_init
static const char *path_init(struct nameidata *nd, unsigned flags)
{
int retval = 0;
const char *s = nd->name->name;
// 如果路径名为空,清除 LOOKUP_RCU 标志
if (!*s)
flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU;
nd->last_type = LAST_ROOT;
// 重要:path_openat的参数flags保存在nameidata的flags成员中
nd->flags = flags | LOOKUP_JUMPED | LOOKUP_PARENT;
nd->depth = 0;
// 如果设置 `LOOKUP_ROOT`
// 表示 nameidata 中的 root 字段是由调用者提供的
if (flags & LOOKUP_ROOT) {
struct dentry *root = nd->root.dentry;
struct inode *inode = root->d_inode;
if (*s) {
if (!d_can_lookup(root))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
retval = inode_permission(inode, MAY_EXEC);
if (retval)
return ERR_PTR(retval);
}
nd->path = nd->root;
nd->inode = inode;
// 如果是 RCU 快速模式,则保存序列锁(处理竞争)
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
rcu_read_lock();
nd->seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
nd->root_seq = nd->seq;
nd->m_seq = read_seqbegin(&mount_lock);
} else {
// 不是RCU模式
// 如果是 REF 模式,则获取 path 的计数引用(处理竞争)
path_get(&nd->path);
}
return s;
}
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
nd->path.mnt = NULL;
nd->path.dentry = NULL;
// mount_lock 是一个全局 seqlock,有点像 rename_lock
// 它可以用来检查任何挂载点的任何修改
nd->m_seq = read_seqbegin(&mount_lock);
// CASE1
// 如果是以 / 开头,也就是说明是绝对路径
// 获取文件系统的根目录,并保存在nameidata中
if (*s == '/') {
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU)
rcu_read_lock(); //RCU模式加锁
set_root(nd);
if (likely(!nd_jump_root(nd)))
return s;
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
rcu_read_unlock(); //RCU模式解锁
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
} else if (nd->dfd == AT_FDCWD) {
//如果为相对路径,且未指定相对路径的基准目录
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//current是一个结构体task_struct,当前正在运行进程的进程描述符
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
unsigned seq;
rcu_read_lock();
//在RCU 快速模式下,通过RCU锁初始化nameidata的成员(from:当前进程的目录信息)
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&fs->seq);
nd->path = fs->pwd;
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&fs->seq, seq));
} else {
// 非RCU模式(REF模式),使用自旋锁保证并发安全
// 见下
get_fs_pwd(current->fs, &nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
return s;
} else {
//如果为相对路径,且已经指定了相对路径的基准目录
/* Caller must check execute permissions on the starting path component */
struct fd f = fdget_raw(nd->dfd);
struct dentry *dentry;
if (!f.file)
return ERR_PTR(-EBADF);
dentry = f.file->f_path.dentry;
if (*s) {
if (!d_can_lookup(dentry)) {
fdput(f);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTDIR);
}
}
nd->path = f.file->f_path;
if (flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
rcu_read_lock();
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
} else {
path_get(&nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
fdput(f);
return s;
}
}
static inline void get_fs_pwd(struct fs_struct *fs, struct path *pwd)
{
spin_lock(&fs->lock);
*pwd = fs->pwd;
path_get(pwd);
spin_unlock(&fs->lock);
}
static int nd_jump_root(struct nameidata *nd)
{
if (!nd->root.mnt) {
//获取根目录的path信息,保存到nd->root中
int error = set_root(nd);
}
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//将根文件系统的path、inode记录到nameidata中
struct dentry *d;
nd->path = nd->root;
d = nd->path.dentry;
nd->inode = d->d_inode;
nd->seq = nd->root_seq;
} else {
path_put(&nd->path);
nd->path = nd->root;
path_get(&nd->path);
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
}
nd->state |= ND_JUMPED;
return 0;
}
static int set_root(struct nameidata *nd)
{
//获取当前进程的fs_struct
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
unsigned seq;
do {
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&fs->seq);
//从fs中获取根目录"/"的Path,里面有它对应的dentry,保存在nd->root中
nd->root = fs->root;
nd->root_seq = __read_seqcount_begin(&nd->root.dentry->d_seq);
} while (read_seqcount_retry(&fs->seq, seq));
}
return 0;
}
path_openat->link_path_walk
link_path_walk函数用于实现path walk的核心功能,逐个解析文件路径分量(除了最后一个分量),获取对应的dentry、inode(查找分量对应的dentry/inode通过函数walk_component实现)
TODO
// 计算name中除根路径分量外的第一个路径分量的hash值和名字长度
// 返回值hash_len是64位的无符号整数
// 高32位记录name的长度len,低32位记录name的hash值
static inline u64 hash_name(const void *salt, const char *name)
{
unsigned long hash = init_name_hash(salt);
unsigned long len = 0, c;
c = (unsigned char)*name;
do {
len++;
hash = partial_name_hash(c, hash);
c = (unsigned char)name[len];
} while (c && c != '/'); // 截断/
return hashlen_create(end_name_hash(hash), len);
}
// link_path_walk:循环查找最后一个分量之前的所有分量
static int link_path_walk(const char *name, struct nameidata *nd)
{
int err;
int depth = 0; // depth <- nd->depth
// 跳过开始的 / 字符(根目录)
// 指针移动,/dev/binder变成 dev/binder
while (*name=='/'){
name++;
}
// 如果路径只包含 /,搜索完成,返回
if (!*name)
return 0;
/* At this point we know we have a real path component. */
//轮询处理各个文件路径名
for(;;) {
u64 hash_len;
int type;
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1667
//may_lookup 检查是否拥有中间目录的权限,需要有执行权限 MAY_EXEC
err = may_lookup(nd);
if (err)
return err;
//static inline u64 hash_name(const vo id *salt, const char *name)
// 用父 dentry 的地址 + 当前 denty 的 name 计算 hash 值
// 逐个字符的计算出,当前节点名称的哈希值,遇到 '/' 或者 '\0' 退出
// 计算当前目录的 hash_len,这个变量高 4 byte 是当前目录 name 字串长度,低 4byte 是当前目录(路径)的 hash 值,hash 值的计算是基于当前目录的父目录 dentry(nd->path.dentry)来计算的,所以它跟其目录(路径)dentry 是关联的
hash_len = hash_name(nd->path.dentry, name);
type = LAST_NORM;
// 如果目录的第一个字符是.,当前节点长度只能为 1 或者 2
// `.` 或者 `..`
if (name[0] == '.') switch (hashlen_len(hash_len)) {
case 2:
if (name[1] == '.') {
// 如果是 2,第二个字符也是.
type = LAST_DOTDOT;
//.. 需要查找当前目录的父目录
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_JUMPED;
}
break;
case 1:
// 回到 for 循环开始,继续下一个节点
type = LAST_DOT;
}
if (likely(type == LAST_NORM)) {
// LAST_NORM:普通目录
// 第一次循环parent代表根目录"/"(在path_init中获取到)
// 第二次循环parent代表目录"dev"
// ......
struct dentry *parent = nd->path.dentry;
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_JUMPED;
if (unlikely(parent->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_HASH)) {
// 当前目录项需要重新计算一下 hash 值
struct qstr this; //初始化并设置this的值
// 调用 parent 这个 dentry 的 parent->d_op->d_hash 方法计算 hash 值
err = parent->d_op->d_hash(parent, &this);
if (err < 0)
return err;
hash_len = this.hash_len;
name = this.name;
}
}
// 更新 nameidata last 结构体(解析完成)
nd->last.hash_len = hash_len;
nd->last.name = name;
nd->last_type = type;
// 这里使 name 指向下一级目录
// 指针移动,第一次循环时,dev/binder 变成了 /binder
name += hashlen_len(hash_len);
//注意通常循环处理到最后一个分量时,if (!*name)是为true的
if (!*name)
goto OK;
/*
* If it wasn't NUL, we know it was'/'. Skip that
* slash, and continue until no more slashes.
*/
//指针移动,第一次循环时,/binder 变成了 binder
do {
name++;
} while (unlikely(*name == '/'));
if (unlikely(!*name)) {
// 假设 open file 文件名路径上没有任何 symlink,则如果这个条件满足,说明整个路径都解析完了
// 还剩最后的 filename 留给 do_last() 解析,此函数将从下面的!nd->depth 条件处返回
OK:
// pathname body, done
if (!nd->depth)
// 路径最后一个分量,不管是否是symlink,
// 都会走到这里,不会执行walk_component()
// 此时已经到达了最终目标,路径行走任务完成
// 如果 open file 完整路径上没有任何 symlink,nd->depth 等于 0
return 0;
name = nd->stack[nd->depth - 1].name;
/* trailing symlink, done */
if (!name)
// 此时已经到达了最终目标,路径行走任务完成
return 0;
/* last component of nested symlink */
// symlink case
// symlink即软链接
// 只有嵌套在文件路径中的symlink才可能走这里
// 如果是位于文件路径末尾的symlink,都会先视为最后一个分量,不会走这里
err = walk_component(nd, WALK_FOLLOW);
} else {
/* not the last component */
// 常规目录 case,非 symlink 的 case
// 不是最后一个分量,查找对应的dentry、inode
// 检查是否是挂载点
err = walk_component(nd, WALK_FOLLOW | WALK_MORE);
}
if (err < 0)
return err;
if (err) {
// err>0的场景,对应于下面代码中pick_link函数返回1
// 处理符号链接的返回值(即如果中间分量是一个symlink)
const char *s = get_link(nd);
if (IS_ERR(s))
return PTR_ERR(s);
err = 0;
// s指symlink对应的真实路径
if (unlikely(!s)) {
/* jumped */
put_link(nd);
} else {
//只有嵌套在文件路径中的symlink,才会走到这里
//如"/a/b/c",检查分量a时,发现它其实是个嵌套symlink,代表文件路径"e/f"
//在执行walk_component->get_link后,返回的link就是"e/f"
//这时候,name就是"b/c",将它保存在nd->stack中,并自增depth
//walk_component完symlink对应的真实路径后,才会取出来"b/c"
//对它执行walk_component()
nd->stack[nd->depth - 1].name = name;
name = s;
// 继续处理
// 将"e/f"赋值给name,继续循环,执行walk_component()
continue;
}
}
if (unlikely(!d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))) {
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
if (unlazy_walk(nd))
return -ECHILD;
}
return -ENOTDIR;
}
}
}
link_path_walk 函数中会调用 walk_component 函数来进行路径搜索(向上或者向下),这个是较为复杂的逻辑,有很多场景,典型的如:
.或..- 普通的目录,这里又会检测当前目录是否为其他文件系统的挂载点
- 符号链接
对于本文前面提到的vfs path walk的例子,对于Binder文件系统挂载而言,/dev/binder是/binderfs/binder的symlink,不过由于binder是路径/dev/binder的最后一个分量,所以它在第一次执行link_path_walk(),不会对其用walk_component()进行查找。整体的处理逻辑,得看调用link_path_walk()的地方path_openat()
TODO
static struct file *path_openat(struct nameidata *nd,
const struct open_flags *op, unsigned flags)
{
//s即"/dev/binder"
const char *s = path_init(nd, flags);
//在第一次循环时,s是"/dev/binder",执行link_path_walk(),"binder"是最后一个分量,
//跳出link_path_walk()的循环处理,调用open_last_lookups()处理,但发现"binder"是一个symlink。
//open_last_lookups()会返回"binder"对应的"binderfs/binder"(又或者是"dev/binderfs/binder"?)。
//第二次循环时,s已经是"binderfs/binder", 再次执行link_path_walk(),"binder"是最后一个分量,
//不过这个"binder"不同于上次循环那个,不是symlink,而是一个真实存在的路径分量
//最后调用open_last_lookups()即可获得最后一个分量"binder"对应的dentry、inode等信息
while (!(error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) &&
(error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) {
......
s = trailing_symlink(nd);
......
}
}
path_openat->link_path_walk->walk_component(走过中间节点)
walk_component 方法对 nd(中间结果)中的目录进行遍历,当前的子路径一定是一个中间节点(目录OR符号链接),主要流程如下:
handle_dots:处理当前中间节点(分量)为.或者..的场景,TODO- 优先使用
lookup_fast函数:如果当前的目录是一个普通目录,路径行走有两个策略:先在效率高的 rcu-walk 模式__d_lookup_rcu下遍历,如果失败了就在效率较低的 ref-walk 模式__d_lookup下遍历 - 如果
lookup_fast查找失败,则调用lookup_slow函数(有条件限制)。在 ref-walk 模式下会 首先在内存缓冲区查找相应的目标(lookup_fast),如果找不到就启动具体文件系统(如ext4)自己的lookup进行查找(lookup_slow) - 在 dcache 里找到了当前目录对应的 dentry 或者是通过
lookup_slow寻找到当前目录对应的 dentry,这两种场景都会去设置path结构体里的dentry、mnt成员,并且将当前路径更新到path结构体(对dcache的分析参考后文) - 当
path结构体更新后,最后调用step_info->path_to_nameidata将path结构体更新到nd.path,参考,这样nd里的path就指向了当前目录了,至此完成一级目录的解析查找,返回link_path_walk()将基于nd.path作为父目录解析下一级目录,继续link_path_walk的循环查找直至退出
TODO:快速模式慢速模式下的调用顺序,从walk_component中lookup_fast的返回值err可知:
err>0:err == 0:err<0:直接返回错误(如经典的-ECHILD)
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1763
static int walk_component(struct nameidata *nd, int flags)
{
struct path path;
struct inode *inode;
unsigned seq;
int err;
// 如果不是 LAST_NORM 类型,就交由 handle_dots 处理
if (unlikely(nd->last_type != LAST_NORM)) {
err = handle_dots(nd, nd->last_type);
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
return err;
}
// 快速查找
err = lookup_fast(nd, &path, &inode, &seq);
// 重点:当lookup_fast返回1时,说明快速路径查找成功,否则回退到慢速查找ref-walk模式
if (unlikely(err <= 0)) {
if (err < 0){
return err;
}
// 如果快速查找模式失败,则进行慢速查找模式
// lookup_fast失败,至少说明被查找的目录分量不在dcache中
path.dentry = lookup_slow(&nd->last, nd->path.dentry,
nd->flags);
if (IS_ERR(path.dentry))
return PTR_ERR(path.dentry);
path.mnt = nd->path.mnt;
// TODO:follow_managed
err = follow_managed(&path, nd);
if (unlikely(err < 0))
return err;
if (unlikely(d_is_negative(path.dentry))) {
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -ENOENT;
}
seq = 0; /* we are already out of RCU mode */
inode = d_backing_inode(path.dentry);
}
//检查是否是链接、挂载点
//是链接,则获取到对应的真实路径
//是挂载点,则获取最后一个挂载在挂载点的文件系统信息
return step_into(nd, &path, flags, inode, seq);
}
先看下handle_dots的实现逻辑,这里也区分了快速(follow_dotdot_rcu)/慢速(follow_dotdot)的逻辑,前面提到do_filp_open 会首先使用 RCU 进行快速查找,如果未查找到再用普通策略,这里也是一样
set_root_rcu(nd)的作用是设置 nd 的根目录(nd.root),回想下在初始化的 path_init 函数里也设置过这个成员,如果是绝对路径的话就会把这个 nd.root 设置成当前进程的根目录(为了和系统根目录区分,这里称 nd.root 为预设根目录),但如果是相对路径的话,就没有对 nd.root 进行初始化。所以,现在的情况是路径中出现了..,就说明需要向上走一层,也就有可能会访问根目录,所以现在正是获取根目录的时候
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1679
static inline int handle_dots(struct nameidata *nd, int type)
{
if (type == LAST_DOTDOT) {
if (!nd->root.mnt)
set_root(nd);
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
return follow_dotdot_rcu(nd);
} else
return follow_dotdot(nd);
}
/*
注意到这里并没有对 follow_dotdot(rcu) 的返回值进行检查,为什么?
这是因为 `..` 出现在路径里就表示要向上走一层,也就是要走到父目录里面去,
而父目录一定是存在内存中而且对于当前的进程来说一定也是合法的,
否则在读取父目录的时候就已经出错了
*/
return 0;
}
先简单分析下follow_dotdot_rcu的实现:
// 比较两个path是否相等
static inline int path_equal(const struct path *path1, const struct path *path2)
{
return path1->mnt == path2->mnt && path1->dentry == path2->dentry;
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1325
static int follow_dotdot_rcu(struct nameidata *nd)
{
//设置 nd 的根目录(nd.root)
struct inode *inode = nd->inode;
/* while循环1:本质是处理当前层级的挂载点状态,包含了三种状态:
case1:当前目录就是前面获取的预设根目录,那么什么都不做,退出(break)
case2:当前目录不是预设根目录,但也不是当前文件系统的根目录,那么直接获取当前目录的父目录即可
case3:当前目录不是预设根目录,但它是当前文件系统的根目录,那么往上走就会跑到别的文件系统(路径穿透)
*/
while (1) {
//如果当前路径就是预设根目录的话,就什么也不做直接跳出循环
//在/目录中,运行cd ../../后仍然是/
if (path_equal(&nd->path, &nd->root))
break;
// 当前路径不是预设根目录,但也不是当前文件系统的根目录,
// 那么向上走一层也是很简单的事,直接将父目录项拿过来就是了
if (nd->path.dentry != nd->path.mnt->mnt_root) {
struct dentry *old = nd->path.dentry;
// 获得父目录
struct dentry *parent = old->d_parent;
unsigned seq;
inode = parent->d_inode;
seq = read_seqcount_begin(&parent->d_seq);
// 如果当前的 dentry 发生了改变(其他进程修改或者删除),就返回错误
if (unlikely(read_seqcount_retry(&old->d_seq, nd->seq))){
//只有 RCU 失败才会返回 -ECHILD 以启动普通策略,下同
return -ECHILD;
}
// 设置nameidata当前路径为它的父目录
nd->path.dentry = parent;
nd->seq = seq;
//path_connected - Verify that a path->dentry is below path->mnt.mnt_root
if (unlikely(!path_connected(&nd->path)))
return -ENOENT;
// 还在当前的文件系统里面,可以退出循环1
break;
} else {
// 当 nd->path.dentry == nd->path.mnt->mnt_root时
// 这里隐含了 .. 刚好是该文件系统的/目录(不一定是rootfs)
//到最后,当前路径一定是某个文件系统的根目录,往上走有可能就会走到另一个文件系统里去了
struct mount *mnt = real_mount(nd->path.mnt);
// 获取父挂载描述符(mount)
struct mount *mparent = mnt->mnt_parent;
// 获取挂载点(重要:拿到另外一个文件系统的挂载点dentry,参考上文的挂载图红色的箭头)
struct dentry *mountpoint = mnt->mnt_mountpoint;
// 获取挂载点的索引节点
struct inode *inode2 = mountpoint->d_inode;
// 获取 mountpoint->d_seq 序列锁的初始 count,用于多线程竞争
unsigned seq = read_seqcount_begin(&mountpoint->d_seq);
// 使用全局序列锁 mount_lock 检查当前路径分量有没有发生改变。如果有,返回 -ECHILD
if (unlikely(read_seqretry(&mount_lock, nd->m_seq)))
return -ECHILD;
// 当前的文件系统是不是根文件系统,也就是 rootfs 文件系统。如果是则跳出while(1)
if (&mparent->mnt == nd->path.mnt)
break;
/* we know that mountpoint was pinned */
// 现在知道当前路径分量处于挂载点
// 更新nd->path.dentry的值,这个值在下面一个循环中会用到
nd->path.dentry = mountpoint;
// 设置为父挂载描述符
nd->path.mnt = &mparent->mnt;
inode = inode2;
nd->seq = seq;
}
}
// d_mountpoint 函数检查 dentry 的 d_flags 有没有设置 DCACHE_MOUNTED,即检查该目录是否是挂载点
/*
1、当跳出这个 while(1) 循环时已经站在某个目录上了
一般来说这个目录就是想要的目标,而不会是一个挂载点,但也有例外(比如该目录就是一个挂载点)
2、d_mountpoint() 就是检查标志位 DCACHE_MOUNTED,然后在某个散列表中查找属于这个挂载点的 mount 结构,如果找到了(如果某个目录既是挂载点但又没有任何文件系统挂载在上面那就说明这个目录可能拥有自动挂载的属性),就往下走一层,走到挂载文件系统的根目录上,然后再回到 while (unlikely(d_mountpoint(nd->path.dentry))) 再判断、查找、向下走,周而复始直到某个非挂载点
3、找到了这个非挂载点那就是最后需要的dentry了
*/
// while循环2:本质是处理穿透后层级的挂载点状态
while (unlikely(d_mountpoint(nd->path.dentry))) {
// 如果是挂载点
struct mount *mounted;
// 在散列表中通过{父挂载描述符,名称}方式查找对应的挂载描述符
mounted = __lookup_mnt(nd->path.mnt, nd->path.dentry);
// 检查期间挂载点是否有改变(随时检查)
if (unlikely(read_seqretry(&mount_lock, nd->m_seq)))
return -ECHILD;
// 如果没有在散列表中找到,退出循环
if (!mounted){
//退出循环2
break;
}
// 现在更新为找到的文件系统的挂载描述符
nd->path.mnt = &mounted->mnt;
// 现在更新为找到的文件系统的根目录,接着继续循环,如果根目录也为挂载点
// 那么继续找,直到找到一个根目录不为挂载点的文件系统
nd->path.dentry = mounted->mnt.mnt_root;
inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
nd->seq = read_seqcount_begin(&nd->path.dentry->d_seq);
}
nd->inode = inode;
return 0;
}
初看follow_dotdot_rcu的实现逻辑有点绕,这里稍微总结下,需要理解核心理解是VFS挂载的特殊性:
- 某个dentry可以被重复挂载(不同的文件系统、相同文件系统的不同物理分区等)
- 除了检查当前的路径分量并穿透到实际的挂载点,然后再检查此时对应的
..是否为一个挂载点;如果是则需要继续找到..上实际的挂载的文件系统的挂载点(根目录不为挂载点)
follow_dotdot_rcu函数包含两个循环过程,第一个循环 while(1),主要检查对象是当前路径的挂载状态,其主要任务如下:
- 检查当前目录是否是挂载点根目录 (
dentry == mnt->mnt_root) - 如果是挂载点根,则穿透挂载点到宿主文件系统
- 如果不是挂载点根,则切换到父目录
- 阶段1主要完成目录层级上升(可能穿透挂载点)
第二个循环 while(d_mountpoint),主要检查对象是穿透后路径的挂载状态,其主要任务如下:
- 检查当前目录(上一个循环退出后的结果)是否是挂载点(
d_mountpoint(dentry)) - 如果是挂载点,则穿透到挂载的文件系统根
- 循环检查新位置的挂载状态
- 阶段2主要处理穿透后的挂载点覆盖
若当前nameidata指向的目录不是..,那么接下来看下walk_component中最核心的涉及到Dentry查找的两个函数:lookup_fast与lookup_slow
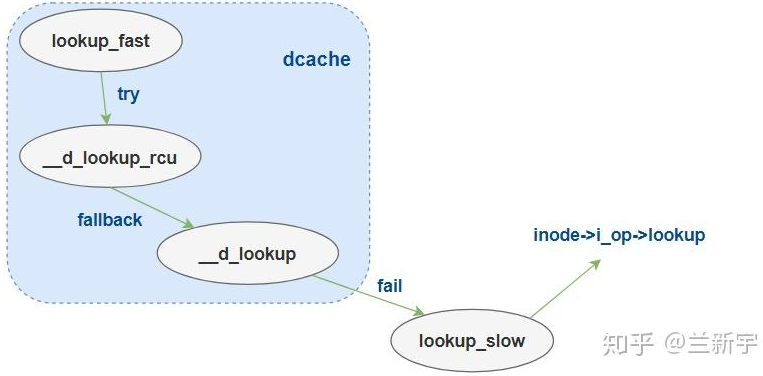
路径查找的快速模式:walk_component->lookup_fast
lookup_fast()函数根据路径分量的名称,快速找到对应的dentry、inode的实现,主要分为rcu-walk和ref-walk(局部)两个分支,二者都是从dentry_hashtable中查询,但是在并发实现上有差异
- rcu-walk:实现是
__d_lookup_rcu(),RCU模式用于无锁读取,提高性能,但需要处理序列号验证 - ref-walk:实现是
__d_lookup()+lookup_slow,简单描述就是在 Ref-walk(引用行走)模式下,首先尝试使用__d_lookup()进行快速缓存查找;如果失败(缓存未命中),则回退到使用lookup_slow进行慢速查找,后者可能会涉及访问底层文件系统的lookup函数__d_lookup也是用于在目录项缓存(dcache)中查找匹配的 dentry 的函数,它根据给定的父目录 dentry 和文件名(包含哈希值)进行查找,该函数在非 RCU 模式下工作,使用自旋锁来保护并发访问,确保数据一致性
即在快速模式,慢速模式都会调用lookup_fast,快速模式中的lookup_fast对应的实现是__d_lookup_rcu,而慢速模式下的lookup_fast对应的是__d_lookup
|- lookup_fast()
|- __d_lookup_rcu() //实现了rcu-walk
|- d_hash() //根据hash值,从dentry_hashtable中获取对应的hlist_bl_head
|- hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu() //遍历链表hlist_bl_head,寻找对应的dentry
|- __d_lookup() //实现了ref-walk
lookup_fast的实现代码如下:
/*
参数:
nd: 指向nameidata结构的指针,包含路径查找的当前状态(如当前目录、标志位等)
path: 指向path结构的指针,用于返回找到的路径(挂载点和dentry)
inode: 指向inode指针的指针,用于返回找到的inode
seqp: 指向无符号整数的指针,用于在RCU模式下返回序列号(用于一致性检查)
返回值:
1: 成功找到dentry并完成处理(期望的返回值)
0: 未找到dentry,需要退回到慢速查找(slow lookup)
负值: 错误码(如-ECHILD表示需要退出RCU模式,-ENOENT表示文件不存在)
*/
static int lookup_fast(struct nameidata *nd,
struct path *path, struct inode **inode,
unsigned *seqp)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt = nd->path.mnt;
struct dentry *dentry, *parent = nd->path.dentry;
int status = 1;
int err;
//flags里有LOOKUP_RCU标记,则执行rcu-walk,否则执行ref-walk
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//分支一:RCU模式分支
unsigned seq;
bool negative;
// rcu-walk
// 首先调用 __d_lookup_rcu 在dcache中通过字符串比较查找目标 dentry,如果找到了就返回该 dentry。传入参数parent是当前目录的dentry,nd->last是要查找的文件名(struct qstr)
//返回:如果查找失败(!dentry),调用unlazy_walk(nd)尝试退出RCU模式。如果unlazy_walk失败(返回非零),则返回-ECHILD;否则返回0,表示需要回退到慢速查找
dentry = __d_lookup_rcu(parent, &nd->last, &seq);
if (unlikely(!dentry)) {
// 移除flags里的LOOKUP_RCU标记,尝试切换到ref-walk
// 成功则在下一个分量的lookup中,会采用ref-walk
// 当前的分量,看流程,不会换到ref-walk,而是用lookup_slow进行查找
// 如果没有找到就跳转到 unlazy。在这里会使用 unlazy_walk 就地将查找模式切换到 ref-walk ;如果还不行就只好返回到 do_filp_open 重新操作
if (unlazy_walk(nd)){
// 调用unlazy_walk退出RCU模式,该函数成功返回`0`,失败返回`-ECHILD`
// 进入该分支表示unlazy_walk失败了
return -ECHILD;
}
//unlazy_walk成功了
return 0;
}
//这里,RCU模式,查找成功后需要对seqcount进行二次校验,避免查找过程中有其他线程修改了该dentry
//获取dentry对应的inode(d_backing_inode)并检查是否为负dentry(表示文件不存在)
*inode = d_backing_inode(dentry);
// 立即保存dentry是否为negative状态
negative = d_is_negative(dentry);
// 若检查期间 dentry 有没有发生改变
// 使用read_seqcount_retry检查dentry的序列号是否有效(确保在查找过程中没有并发修改)
if (unlikely(read_seqcount_retry(&dentry->d_seq, seq))){
//如果任何序列号检查失败,返回-ECHILD,表示需要重新尝试
return -ECHILD;
}
// 这个序列号用来验证这期间父目录的 dentry 没有发生改变,内存屏蔽在孩子调用的
// read_seqcount_begin 中已被设置了(也就是前面调用的 read_seqcount_begin)
// 所以这里调用没有内存屏蔽的 __read_seqcount_retry 函数
//使用__read_seqcount_retry检查父dentry的序列号是否有效。如果任何序列号检查失败,返回-ECHILD,表示需要重新尝试
if (unlikely(__read_seqcount_retry(&parent->d_seq, nd->seq)))
return -ECHILD;
*seqp = seq;
//重要:重新验证dentry(d_revalidate),调用d_revalidate函数验证dentry是否仍然有效(例如文件是否被删除或重命名)。如果验证成功(status > 0),继续处理
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(status > 0)) {
/*
* Note: do negative dentry check after revalidation in
* case that drops it.
*/
if (unlikely(negative)){
//如果dentry为负(文件不存在),返回-ENOENT
return -ENOENT;
}
//设置path->mnt和path->dentry,然后调用__follow_mount_rcu处理挂载点。如果成功,返回1
path->mnt = mnt;
path->dentry = dentry;
// 有可能当前目录是挂载点,或者自动挂载点等伪目标,所以这里要跨过
// TODO
if (likely(__follow_mount_rcu(nd, path, inode, seqp))){
// 快速模式下查找成功
return 1;
}
}
//处理验证失败或需要退出RCU(d_revalidate失败)
//调用unlazy_child尝试退出RCU模式
if (unlazy_child(nd, dentry, seq))
return -ECHILD;
if (unlikely(status == -ECHILD))
/* we'd been told to redo it in non-rcu mode */
//如果status为-ECHILD,表示需要在非RCU模式下重新验证
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
} else {
//ref-walk的前置逻辑:使用__d_lookup函数从dcache中查找dentry
//如果找不到(!dentry),直接返回0,表示需要慢速查找
dentry = __d_lookup(parent, &nd->last);
if (unlikely(!dentry))
return 0; //dcache未命中
// dcache命中后,一样要d_revalidate检测
status = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
}
if (unlikely(status <= 0)) {
if (!status)
d_invalidate(dentry); //调用d_invalidate使dentry无效,见下文
//调用dput释放dentry引用(dentry已经失效了)
dput(dentry);
return status;
}
if (unlikely(d_is_negative(dentry))) {
dput(dentry);
return -ENOENT;
}
//更新path成员
path->mnt = mnt;
path->dentry = dentry;
// 处理按照某种方式管理的目录(自动挂载工具 autofs 管理这个目录的跳转,挂载点或自动挂载点)
err = follow_managed(path, nd);
if (likely(err > 0))
*inode = d_backing_inode(path->dentry);
return err;
}
在上面代码的尾部,d_revalidate与d_is_negative完成了什么职责呢?follow_managed这个函数的作用是什么?
TODO
注意lookup_fast中的unlazy_walk/unlazy_child函数,这二者都是模式切换函数,是RCU-walk的核心退出机制。当 RCU-walk无法继续时(如序列号检查失败、需要执行可能阻塞的操作),必须安全地退出到 Ref-walk
unlazy_walk(nd):尝试将当前 nameidata从 RCU-walk模式退出。它会尝试获取所有当前遍历到的 dentry 的引用和锁,以安全地锚定当前状态。如果成功,nd->flags中的LOOKUP_RCU标志会被清除,后续查找在 Ref-walk中进行unlazy_child(nd, dentry, seq):类似于unlazy_walk,但用于处理特定子 dentry 的退出
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L683
static int unlazy_walk(struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct dentry *parent = nd->path.dentry;
BUG_ON(!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU));
// 清除nd->flags中的LOOKUP_RCU标志
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU;
if (unlikely(!legitimize_links(nd)))
goto out2;
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->path, nd->seq)))
goto out1;
if (nd->root.mnt && !(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT)) {
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->root, nd->root_seq)))
goto out;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
BUG_ON(nd->inode != parent->d_inode);
return 0;
out2:
nd->path.mnt = NULL;
nd->path.dentry = NULL;
out1:
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT))
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
out:
rcu_read_unlock();
return -ECHILD;
}
继续,这里看下rcu-walk即__d_lookup_rcu()的实现细节, __d_lookup_rcu()遍历查找目标dentry的时候,使用了顺序锁seqlock,读操作不会被写操作阻塞,写操作也不会被读操作阻塞。但读操作可能会反复读取相同的数据:当它发现sequence发生了变化,即它执行期间,有写操作更改了数据。此外seqlock要求进入临界区的写操作只有一个,多个写操作之间仍然是互斥的
在__d_lookup_rcu函数中,dentry->d_seq的类型是seqcount_spinlock_t,seqcount_spinlock_t经过一些复杂的宏定义包含了seqcount_t,可以简单认为seqcount_spinlock_t就是一个int序列号
/*参数
parent: 父目录的 dentry,用于限定查找范围
name: 要查找的文件名(包含哈希值、长度和字符串)
seqp: 输出参数,返回找到的 dentry 的序列号,用于后续验证
*/
struct dentry *__d_lookup_rcu(const struct dentry *parent,
const struct qstr *name,
unsigned *seqp)
{
//name->hash_len:文件名哈希值,在路径查找前期已计算好,避免重复计算
u64 hashlen = name->hash_len;
const unsigned char *str = name->name;
//根据哈希值计算哈希桶位置。hashlen_hash提取哈希部分,d_hash映射到具体哈希桶
struct hlist_bl_head *b = d_hash(hashlen_hash(hashlen));
struct hlist_bl_node *node;
struct dentry *dentry;
//使用 RCU 安全的宏遍历哈希桶中的所有 dentry,这个遍历是无锁的,依赖于 RCU 的读侧临界区保护
//也即是遍历dentry hashtable的冲突链
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(dentry, node, b, d_hash) {
unsigned seq;
//序列号获取: 使用 raw_seqcount_begin读取 dentry 的序列号起始值
//重试标签(seqretry): seqretry标签用于在检测到数据竞争时重新开始检查。
seqretry:
seq = raw_seqcount_begin(&dentry->d_seq);
//父目录匹配: 确保 dentry 的父目录与给定的 parent匹配
if (dentry->d_parent != parent)
continue;
//有效性检查: d_unhashed检查 dentry 是否仍存在于哈希表中
if (d_unhashed(dentry))
continue;
// 两种比较路径1.自定义比较函数 (DCACHE_OP_COMPARE 2、标准匹配
if (unlikely(parent->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_COMPARE)) {
int tlen;
const char *tname;
//hash预检查: 先比较哈希值,快速过滤不匹配的项
if (dentry->d_name.hash != hashlen_hash(hashlen))
continue;
tlen = dentry->d_name.len;
tname = dentry->d_name.name;
/* we want a consistent (name,len) pair */
//序列号验证:在读取文件名和长度后,验证序列号是否变化。如果变化,说明数据可能不一致,跳回 seqretry重试
if (read_seqcount_retry(&dentry->d_seq, seq)) {
//序列号重试:检测到数据竞争时,通过 cpu_relax()让出 CPU,然后重试
//内存屏障:序列号操作包含必要的内存屏障,确保读写顺序
// 注意:序列号验证失败不会导致函数失败,而是触发重试
cpu_relax();
goto seqretry;
}
//自定义比较: 调用文件系统特定的 d_compare函数进行精确比较
if (parent->d_op->d_compare(dentry,
tlen, tname, name) != 0)
continue;
} else {
//标准比较(无自定义函数)
//哈希和长度检查:比较完整的 hash_len(包含哈希和长度)
if (dentry->d_name.hash_len != hashlen)
continue;
//内存比较: 使用 dentry_cmp进行字符串内存比较
if (dentry_cmp(dentry, str, hashlen_len(hashlen)) != 0)
continue;
}
*seqp = seq;
return dentry;
}
//如果遍历完整个哈希桶都没有找到匹配的 dentry,返回 NULL
return NULL;
}
那么,哪些可能的场景是会发read_seqcount_retry检测失败呢(不一致)?TODO
接着看下慢速模式即__d_lookup()的实现,__d_lookup遍历查找目标dentry的时候,使用了自旋锁spin_lock,多个读操作会发生锁竞争。它还会更新查找到的dentry的引用计数(因此叫做ref-walk)。RCU仍然用于ref-walk中的dentry哈希查找,但不是在整个ref-walk过程中都使用,频繁地加减reference count可能造成cacheline的刷新,这也是ref-walk开销更大的原因之一
/*
parent: 父目录的 dentry,用于限定查找范围
name: 要查找的文件名(包含哈希值、长度和字符串)
*/
struct dentry *__d_lookup(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
unsigned int hash = name->hash;
// 同rcu,d_hash(hash)根据哈希值计算对应的哈希桶(链表头),所有哈希值相同的 dentry 都链接在这个桶中(解决哈希冲突)
struct hlist_bl_head *b = d_hash(hash);
struct hlist_bl_node *node;
//found初始化为 NULL,用于存储找到的 dentry
struct dentry *found = NULL;
struct dentry *dentry;
//RCU读锁保护
rcu_read_lock();
//进入 RCU 读侧临界区。这允许函数安全地遍历哈希表中的链表,而无需担心链表结构被并发修改(如删除节点)。RCU 确保在遍历期间,链表节点不会被释放
//遍历链表b里的dentry(遍历哈希桶中的冲突链),查找目标dentry
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(dentry, node, b, d_hash) {
//使用 hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu宏遍历哈希桶中的每个 dentry。这个宏是 RCU 安全的,允许无锁遍历链表。每次迭代中,dentry指向当前遍历的 dentry,node是内部使用的链表节点指针。
//name_hash不对,不是要找的
if (dentry->d_name.hash != hash)
continue;
//获取 dentry 锁,对当前 dentry 获取自旋锁。这是因为后续检查(父目录、哈希状态、文件名)需要防止并发修改(如 d_move操作)。锁保护确保在检查期间 dentry 的状态不会改变
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
//parent 不对,不是要找的
if (dentry->d_parent != parent)
goto next;
//d_unhashed检查 dentry 是否已被从哈希表中移除(如被删除或无效化)。如果已移除,跳转到 next,因为这样的 dentry 不再有效
if (d_unhashed(dentry))
goto next;
//full name 比对,不是要找的,d_same_name函数比较 dentry 的文件名与目标文件名是否完全匹配(包括字符串比较)。如果不匹配,跳转到 next。这是最精确的检查,确保找到正确的 dentry
if (!d_same_name(dentry, parent, name))
goto next;
//找到匹配的 dentry
//如果所有检查都通过,增加 dentry 的引用计数(d_lockref.count),防止 dentry 被提前释放
dentry->d_lockref.count++;
//设置 found为当前 dentry,释放锁,并跳出循环
found = dentry;
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
break;
//next标签用于释放当前 dentry 的锁,然后继续遍历下一个 dentry
//循环结束后,退出 RCU 读侧临界区(rcu_read_unlock)
next:
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return found;
}
__d_lookup函数中的注释提到,并发重命名操作(rename)可能干扰链表遍历,导致假阴性(false-negative)结果。这是由更上层的 rename_lock序列锁来保护的,不在本函数范围内
路径查找:walk_component->lookup_slow
与上述方法不同,lookup_fast的两种模式,都是查询的dentry_hashtable,lookup_slow是兜底方案,即当lookup_fast失败后,才会调用。lookup_slow()是通过当前所在的文件系统,获取对应的信息,创建对应的dentry和inode,将新的dentry添加到dentry_hashtable中
这里有个比较重要的细节,由于lookup_slow的主要功能是处理 dcache 未命中的情况,通过文件系统特定的查找方法(如 inode->i_op->lookup)来查找目录项。这个过程可能阻塞(至少需要更安全的写锁保护),因为它可能涉及磁盘 I/O 或其他慢速操作。此外,函数还需要处理并发查找(基于等待队列机制)和 dentry 重新验证
|- lookup_slow() //在lookup_fast()中没有找到dentry,会获取父dentry对应的inode,通过inode->i_op->lookup去查找、创建
|- __lookup_slow()
|- d_alloc_parallel() //创建一个新的dentry,并用in_lookup_hashtable检测、处理并发的创建操作
|- inode->i_op->lookup 通过父dentry的inode去查找对应的dentry:其实就是通过它所在的文件系统,获取对应的信息,创建对应的dentry
lookup_slow 的实现如下,首先调用 d_alloc_parallel 给当前路径分配一个新的 dentry,然后调用 inode->i_op->lookup(),注意这里的 inode 是当前路径的父路径 dentry 的 d_inode 成员。inode->i_op 是具体的文件系统 inode operations 函数集,如对 ext4 文件系统就是 ext4 fs 的 inode operations 函数集 ext4_dir_inode_operations,其 lookup 函数是 ext4_lookup()
/* Fast lookup failed, do it the slow way */
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1625
/*
name: 要查找的文件名(封装在 struct qstr中)
dir: 父目录的 dentry
flags: 查找标志(如 LOOKUP_NO_REVAL、LOOKUP_RCU等)
返回值: 成功时返回找到的 dentry,失败时返回错误指针(如 ERR_PTR(-ENOENT))
*/
static struct dentry *lookup_slow(const struct qstr *name,
struct dentry *dir,
unsigned int flags)
{
//初始化 dentry为错误码 -ENOENT,表示文件不存在
struct dentry *dentry = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT), *old;
//获取父目录的 inode
struct inode *inode = dir->d_inode; // 指向当前路径的父路径
//声明一个等待队列 wq,用于处理多个进程同时查找相同 dentry 的并发情况
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
//获取 inode 的共享锁(inode_lock_shared),允许多个读取者同时访问,但确保数据一致性。这是慢速路径的典型操作,因为后续操作可能阻塞
inode_lock_shared(inode);
// 检查目录状态,使用 IS_DEADDIR宏检查目录是否已被标记为死亡(例如,由于卸载或删除)。如果是,直接跳转到 out标签,返回错误。这避免了在无效目录上进行操作
/* Don't go there if it's already dead */
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(inode)))
goto out;
again:
// 新建 dentry 节点,并初始化相关关联
/*
调用 d_alloc_parallel函数在 dcache 中分配或查找 dentry。这个函数处理并发查找:
1. 如果其他进程正在查找相同的 dentry,当前进程可能睡眠等待,直到查找完成
2. 返回一个 dentry,可能是新分配的(处于查找中状态)或已存在的
3. 如果 d_alloc_parallel返回错误(如内存不足),跳转到 out清理并返回错误
*/
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, name, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
goto out;
//d_in_lookup(dentry)检查 dentry 是否处于查找中状态。如果不是,说明 dentry 已经存在于 dcache 中,但可能需要重新验证
if (unlikely(!d_in_lookup(dentry))) {
//重要case1:dentry已存在,需要重新验证
if (!(flags & LOOKUP_NO_REVAL)) {
//如果没有设置 LOOKUP_NO_REVAL标志(表示不需要重新验证),调用 d_revalidate函数验证 dentry 的有效性(例如,检查文件是否被删除或修改)
//如果 d_revalidate返回 0,表示 dentry 无效,调用 d_invalidate使 dentry 无效,释放引用(dput),并跳回 again重试查找
int error = d_revalidate(dentry, flags);
if (unlikely(error <= 0)) {
if (!error) {
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
goto again;
}
//如果error返回负数错误,释放 dentry 并返回错误
dput(dentry);
dentry = ERR_PTR(error);
}
//如果error返回正数,表示 dentry 有效,继续使用
//这个步骤确保了即使 dentry 在 dcache 中,也可能是陈旧的,需要验证
}
} else {
//重要case2:dentry是新建的,需要调用文件系统lookup方法
// 在 ext4 fs 中,会调用 ext4_lookup 寻找,此函数涉及到 IO 操作,性能较 dcache 会低
// 定义:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/ext4/namei.c#L3905
//如果 dentry 处于查找中状态(由 d_alloc_parallel新分配),调用文件系统特定的 lookup方法(如 ext4_lookup)。这个函数会访问文件系统底层(如读取磁盘目录内容)来查找文件,可能阻塞
old = inode->i_op->lookup(inode, dentry, flags);
//d_lookup_done标记查找完成,唤醒其他等待在等待队列 wq上的进程
d_lookup_done(dentry);
//如果 lookup返回一个旧的 dentry(可能由于并发查找已完成),释放新分配的 dentry(dput)并使用旧的 dentry。这避免了重复创建 dentry
if (unlikely(old)) {
// 如果 dentry 是一个目录的 dentry,则有可能 old 是有效的;否则如果 dentry 是文件的 dentry 则 old 是 null
dput(dentry);
dentry = old;
}
}
out:
//释放 inode 的共享锁(inode_unlock_shared)
inode_unlock_shared(inode);
//返回找到的 dentry 或错误指针。如果成功,dentry 可能是一个正面(positive)dentry(有 inode)或负面(negative)dentry(无 inode,表示文件不存在)
return dentry;
}
上面lookup_slow的实现有两处细节:
第一个是lookup_slow的else分支的含义是什么?
d_in_lookup(dentry)为true:表示这是一个新分配的、处于”查找中”状态的dentry- 需要文件系统介入:调用
inode->i_op->lookup()方法,让文件系统(如ext4)从磁盘读取目录内容,填充这个dentry - 处理并发:
d_lookup_done()标记查找完成,唤醒其他等待的进程。如果lookup返回一个现有的dentry(old),说明其他进程已经完成了查找,使用现有的dentry
第二个问题是:d_alloc_parallel的实现机制是什么?从其实现可以看出与lookup_fast类似,都采用了先快速无锁查找,失败后回退到加锁模式的策略。这种设计是为了在并发环境下高效地处理目录项(dentry)的查找和创建。即d_alloc_parallel函数的主要任务是:
- 查找或创建dentry:在dcache的哈希表中查找匹配的dentry,如果不存在则创建一个新的
- 处理并发查找:使用等待队列机制协调多个进程同时查找同一个dentry的情况
- 封装为通用函数,可以被多种上下文调用
d_alloc_parallel的主要目标是在目录缓存(dcache)中查找或创建一个 dentry,并处理多个进程并发查找同一 dentry 的情况。在慢速路径(Ref-walk)时被调用,实现上依然分为RCU快速模式(调用 __d_lookup_rcu)与慢速模式两步,大致步骤如下:
- 步骤 1:尝试 RCU 查找,调用
__d_lookup_rcu(parent, name, &d_seq)进行无锁查找。如果找到有效的 dentry,则返回它 - 步骤 2: 检查序列号,使用
read_seqretry和read_seqcount_retry验证查找过程中数据是否发生变化。如果变化,则重试(goto retry) - 步骤 3:检查并发查找,如果 RCU 查找失败,函数检查是否有其他进程正在查找同一 dentry(通过 d_in_lookup_hash列表)。如果找到,则调用
d_wait_lookup(避免了多个进程同时创建相同 dentry 的资源浪费,并确保数据一致性)等待该查找完成,然后验证结果 - 步骤 4:创建新 dentry,如果没有其他进程在查找,则创建一个新 dentry 并将其添加到查找列表中,以便其他进程可以等待
d_alloc_parallel与lookup_fast中RCU操作的区别是什么?
lookup_fast中的RCU操作:是在路径查找的RCU-walk模式下进行的,目的是无锁地快速查找路径组件d_alloc_parallel中的RCU操作:是在dcache模块内部使用的,用于无锁地遍历哈希表,与路径查找模式无关
TODO
lookup_slow的实现逻辑梳理如下(有些绕):
TODO
在上面lookup_slow的实现中,什么情况下会进入文件系统的 inode->i_op->lookup函数?
lookup_slow-> inode->lookup的实现(ext4)
这里简单介绍下 ext4_lookup() 的实现,其原型为 static struct dentry *ext4_lookup(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags),参数 dir 为当前目录 dentry 的父目录,参数 dentry 为需要查找的当前目录。ext4_lookup() 首先调用了 ext4_find_entry(),此函数根据当前路径的 dentry 的 d_name 成员在当前目录的父目录文件(用 inode 表示)里查找,这个会 open 父目录文件会涉及到 IO 读操作(具体可以分析 ext4_bread 函数的 实现)。查找到后,得到当前目录的 ext4_dir_entry_2,此结构体里有当前目录的 inode number,然后根据此 inode number 调用 ext4_iget() 函数获得这个 inode number 对应的 inode struct,得到这个 inode 后调用 d_splice_alias() 将 dentry 和 inode 绑定,即将 inode 赋值给 dentry 的 d_inode 成员
当 ext4 文件系统的 lookup 完成后,此时的 dentry 已经有绑定的 inode 了,即已经设置了其 d_inode 成员了,然后调用 d_lookup_done() 将此 dentry 从 lookup hash 链表上移除(它是在 d_alloc_parallel 里被插入 lookup hash 的),这个 lookup hash 链表的作用是避免其它线程也同时来查找当前目录造成重复 alloc dentry 的问题
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/ext4/namei.c#L1569
static struct dentry *ext4_lookup(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags)
{
struct inode *inode;
struct ext4_dir_entry_2 *de;
struct buffer_head *bh;
......
bh = ext4_find_entry(dir, &dentry->d_name, &de, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(bh))
return (struct dentry *) bh;
inode = NULL;
if (bh) {
__u32 ino = le32_to_cpu(de->inode);
brelse(bh);
if (!ext4_valid_inum(dir->i_sb, ino)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir, "bad inode number: %u", ino);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
if (unlikely(ino == dir->i_ino)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir, "'%pd' linked to parent dir",
dentry);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
// 获取inode 结构
inode = ext4_iget_normal(dir->i_sb, ino);
if (inode == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir,
"deleted inode referenced: %u",
ino);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
......
}
//调用d_splice_alias将inode 与dentry绑定
return d_splice_alias(inode, dentry);
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/dcache.c#L2925
在ext4_lookup中比较重要的是d_splice_alias的实现,该函数用于处理 dentry 与 inode 的关联,特别是在存在别名(alias)的情况下。该函数通常在文件系统的 lookup方法中被调用,当查找操作发现 inode 已经存在时,用于正确处理 dentry 的别名情况
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/dcache.c#L2925
/*
inode: 要关联的 inode 指针
dentry: 新创建的 dentry 指针
*/
struct dentry *d_splice_alias(struct inode *inode, struct dentry *dentry)
{
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return ERR_CAST(inode);
//完整性检查:使用 BUG_ON确保 dentry 是未哈希的(unhashed),即还没有添加到 dcache 的哈希表中。这是必要的,因为函数准备将 dentry 添加到 dcache
BUG_ON(!d_unhashed(dentry));
//处理负 dentry(文件不存在)
//如果 inode为 NULL,表示文件不存在,跳转到 out标签,将 dentry 作为负 dentry(negative dentry)添加到 dcache
if (!inode)
goto out;
security_d_instantiate(dentry, inode);
//目录 inode 的别名处理
//锁定 inode:获取 inode 的自旋锁,保护 inode 的别名列表
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
//目录检查:只有当 inode 是目录时,才需要处理别名情况(普通文件不会进入此逻辑)
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) {
//查找别名:调用 __d_find_any_alias(inode)查找是否已经存在指向相同 inode 的 dentry(别名)
struct dentry *new = __d_find_any_alias(inode);
if (unlikely(new)) {
/* The reference to new ensures it remains an alias */
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
write_seqlock(&rename_lock);
//释放 inode 锁,获取重命名锁(rename_lock)的写锁,保护 dentry 树结构
if (unlikely(d_ancestor(new, dentry))) {
write_sequnlock(&rename_lock);
dput(new);
new = ERR_PTR(-ELOOP);
pr_warn_ratelimited(
"VFS: Lookup of '%s' in %s %s"
" would have caused loop\n",
dentry->d_name.name,
inode->i_sb->s_type->name,
inode->i_sb->s_id);
} else if (!IS_ROOT(new)) {
// 非根别名的处理
//如果别名 dentry 不是根目录,调用 __d_unalias处理别名
//__d_unalias可能涉及重命名或移动操作,以解决命名冲突
int err = __d_unalias(inode, dentry, new);
write_sequnlock(&rename_lock);
if (err) {
dput(new);
new = ERR_PTR(err);
}
} else {
//根别名的处理
//如果别名 dentry 是根目录,直接调用 __d_move将新 dentry 移动到别名 dentry 的位置
__d_move(new, dentry, false);
write_sequnlock(&rename_lock);
}
iput(inode);
return new;
}
}
out:
//普通情况
//调用 __d_add将 dentry 添加到 dcache,并关联 inode
//返回 NULL,表示成功关联了新创建的 dentry
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/dcache.c#L2526
__d_add(dentry, inode);
return NULL;
}
walk_component->step_into
通过walk_component函数前面的lookup_fast/lookup_slow逻辑已经确保当前查询的路径分量已经位于dcache里面了,接着会调用step_into()检查并处理dentry是一个link类型或挂载点的情况
|- step_into() //step_into函数的作用是决定如何进入一个路径组件(如文件或目录),特别是处理符号链接的情况
|- handle_mounts() //处理一个挂载点的情况,获取最后一个挂载在挂载点的文件系统信息
|- __follow_mount_rcu() //轮询调用__lookup_mnt(),处理重复挂载(查找标记有LOOKUP_RCU时调用)
|- __lookup_mnt()
|- traverse_mounts() //作用与__follow_mount_rcu()类似
|- pick_link() //处理是一个分量是link的情况,获取对应的真实路径
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1742
/*
参数说明
nd:指向 nameidata结构的指针,包含路径查找的当前状态(如当前路径、标志位等)
path:指向 path结构的指针,包含当前组件的挂载点和 dentry
flags:控制标志,如 WALK_MORE(表示还有更多组件要处理)和 WALK_FOLLOW(表示应跟随符号链接)
inode:当前路径组件对应的 inode
seq:序列号,用于 RCU 模式下的一致性验证
*/
static inline int step_into(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path,
int flags, struct inode *inode, unsigned seq)
{
//清理之前的符号链接引用
//如果 flags中没有设置 WALK_MORE(表示当前组件不是多个组件中的中间组件)且 nd->depth不为零(表示有未处理的符号链接),则调用 put_link(nd)来释放之前持有的符号链接引用。这有助于防止引用计数泄漏
if (!(flags & WALK_MORE) && nd->depth)
put_link(nd);
// 检查是否为符号链接且是否需要跟随
// d_is_symlink:检查当前 dentry 是否为符号链接
if (likely(!d_is_symlink(path->dentry)) ||
!(flags & WALK_FOLLOW || nd->flags & LOOKUP_FOLLOW)) {
//如果不是符号链接,或者不需要跟随符号链接(即 flags中没有 WALK_FOLLOW且 nd->flags中没有 LOOKUP_FOLLOW),则直接进入该分量
/* not a symlink or should not follow */
// 重要:将当前 path复制到 nameidata中,更新查找状态
path_to_nameidata(path, nd);
// 更新nameidata的成员,然后返回,可以继续下一个分量了
nd->inode = inode;
nd->seq = seq;
//返回 0,表示成功进入组件,查找可以继续
return 0;
}
/* make sure that d_is_symlink above matches inode */
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//如果当前处于 RCU-walk 模式,则检查 dentry 的序列号是否发生变化(使用 read_seqcount_retry)
//如果序列号不匹配,说明数据在查找过程中被修改,返回 -ECHILD表示需要退出 RCU 模式并回退到 ref-walk 模式
if (read_seqcount_retry(&path->dentry->d_seq, seq))
return -ECHILD;
}
//如果当前是符号链接且需要跟随,则调用 pick_link来处理符号链接的跟随
return pick_link(nd, path, inode, seq);
}
如果当前的分量是一个link,那么就会进入pick_link的实现:
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1692
/*
nd: 指向 nameidata结构的指针,包含整个路径查找的状态
link: 指向 path结构的指针,表示要跟随的符号链接本身的路径(其 dentry是符号链接文件本身)
inode: 符号链接文件对应的 inode
seq: 在 RCU 模式下获取的序列号,用于验证数据一致性
*/
static int pick_link(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *link,
struct inode *inode, unsigned seq)
{
int error;
struct saved *last;
// 如果当前路径中已包含的符号链接数量(嵌套层次)超过了 MAXSYMLINKS = 40
// 防止符号链接的无限循环
if (unlikely(nd->total_link_count++ >= MAXSYMLINKS)) {
// 在返回错误前,会调用 path_to_nameidata(link, nd)更新 nd的状态
// 这确保了错误处理时,nd中的路径信息是准确的,有助于调试或生成准确的错误信息
path_to_nameidata(link, nd);
// 返回错误
return -ELOOP;
}
// 当前为 ref-walk 模式
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU)) {
// 在 ref-walk 模式下,正确管理挂载点(vfsmount)的引用计数
//仅当不在 RCU 模式下才需要处理引用计数,因为 RCU 模式不管理引用计数
//如果符号链接所在的挂载点(link->mnt)与当前查找的挂载点(nd->path.mnt)相同,则调用 mntget(link->mnt)增加该挂载点的引用计数。这是因为后续操作将持有这个 path,需要防止挂载点被意外卸载
if (link->mnt == nd->path.mnt)
mntget(link->mnt);
}
//先为符号链接分配栈空间
//在 nameidata结构中的栈(nd->stack)上分配一个新的 saved结构,用于保存当前状态,以便在跟随完符号链接后能正确回溯
error = nd_alloc_stack(nd);
if (unlikely(error)) {
if (error == -ECHILD) {
// 尝试在RCU模式下验证路径的合法性
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L630
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, link, seq))) {
//验证失败,必须彻底放弃RCU模式并清理状态
drop_links(nd); //丢弃所有已保存的links
nd->depth = 0; // 重置深度
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU; // 清除RCU标志
nd->path.mnt = NULL; // 清理当前路径
nd->path.dentry = NULL;
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT)) // 如果不是从根开始查找,也清理根路径
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
rcu_read_unlock(); // 退出RCU临界区
} else if (likely(unlazy_walk(nd)) == 0)
//成功退出RCU模式,重试分配栈空间
error = nd_alloc_stack(nd);
}
/*小结下上面的过程:
1. legitimize_path(nd, link, seq): 尝试在不退出RCU模式的前提下,验证 link路径的 dentry 和挂载点是否仍然有效(通过序列号 seq)。如果成功,则获取对它们的引用
2. 如果 legitimize_path失败:意味着数据已发生巨大变化,无法安全地退出。此时必须执行硬退出
- drop_links(nd): 释放 nd->stack中所有已保存链接的引用
- 重置 nd的关键状态(深度、标志、当前路径、根路径)
- rcu_read_unlock(): 显式退出 RCU 读取侧临界区
3. 如果 legitimize_path成功:调用 unlazy_walk(nd)尝试安全地退出 RCU 模式并获取所有必要资源的引用。如果成功(返回 0),则重试 nd_alloc_stack
4. 最终,如果错误仍然存在:调用 path_put(link)释放之前对符号链接路径的引用,并返回错误
*/
if (error) {
path_put(link);
return error;
}
}
//保存当前状态到栈中,将当前符号链接的信息保存到 nameidata的栈中,为后续的跟随操作做准备
last = nd->stack + nd->depth++; //计算新栈项的位置并增加深度计数器
last->link = *link; //保存符号链接本身的路径信息(挂载点和 dentry)
clear_delayed_call(&last->done);
nd->link_inode = inode; //将符号链接的 inode 保存在 nameidata中,方便后续使用
last->seq = seq; //保存序列号,用于后续的 RCU 验证
// 返回1,会触发在link_path_walk函数中if(err)的流程
return 1;
}
至此,一轮link_path_walk->walk_component的就完成了,接下来是link_path_walk函数中对walk_component返回值检查的后半部分,继续分析
static int link_path_walk(const char *name, struct nameidata *nd)
{
int err;
......
/* At this point we know we have a real path component. */
for(;;) {
......
err = walk_component(nd, ......);
if (err < 0) //表示错误(如权限不足、文件不存在),直接返回错误
return err;
if (err) {
//表示遇到了符号链接,并且需要跟踪(即调用了 pick_link)
//调用 get_link(nd)获取符号链接的目标路径字符串 s,get_link内部可能会调用文件系统的 ->get_link方法
const char *s = get_link(nd);
//获取链接目标的结果
if (IS_ERR(s))
return PTR_ERR(s);
err = 0;
if (unlikely(!s)) {
/* jumped */
//如果 s为空(unlikely(!s)),表示已经处理了跳转(如 nd_jump_root),调用 put_link(nd)清理链接状态
put_link(nd);
} else {
//递归处理:如果 s非空,保存当前路径位置到堆栈(nd->stack[nd->depth - 1].name = name),然后更新 name为链接目标路径 s,并使用 continue重新开始循环。这意味着接下来会处理链接目标路径,实现递归解析
nd->stack[nd->depth - 1].name = name;
name = s;
continue;
}
}
//表示成功处理组件,没有遇到符号链接或不需要跟踪符号链接
//d_can_lookup:检查当前 dentry 是否可查找(即是否是目录)
if (unlikely(!d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))) {
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//unlazy_walk(nd):尝试从 RCU-walk 模式退出到 Ref-walk 模式
// 如果成功,返回 0;如果失败(例如,由于并发修改无法安全退出),返回非零值(通常为 -ECHILD)
if (unlazy_walk(nd))
return -ECHILD;
}
//如果不是,返回 -ENOTDIR(可靠的返回)
return -ENOTDIR;
}
}
}
此外,对于的返回值,通过前面的do_filp_open的处理就明白了,仅当path_openat的返回值为-ECHILD时,才会触发回退到ref-walk,其他情况会直接返回错误
struct file *do_filp_open(int dfd, struct filename *pathname,
const struct open_flags *op)
{
......
//RCU 模式(首先尝试RCU快速路径)
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU);
if (unlikely(filp == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)))
//正常模式(回退到慢速路径)
filp = path_openat(&nd, op, flags);
......
return filp;
}
既然如此,那么有个问题,在RCU模式下的link_path_walk函数,当进入到!d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry)的分支且unlazy_walk成功(unlazy_walk返回0,最终返回-ENOTDIR),为何不再回退到ref-walk模式了呢?分析见附录
TODO
path_openat->do_last
do_last是 open()系统调用路径查找过程中的最终阶段,负责处理路径的最后一个组件(即要打开的文件本身)。这个函数比较复杂,因为它需要处理各种打开标志(open_flag)的组合,包括文件创建、截断、独占打开等场景。这里列举几个常见flags下的流程
这部分放在后面
path_openat->trailing_symlink
static const char *trailing_symlink(struct nameidata *nd)
{
const char *s;
int error = may_follow_link(nd);
if (unlikely(error))
return ERR_PTR(error);
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_PARENT;
nd->stack[0].name = NULL;
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1019
s = get_link(nd);
return s ? s : "";
}
get_link函数负责从符号链接(symlink)的 inode 中获取链接目标路径。涉及多种情况,包括 RCU 模式处理、安全检查、路径解析等
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1019
//nd: 指向 nameidata结构的指针,包含当前路径查找的状态(如当前路径、查找标志、堆栈信息等)
//成功时返回指向链接目标字符串的指针
static __always_inline
const char *get_link(struct nameidata *nd)
{
//获取当前链接状态:从 nameidata的堆栈中获取最近保存的符号链接信息(last)
struct saved *last = nd->stack + nd->depth - 1;
//提取 dentry 和 inode:dentry是符号链接本身的目录项,inode是符号链接对应的 inode
struct dentry *dentry = last->link.dentry;
struct inode *inode = nd->link_inode;
int error;
const char *res;
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU)) {
//ref-walk模式:直接更新访问时间(touch_atime),并调用 cond_resched()让出 CPU,避免长时间占用
touch_atime(&last->link);
cond_resched();
} else if (atime_needs_update_rcu(&last->link, inode)) {
//rcu-walk模式:检查是否需要更新时间戳(atime_needs_update_rcu)。如果需要,尝试退出 RCU 模式(unlazy_walk)。如果退出失败,返回 -ECHILD错误;成功则更新时间戳
if (unlikely(unlazy_walk(nd)))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
touch_atime(&last->link); //更新时间戳(atime)
}
error = security_inode_follow_link(dentry, inode,
nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU);
if (unlikely(error))
return ERR_PTR(error);
// 重要:获取symlink目标
nd->last_type = LAST_BIND; //设置查找类型:LAST_BIND表示当前处理的是符号链接绑定
//尝试快速路径:首先检查 inode->i_link是否缓存了链接目标。如果存在,直接使用(避免调用文件系统操作)
res = inode->i_link;
if (!res) {
const char * (*get)(struct dentry *, struct inode *,
struct delayed_call *);
//文件系统特定获取: 如果缓存不存在,调用文件系统的 get_link方法(inode->i_op->get_link)
//对ext4文件系统,如ext4_get_link从磁盘读取符号链接内容
get = inode->i_op->get_link;
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
//RCU 模式:先尝试无 dentry 的调用(get(NULL, inode, &last->done)),因为 dentry 在 RCU 模式下可能不安全。如果返回 -ECHILD,退出 RCU 模式后重试
res = get(NULL, inode, &last->done);
if (res == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)) {
if (unlikely(unlazy_walk(nd)))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
res = get(dentry, inode, &last->done);
}
} else {
//Ref-walk 模式: 直接调用 get(dentry, inode, &last->done)
res = get(dentry, inode, &last->done);
}
if (IS_ERR_OR_NULL(res))
return res;
}
// res:symlink路径
if (*res == '/') { //处理绝对路径
if (!nd->root.mnt)
set_root(nd); //如果当前未设置根目录(!nd->root.mnt),调用 set_root(nd)设置进程的根目录
if (unlikely(nd_jump_root(nd)))
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD); //nd_jump_root(nd)将当前查找路径重置为根目录。如果失败(如权限不足),返回 -ECHILD
while (unlikely(*++res == '/'))
;
}
// 规范化路径并最终返回
if (!*res)
res = NULL;
return res;
}
小结:RCU-walk、ref-walk的调用路径
TODO
小结:对整个openat过程的小结
path_openat:path_init()、link_path_walk()、do_last()
-
path_init():用于初始化nameidata里的path成员,如果open文件的路径是绝对路径以根目录/开头,则init为根目录/对应的dentry以及vfsmount,为后续路径目录解析做准备,其返回值s指向open文件的完整路径字符串的开头 -
link_path_walk(const char *name, struct nameidata *nd):name参数即是path_init的返回值s。link_path_walk()完成的工作是逐级解析file路径,直到解析到最后一级路径,最终会将filename保存到nameidata的last成员以供do_last()处理最后的文件 open动作
解析每一级路径时,会从dcache(dentry_hashtable)中查找(fast lookup),如果有找到,将找到的dentry保存到path结构体(mnt&dentry);如果没有找到,说明这个目录之前没有被open过,需要创建dentry(slow path)。创建dentry会先alloc一个dentry,然后调用具体文件系统的lookup函数根据name去查找此目录的ext4_dir_entry_2结构,此结构体里有inode num,根据inode num到inode hash链表里查找,如果有找到,则不用分配inode;如果没有找到,则需要alloc一个inode,然后调用d_splice_alias()将dentry和inode关联起来,即将inode赋值给dentry里的d_inode成员。无论是fast path还是slow path,在各自path的最后会将找到的/分配的dentry保存到path结构体(dentry/mnt),然后调用step_into()将path结构体赋值给nameidata里的path成员(path_to_nameidata),这样nameidata即指向了当前目录,完成了一级目录的解析,然后返回link_path_walk()里接着下一级目录的解析
这一阶段解析的是目录分量,其中也要处理链接及挂载点的情况
do_last()根据link_path_walk()的最终解析查找结果,此时open文件的(目录)路径已经都解析完了,只剩下最后的filename没有解析了。如果open flags里没有O_CREATflag,do_last首先执行lookup_fast()查看file是否有对应的dentry,如果有则将此dentry保存至path结构体;如果有O_CREATflag或者lookup_fast没有找到则执行lookup_open(),这个函数仍然会先在dcache中查找,如果没有找到,创建一个dentry,这个创建dentry的过程和link_path_walk()中 slow path里的一样。无论是lookup_fast路径还是lookup_open路径,这两个路径都会设置path结构体,将找到的当前file的dentry或者分配的dentry保存到path结构体(dentry/mnt),然后会执行到step_into(),将path结构体赋值给nameidata.path(path_to_nameidata),此时nameidata已经指向了当前文件,也即完整的file路径。最后调用vfs_open()以执行具体文件系统的file_operations的open函数,比如ext4 fs,这个open函数是ext4_file_open()
0x06 最后一个分量:do_last的实现
至此基本走读完 link_path_walk 函数的实现,这时已经处于路径中的最后一个分量(只是沿着路径走到最终分量所在的目录),该分量可能是:
TODO
有可能是个常规的目录 OR 符号链接 OR 根本不存在,接下来调用 do_last函数解析最后一个分量,厘清do_last的逻辑需要关注:
- 各类标志位flag的检查(打开模式、属性等、部分flag还存在互斥关系)
- 对
..、挂载点、链接的处理 - 建议通过指定flag进行分析
struct file * path_openat(struct nameidata * nd,
const struct open_flags * op, unsigned flags) {
......
while (! (error = link_path_walk(s, nd)) && (error = do_last(nd, file, op, &opened)) > 0) {
nd->flags &= ~(LOOKUP_OPEN | LOOKUP_CREATE | LOOKUP_EXCL);
s = trailing_symlink(nd);
if (IS_ERR(s)) {
error = PTR_ERR(s);
break;
}
}
......
}
path_openat->do_last:大致走读
do_last 方法实现中,先调用 lookup_fast,寻找路径中的最后一个 component,如果成功,就会跳到 finish_lookup 对应的 label,然后执行 step_into 方法,更新 nd 中的 path、inode 等信息,使其指向目标路径。然后调用 vfs_open 方法,继续执行 open 操作
本文内核版本中,do_last还是存在较多与link_path_walk相同的逻辑,因为最后一个路径分量可能仍然是一个链接或者挂载点,这里只考虑最后一个分量为正常文件的情况,接下来基于几种典型场景分析下do_last方法
- case1:
open(pathname, O_RDONLY)只读打开文件 - case2:
open(pathname, O_PATH) - case3:
open(pathname, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR)
/*
nd: 指向 nameidata结构的指针,包含路径查找的当前状态
file: 指向要打开的 file结构的指针
op: 指向 open_flags结构的指针,包含打开标志(如 O_CREAT、O_TRUNC等)
opened: 输出参数,记录打开操作的结果状态(如 FILE_CREATED)
返回值:成功返回 0,失败返回错误码
*/
static int do_last(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op,
int *opened)
{
//1. 初始化与标志设置
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool will_truncate = (open_flag & O_TRUNC) != 0;
bool got_write = false;
int acc_mode = op->acc_mode;
unsigned seq;
struct inode *inode;
struct path path;
int error;
//清除 LOOKUP_PARENT标志(表示不再查找父目录)
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_PARENT;
//设置查找意图标志(如 LOOKUP_OPEN、LOOKUP_CREATE),从参数而来
nd->flags |= op->intent;
//2. 处理特殊路径组件(非普通文件)
if (nd->last_type != LAST_NORM) {
//如果最后一个组件不是普通文件(如 "." 或 ".."),调用 handle_dots处理
error = handle_dots(nd, nd->last_type);
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
//跳转到 finish_open进行最终打开操作
goto finish_open;
}
//3. 非创建模式(!O_CREAT)的快速路径
if (!(open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
if (nd->last.name[nd->last.len]){
//目录跟随检查:如果路径以斜杠结尾(nd->last.name[nd->last.len] != 0)
// 设置 LOOKUP_FOLLOW和 LOOKUP_DIRECTORY标志,表示要进入目录
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW | LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
}
/* we _can_ be in RCU mode here */
// 熟悉的RCU,最后一个分量当然也可以直接走rcu模式
error = lookup_fast(nd, &path, &inode, &seq);
if (likely(error > 0))
goto finish_lookup; //找到
if (error < 0)
return error; //出错
//未找到,error==0,继续向下执行
BUG_ON(nd->inode != dir->d_inode);
BUG_ON(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU);
} else {
//4. 创建模式(O_CREAT)的特殊处理
/* create side of things */
/*
* This will *only* deal with leaving RCU mode - LOOKUP_JUMPED
* has been cleared when we got to the last component we are
* about to look up
*/
//退出 RCU 模式: 调用 complete_walk确保退出 RCU 模式,因为文件创建需要稳定的环境
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
//审计: 记录目录访问审计信息
audit_inode(nd->name, dir, LOOKUP_PARENT);
/* trailing slashes? */
//如果路径以斜杠结尾,返回 -EISDIR错误(不能创建以斜杠结尾的文件)
if (unlikely(nd->last.name[nd->last.len]))
return -EISDIR;
}
//5. 写权限获取
//如果打开标志涉及写操作(创建、截断、只写、读写),获取挂载点的写权限
if (open_flag & (O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY | O_RDWR)) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (!error)
got_write = true; //got_write标记用于后续的权限释放
/*
* do _not_ fail yet - we might not need that or fail with
* a different error; let lookup_open() decide; we'll be
* dropping this one anyway.
*/
}
//6. 目录锁与查找/创建操作
/*
注意:
- 创建模式使用排他锁(inode_lock),防止并发创建冲突
- 非创建模式使用共享锁(inode_lock_shared),允许并发读取
*/
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_lock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_lock_shared(dir->d_inode);
//lookup_open执行实际的查找或创建操作。这个函数是处理 O_CREAT逻辑的核心
error = lookup_open(nd, &path, file, op, got_write, opened);
//7. 处理 lookup_open的结果
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_unlock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_unlock_shared(dir->d_inode);
if (error <= 0) {
if (error)
goto out; //出错处理
// error==0时,说明文件已打开
// 如果 error == 0,表示文件已成功打开(可能在 lookup_open中通过原子操作打开)
// 如果是新创建的文件(FILE_CREATED)或不是普通文件,取消截断标志
// 记录审计信息,跳转到 opened标签进行后续处理
if ((*opened & FILE_CREATED) ||
!S_ISREG(file_inode(file)->i_mode))
will_truncate = false;
audit_inode(nd->name, file->f_path.dentry, 0);
goto opened;
}
//8. 新创建文件的特殊处理
if (*opened & FILE_CREATED) {
/*
对于新创建的文件:
- 清除 O_TRUNC标志(新文件不需要截断)
- 更新 nameidata状态
- 跳转到 finish_open_created进行权限检查
*/
/* Don't check for write permission, don't truncate */
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
will_truncate = false;
acc_mode = 0;
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
goto finish_open_created;
}
/*
* If atomic_open() acquired write access it is dropped now due to
* possible mount and symlink following (this might be optimized away if
* necessary...)
*/
if (got_write) {
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
got_write = false;
}
//9. 已存在文件的处理
/*
处理挂载点: 调用 follow_managed处理可能的挂载点
文件存在性检查: 如果 dentry 为负(表示文件不存在),返回 -ENOENT
*/
error = follow_managed(&path, nd);
if (unlikely(error < 0))
return error;
if (unlikely(d_is_negative(path.dentry))) {
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -ENOENT;
}
/*
* create/update audit record if it already exists.
*/
audit_inode(nd->name, path.dentry, 0);
//10. 独占创建检查
if (unlikely((open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_CREAT)) == (O_EXCL | O_CREAT))) {
//如果同时指定了 O_EXCL和 O_CREAT,但文件已存在,返回 -EEXIST
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -EEXIST;
}
seq = 0; /* out of RCU mode, so the value doesn't matter */
inode = d_backing_inode(path.dentry);
finish_lookup:
//11. 进入最终分量,熟悉的step_into
//调用 step_into进入最终组件,处理符号链接等特殊情况
error = step_into(nd, &path, 0, inode, seq);
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
finish_open:
//12. 最终打开准备
/*
完成路径查找: 调用 complete_walk确保退出 RCU 模式
目录检查:
- 如果以 O_CREAT打开目录,返回 -EISDIR
- 如果要求打开目录但对象不是目录,返回 -ENOTDIR
截断检查:如果不是普通文件,取消截断标志
*/
/* Why this, you ask? _Now_ we might have grown LOOKUP_JUMPED... */
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
audit_inode(nd->name, nd->path.dentry, 0);
error = -EISDIR;
if ((open_flag & O_CREAT) && d_is_dir(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
error = -ENOTDIR;
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
if (!d_is_reg(nd->path.dentry))
will_truncate = false;
if (will_truncate) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (error)
goto out;
got_write = true;
}
finish_open_created:
//13. 权限检查与文件打开
/*
权限检查:调用 may_open检查访问权限
实际打开: 调用 vfs_open执行文件打开操作,设置 FILE_OPENED标志
*/
error = may_open(&nd->path, acc_mode, open_flag);
if (error)
goto out;
BUG_ON(*opened & FILE_OPENED); /* once it's opened, it's opened */
error = vfs_open(&nd->path, file, current_cred());
if (error)
goto out;
*opened |= FILE_OPENED;
opened:
//14. 后续处理与清理
error = open_check_o_direct(file); //直接 I/O 检查: open_check_o_direct
if (!error)
error = ima_file_check(file, op->acc_mode, *opened);
if (!error && will_truncate)
error = handle_truncate(file); //文件截断: 如果设置了 will_truncate,调用 handle_truncate
out:
if (unlikely(error) && (*opened & FILE_OPENED))
fput(file);
if (unlikely(error > 0)) {
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
if (got_write)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
return error;
}
继续分析下do_last中调用的几个关键函数如lookup_open、complete_walk、may_open等函数
lookup_open函数用于处理文件打开操作中的 dentry 查找和文件创建,主要作用如下:
- 在目录缓存(dcache)中查找目标 dentry
- 处理
O_CREAT标志,可能创建新文件 - 处理原子打开(atomic open)操作
- 返回找到的路径或错误代码
注意到在O_CREAT选项是在已经退出了RCU模式下执行的
/*
nd:指向 nameidata结构,包含路径查找的当前状态(如当前目录、查找标志等)
path:输出参数,返回找到的路径(挂载点和 dentry)
file:指向要打开的 file结构
op:指向 open_flags结构,包含打开标志(如 O_CREAT、O_EXCL)和模式
got_write:布尔值,表示调用者是否已获取写权限(如通过 mnt_want_write)
opened:输出参数,用于返回打开状态(如 FILE_CREATED表示文件被创建)
*/
static int lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path,
struct file *file,
const struct open_flags *op,
bool got_write, int *opened)
{
//1. 初始化
//从 nd中获取当前目录的 dentry 和 inode
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
struct inode *dir_inode = dir->d_inode;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
struct dentry *dentry;
int error, create_error = 0;
umode_t mode = op->mode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
//检查目录是否已被标记为死亡(IS_DEADDIR)
// 如果是,返回 -ENOENT(文件不存在)
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(dir_inode)))
return -ENOENT;
//清除 opened中的 FILE_CREATED标志,因为后续可能设置它
*opened &= ~FILE_CREATED;
//2. 查找 dentry
//注意这里调用了d_lookup,基于rename_lock查询dcache
dentry = d_lookup(dir, &nd->last);
// 这里是对最后一个分量的ref-walk的实现了
// 如果找不到就创建dentry
for (;;) {
if (!dentry) {
//如果 dentry 为 NULL,调用 d_alloc_parallel分配一个新的 dentry 并添加到 dcache。该函数处理并发创建,可能阻塞等待其他进程完成
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, &nd->last, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return PTR_ERR(dentry);
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry))
break;
error = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(error > 0))
break;
if (error)
goto out_dput;
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
dentry = NULL;
}
//3. 处理已缓存的positive dentry
if (dentry->d_inode) {
//如果 dentry 已经有 inode,表示文件已存在,跳转到 out_no_open,后续通过文件操作(f_op->open)打开文件。
/* Cached positive dentry: will open in f_op->open */
goto out_no_open;
}
/*
* Checking write permission is tricky, bacuse we don't know if we are
* going to actually need it: O_CREAT opens should work as long as the
* file exists. But checking existence breaks atomicity. The trick is
* to check access and if not granted clear O_CREAT from the flags.
*
* Another problem is returing the "right" error value (e.g. for an
* O_EXCL open we want to return EEXIST not EROFS).
*/
//4. 处理 O_CREAT标志和权限检查
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if (!IS_POSIXACL(dir->d_inode))
mode &= ~current_umask();
if (unlikely(!got_write)) {
// 没有写权限
create_error = -EROFS;
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_TRUNC))
goto no_open;
/* No side effects, safe to clear O_CREAT */
} else {
//如果有写权限,调用 may_o_create检查是否允许创建文件(如权限、文件名长度等)
create_error = may_o_create(&nd->path, dentry, mode);
if (create_error) {
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (open_flag & O_EXCL)
goto no_open;
}
}
} else if ((open_flag & (O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY|O_RDWR)) &&
unlikely(!got_write)) {
//没有 O_CREAT但有写操作标志(O_TRUNC、O_WRONLY、O_RDWR)且没有写权限,跳转到 no_open
/*
* No O_CREATE -> atomicity not a requirement -> fall
* back to lookup + open
*/
goto no_open;
}
//5. 尝试原子打开
if (dir_inode->i_op->atomic_open) {
// 如果目录 inode 支持原子打开操作(atomic_open),调用它
// 原子打开尝试在单个操作中完成查找和打开,避免竞争条件
error = atomic_open(nd, dentry, path, file, op, open_flag,
mode, opened);
if (unlikely(error == -ENOENT) && create_error)
error = create_error;
return error;
}
//回退到非原子打开(no_open路径)
no_open:
if (d_in_lookup(dentry)) {
struct dentry *res = dir_inode->i_op->lookup(dir_inode, dentry,
nd->flags);
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (IS_ERR(res)) {
error = PTR_ERR(res);
goto out_dput;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = res;
}
}
//7. 创建新文件
/* Negative dentry, just create the file */
// 如果 dentry 没有 inode(负面 dentry)且设置了 O_CREAT,则创建新文件
if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
*opened |= FILE_CREATED;
audit_inode_child(dir_inode, dentry, AUDIT_TYPE_CHILD_CREATE);
if (!dir_inode->i_op->create) {
//检查目录是支持 create操作
error = -EACCES;
goto out_dput;
}
//调用 create方法创建文件,并发送文件创建通知
error = dir_inode->i_op->create(dir_inode, dentry, mode,
open_flag & O_EXCL);
if (error)
goto out_dput;
fsnotify_create(dir_inode, dentry);
}
//8. 处理创建错误
if (unlikely(create_error) && !dentry->d_inode) {
//如果有 create_error且 dentry 仍然没有 inode,返回创建错误
error = create_error;
goto out_dput;
}
//成功退出
//设置输出路径的 dentry 和挂载点,返回 1 表示成功
//由调用者将负责打开文件
out_no_open:
path->dentry = dentry;
path->mnt = nd->path.mnt;
return 1;
//10. 错误处理
out_dput:
//释放 dentry 的引用
dput(dentry);
return error;
}
do_last中的complete_walk函数用于在路径遍历成功后进行必要的清理和验证(以确保路径查找的结果是正确和一致)。它主要处理两件事:
- 从 RCU-walk 模式安全退出(如果当前处于该模式)
- 对最终找到的 dentry 进行弱验证(revalidation),确保其有效性
static int complete_walk(struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct dentry *dentry = nd->path.dentry;
int status;
//1. 退出 RCU-walk 模式
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT)){
//清理根挂载点: 如果查找不是从根目录开始的(!LOOKUP_ROOT),则将 nd->root.mnt设置为 NULL。这是因为在 RCU-walk 模式下,nd->root可能只是临时引用,退出时需要清理以避免无效引用
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
}
//调用 unlazy_walk(nd)函数安全退出 RCU-walk 模式
//该函数会尝试获取所有相关 dentry 和挂载点的引用和锁,以确保数据一致性。如果失败(返回非零),则返回 -ECHILD错误,表示需要完全退出 RCU 模式并重新执行查找
if (unlikely(unlazy_walk(nd)))
return -ECHILD;
}
//2. 检查是否需要验证
//跳转检查: LOOKUP_JUMPED标志表示路径查找过程中发生了跳转,例如跟随了符号链接或处理了挂载点。如果没有发生跳转(!LOOKUP_JUMPED),说明查找路径是直接的,不需要额外验证,直接返回成功(0)
if (likely(!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_JUMPED)))
return 0;
......
if (!status)
status = -ESTALE;
return status;
}
may_open函数用于在打开文件前进行最终的权限和标志检查。它确保打开操作基于文件类型、访问模式和标志是允许的。该函数通常在找到文件 inode 后、实际打开文件前执行
static int may_open(const struct path *path, int acc_mode, int flag)
{
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry;
struct inode *inode = dentry->d_inode;
int error;
if (!inode)
return -ENOENT;
//文件类型检查
//检查 inode 的文件类型(通过 i_mode的高位)
switch (inode->i_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFLNK: //符号链接(S_IFLNK)
return -ELOOP; //如果文件是符号链接,返回 -ELOOP(符号链接循环过多或不允许直接打开符号链接)。在路径查找中,符号链接通常已被跟随,但直接打开符号链接本身是不允许的
case S_IFDIR: // 目录(S_IFDIR)
if (acc_mode & MAY_WRITE){
//如果文件是目录,并且请求写访问(acc_mode包含 MAY_WRITE),返回 -EISDIR(是一个目录)。目录不能以写方式打开(除非使用特殊标志如 O_DIRECTORY,但这里不处理),这防止了误操作
return -EISDIR;
}
break;
case S_IFBLK: //块设备或字符设备(S_IFBLK 或 S_IFCHR)
case S_IFCHR:
if (!may_open_dev(path))
return -EACCES;
/*FALLTHRU*/
case S_IFIFO: //FIFO 或套接字(S_IFIFO 或 S_IFSOCK)
case S_IFSOCK:
flag &= ~O_TRUNC; //如果文件是 FIFO(命名管道)或套接字,清除 flag中的 O_TRUNC标志。因为这些文件类型不能被截断(截断操作无意义),所以忽略 O_TRUNC以避免错误
break;
}
//调用 inode_permission检查 inode 的权限。参数 MAY_OPEN | acc_mode表示检查打开文件的权限以及具体的访问模式(读、写、执行)
//inode_permission可能检查文件系统的权限位(如 Unix 权限)、ACL 或安全模块(如 SELinux)的规则
//如果权限检查失败,返回错误码(如 -EACCES)
error = inode_permission(inode, MAY_OPEN | acc_mode);
if (error)
return error;
......
return 0;
}
case1:只读打开文件
如open(pathname, O_RDONLY),使用只读方式打开(先查找到然后再打开)一个文件,在do_last中的运作路径:
static inline int build_open_flags(int flags, umode_t mode, struct open_flags *op)
{
//非创建文件, mode 设置为 0
op->mode = 0;
// acc_mode:权限检查 MAY_OPEN | MAY_READ
// 对于目标文件至少需要打开和读取的权限
acc_mode = MAY_OPEN | ACC_MODE(flags);
op->open_flag = flags;
// intent 用来标记对最终目标想要做什么操作(至少LOOKUP_OPEN)
op->intent = flags & O_PATH ? 0 : LOOKUP_OPEN;
op->lookup_flags = lookup_flags;
return 0;
}
只读打开模式下do_last主要实现:
static int do_last(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op,
int *opened)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool will_truncate = (open_flag & O_TRUNC) != 0;
bool got_write = false;
int acc_mode = op->acc_mode;
unsigned seq;
struct inode *inode;
struct path path;
int error;
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_PARENT;
nd->flags |= op->intent;
......
if (!(open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
// 当前非创建文件,进入此流程
// 判断 last.name 是否以 / 结尾
if (nd->last.name[nd->last.len])
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW | LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
/* we _can_ be in RCU mode here */
/*
三种返回值?:
- 如果返回 0,则表示成功找到
- 返回 1,表示内存中没有,需要 lookup_real
- 返回小于 0,则表示需要从当前 rcu-walk 转到 ref-walk
*/
error = lookup_fast(nd, &path, &inode, &seq);
if (likely(error > 0))
goto finish_lookup;
if (error < 0)
return error;
......
} else {
......
}
......
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_lock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_lock_shared(dir->d_inode);
//
error = lookup_open(nd, &path, file, op, got_write, opened);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_unlock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_unlock_shared(dir->d_inode);
if (error <= 0) {
if (error)
goto out;
if ((*opened & FILE_CREATED) ||
!S_ISREG(file_inode(file)->i_mode))
will_truncate = false;
audit_inode(nd->name, file->f_path.dentry, 0);
goto opened;
}
if (*opened & FILE_CREATED) {
/* Don't check for write permission, don't truncate */
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
will_truncate = false;
acc_mode = 0;
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
goto finish_open_created;
}
/*
* If atomic_open() acquired write access it is dropped now due to
* possible mount and symlink following (this might be optimized away if
* necessary...)
*/
if (got_write) {
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
got_write = false;
}
error = follow_managed(&path, nd);
if (unlikely(error < 0))
return error;
if (unlikely(d_is_negative(path.dentry))) {
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -ENOENT;
}
/*
* create/update audit record if it already exists.
*/
audit_inode(nd->name, path.dentry, 0);
if (unlikely((open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_CREAT)) == (O_EXCL | O_CREAT))) {
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -EEXIST;
}
seq = 0; /* out of RCU mode, so the value doesn't matter */
inode = d_backing_inode(path.dentry);
finish_lookup:
error = step_into(nd, &path, 0, inode, seq);
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
finish_open:
/* Why this, you ask? _Now_ we might have grown LOOKUP_JUMPED... */
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
audit_inode(nd->name, nd->path.dentry, 0);
error = -EISDIR;
if ((open_flag & O_CREAT) && d_is_dir(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
error = -ENOTDIR;
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
if (!d_is_reg(nd->path.dentry))
will_truncate = false;
if (will_truncate) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (error)
goto out;
got_write = true;
}
finish_open_created:
// 准备好打开文件操作
// may_open:权限和标志位的检查
error = may_open(&nd->path, acc_mode, open_flag);
if (error)
goto out;
BUG_ON(*opened & FILE_OPENED); /* once it's opened, it's opened */
// 核心:终于可以做打开文件的操作了
error = vfs_open(&nd->path, file, current_cred());
if (error)
goto out;
*opened |= FILE_OPENED;
opened:
error = open_check_o_direct(file);
if (!error)
error = ima_file_check(file, op->acc_mode, *opened);
if (!error && will_truncate)
error = handle_truncate(file);
out:
if (unlikely(error) && (*opened & FILE_OPENED))
fput(file);
if (unlikely(error > 0)) {
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
if (got_write)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
return error;
}
lookup_open负责处理路径查找的最终分量(final component)并协调文件创建与打开操作,lookup_open的实现机制类似于lookup_slow,先使用 d_lookup 在内存中找(快速查找),如果未命中就启动 d_alloc_parallel-> 在具体文件系统里面去找(慢速查找),当它成功返回时会将 path 指向找到的目标,lookup_open的实现流程描述如下:
1、缓存优先:通过 d_lookup 在父目录的哈希链中查找目标 dentry,若命中则跳过后续分配
2、若缓存未命中,则通过d_alloc_parallel并行分配 dentry,避免重复创建(避免多线程重复分配同一 dentry)
- 无锁设计:使用 RCU 和等待队列机制同步,仅首个线程执行实际分配,后续线程等待结果
-
状态标记:通过
d_in_lookup(dentry)检测DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP标志,表示该 dentry 正在通过具体文件系统的->lookup()方法初始化(如磁盘 I/O)。通过DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP标志协调并发初始化,避免全局锁d_alloc_parallel用于高并发环境下并行分配和查找目录项(dentry),其设计目标是减少锁竞争并优化多线程场景下的性能,在父目录下并行查找或分配指定名称的 dentry,避免多线程重复创建同一 dentry,并确保状态同步 - 若 dentry 已存在:返回现有 dentry,避免重复分配;此外,若其他线程正在初始化同一 dentry,当前线程阻塞直至其完成(触发等待队列机制,通过
d_wait队列唤醒),关联d_alloc_parallel->d_wait_lookup函数 - 若不存在:分配新 dentry 并加入正在查找哈希链(
in_lookup_hash),并将此dentry标记为DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP,后续线程可等待其初始化完成
3、dentry 验证与重试,需要保证缓存一致性,即通过d_revalidate 检查 dentry 是否过期(如被其他进程删除),若失效则调用 d_invalidate 将其移出缓存并重试
4、O_CREAT 标志处理与权限校验,O_CREAT 需检查文件是否存在,但检查与创建需保证原子性;同时检查权限是否满足,may_o_create 验证父目录的写权限及文件系统支持,若进程无写权限(!got_write),返回 -EROFS(只读)
5、文件系统协作模式,优先高性能路径,如支持 atomic_open 的文件系统(如 Ext4)可合并查找与打开操作,减少锁竞争;其次再以传统模式进行兜底。如O_CREAT + O_EXCL 模式组合通过文件系统钩子(create/atomic_open)确保创建的唯一性
6、结果返回与错误处理
- 成功路径:返回
1通知上层调用f_op->open(如ext4_file_open)可以打开文件 - 错误处理:释放 dentry 引用并返回错误码(如
-ENOENT、-EACCES等)
小结下,lookup_open函数通过缓存查找d_lookup、并行分配d_alloc_parallel以及原子操作 atomic_open形成三级加速路径
//do_sys_open->do_sys_openat2->do_filp_open->path_openat->do_last->lookup_open
// 主要功能:查找或创建目标文件的 dentry(目录项)
// 这里只考虑传统 lookup + create 流程
static int lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path,
struct file *file,
const struct open_flags *op,
bool got_write, int *opened)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry; // 父目录的 dentry
struct inode *dir_inode = dir->d_inode;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
struct dentry *dentry;
int error, create_error = 0;
umode_t mode = op->mode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(dir_inode)))
return -ENOENT;
*opened &= ~FILE_CREATED;
// fast查找,从缓存中查找dentry
dentry = d_lookup(dir, &nd->last);
for (;;) {
if (!dentry) {
// 并行分配 dentry
// d_alloc_parallel 见后文分析
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, &nd->last, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return PTR_ERR(dentry);
}
/*
如果检测到目前是慢速模式
即当 d_in_lookup(dentry) 返回 true 时
说明此 dentry 正在被其他线程初始化(例如通过文件系统的 ->lookup() 执行磁盘 I/O)
此时立即 break 跳出循环,避免重复操作
*/
if (d_in_lookup(dentry))
break;
//如果非慢速查找
//验证 dentry 有效性
error = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(error > 0))
break; //有效则退出循环
if (error)
goto out_dput; //错误处理
d_invalidate(dentry); //无效则丢弃并重试
dput(dentry);
dentry = NULL;
}
if (dentry->d_inode) {
/* Cached positive dentry: will open in f_op->open */
goto out_no_open;
}
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if (!IS_POSIXACL(dir->d_inode))
mode &= ~current_umask();
if (unlikely(!got_write)) {
create_error = -EROFS;
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_TRUNC))
goto no_open;
/* No side effects, safe to clear O_CREAT */
} else {
// 检查创建权限
create_error = may_o_create(&nd->path, dentry, mode);
if (create_error) {
// 权限不足时清除 O_CREAT
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
// O_EXCL 依赖 O_CREAT
if (open_flag & O_EXCL)
goto no_open;
}
}
} else if ((open_flag & (O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY|O_RDWR)) &&
unlikely(!got_write)) {
/*
* No O_CREATE -> atomicity not a requirement -> fall
* back to lookup + open
*/
goto no_open;
}
// 原子打开模式(优先)
if (dir_inode->i_op->atomic_open) {
error = atomic_open(nd, dentry, path, file, op, open_flag,
mode, opened);
if (unlikely(error == -ENOENT) && create_error)
error = create_error;
return error;
}
no_open:
// 传统模式(兜底)
/*
两步操作:
1. 先通过 ->lookup 完成磁盘查找,再通过 ->create 创建文件
2. 状态同步:d_lookup_done 清除 DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP 标志,表示慢速查找完成
*/
if (d_in_lookup(dentry)) {
// d_in_lookup的作用是什么?
// 如果没有找到,调用文件系统的lookup 方法进行查找
struct dentry *res = dir_inode->i_op->lookup(dir_inode, dentry,nd->flags);
// 由于->lookup已经完成了
// 清除 DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP 标志
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (IS_ERR(res)) {
error = PTR_ERR(res);
goto out_dput;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = res;
}
}
/* Negative dentry, just create the file */
if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
*opened |= FILE_CREATED;
audit_inode_child(dir_inode, dentry, AUDIT_TYPE_CHILD_CREATE);
if (!dir_inode->i_op->create) {
error = -EACCES;
goto out_dput;
}
// 如果没有找到且设置了O_CREAT, 调用文件系统的create方法进行创建
// 对应ext4文件系统,ext4_create方法
// 正常情况下,ext4_create会成功创建inode并且和dentry建立关联关系(前文)
error = dir_inode->i_op->create(dir_inode, dentry, mode,
open_flag & O_EXCL);
if (error)
goto out_dput;
fsnotify_create(dir_inode, dentry);
}
if (unlikely(create_error) && !dentry->d_inode) {
error = create_error;
goto out_dput;
}
out_no_open:
// 找到了,设置path的值
path->dentry = dentry; // 返回最终 dentry
path->mnt = nd->path.mnt;
return 1; // 表示需执行 f_op->open
out_dput:
dput(dentry); // 错误时释放 dentry
return error;
}
在do_last函数的标签finish_open_created中通过调用vfs_open最终完成了对文件打开操作,简单分析下基于ext4文件系统的运作过程
首先在vfs_open->do_dentry_open 方法,该方法中看到了熟悉的 inode->i_fop 成员,该成员的值是在 init_special_inode 中设置的,由于这里讨论的文件系统是 ext4,所以会命中 S_ISBLK(mode) 的逻辑
void init_special_inode(struct inode *inode, umode_t mode, dev_t rdev)
{
inode->i_mode = mode;
if (S_ISCHR(mode)) {
inode->i_fop = &def_chr_fops;
inode->i_rdev = rdev;
} else if (S_ISBLK(mode)) {
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/block_dev.c#L2142
inode->i_fop = &def_blk_fops;
inode->i_rdev = rdev;
}
//...
}
当用户调用 open() 系统调用时,VFS 层会初始化一个 struct file 对象 f,f->f_op 被赋值为目标文件所属文件系统的 file_operations 结构体,此处为 ext4_file_operations,因此,执行 f->f_op->open 实际调用的是 ext4_file_open()。这里体现了 VFS 的协作流程,即 VFS 通过路径解析找到文件的 dentry 和 inode,根据 inode 关联的文件系统类型(如 ext4),将 file 结构 f->f_op 绑定到 ext4_file_operations,那么执行 open 操作时,路由到具体文件系统的实现函数 ext4_file_open
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/open.c#L855
int vfs_open(const struct path *path, struct file *file,
const struct cred *cred)
{
struct dentry *dentry = d_real(path->dentry, NULL, file->f_flags);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return PTR_ERR(dentry);
file->f_path = *path;
return do_dentry_open(file, d_backing_inode(dentry), NULL, cred);
}
// fs/open.c
static int do_dentry_open(struct file *f,
struct inode *inode,
int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *))
{
...
f->f_inode = inode;
...
f->f_op = fops_get(inode->i_fop);
...
if (!open)
//ext4_file_open
open = f->f_op->open;
if (open) {
error = open(inode, f);
...
}
f->f_mode |= FMODE_OPENED;
...
return 0;
...
}
最终通过ext4_file_open 方法完成了打开文件操作,在 ext4 文件系统中,f->f_op->open 对应的实际函数是 ext4_file_open(),这一关联通过 ext4 定义的 file_operations 结构体实现。ext4_file_open 最终完成这些工作:
- 初始化文件状态:检查文件是否加密(fscrypt)、是否启用日志(jbd2)等
- 处理大文件标志:若文件超过
2GB,设置O_LARGEFILE标志 - 调用通用逻辑:最终通过
generic_file_open()完成 VFS 层的通用文件打开流程
static int ext4_file_open(struct inode * inode, struct file * filp)
case2:文件创建场景
模式如下,创建一个新文件(O_CREAT),并赋予该文件用户可读(S_IRUSR)和用户可写(S_IWUSR)权限,然后以只写(O_WRONLY)的方式打开这个文件。O_EXCL 在这里保证该文件必须被创建,如果该文件已经存在则失败返回
- mode:
- acc_mode:
- intent:
open(pathname, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR)
static inline int build_open_flags(int flags, umode_t mode, struct open_flags *op)
{
int lookup_flags = 0;
int acc_mode;
flags &= VALID_OPEN_FLAGS;
if (flags & (O_CREAT | __O_TMPFILE))
//mode:S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR
op->mode = (mode & S_IALLUGO) | S_IFREG;
...
/* Must never be set by userspace */
flags &= ~FMODE_NONOTIFY & ~O_CLOEXEC;
...
// acc_mode:MAY_OPEN | MAY_WRITE
acc_mode = MAY_OPEN | ACC_MODE(flags);
op->open_flag = flags;
...
op->acc_mode = acc_mode;
//intent:LOOKUP_OPEN
op->intent = flags & O_PATH ? 0 : LOOKUP_OPEN;
if (flags & O_CREAT) {
op->intent |= LOOKUP_CREATE;
if (flags & O_EXCL)
op->intent |= LOOKUP_EXCL;
}
...
return 0;
}
对应的do_last核心实现:
static int do_last(struct nameidata *nd,
struct file *file, const struct open_flags *op,
int *opened)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
bool will_truncate = (open_flag & O_TRUNC) != 0;
bool got_write = false;
int acc_mode = op->acc_mode;
unsigned seq;
struct inode *inode;
struct path path;
int error;
......
if (!(open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
......
} else {
// O_CREAT模式
//complete_walk:告别 rcu-walk 模式
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
audit_inode(nd->name, dir, LOOKUP_PARENT);
/* trailing slashes? */
// 判断这个最终目标是不是以 / 结尾
// 如果是的话就表示最终目标是一个目录那就返回 EISDIR
// 并报错 Is a directory
if (unlikely(nd->last.name[nd->last.len]))
return -EISDIR;
}
if (open_flag & (O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY | O_RDWR)) {
// 尝试取得当前文件系统的写权限(有可能写入)
// 最终会让lookup_open决定
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (!error)
got_write = true; //不退出,先打个标记
/*
* do _not_ fail yet - we might not need that or fail with
* a different error; let lookup_open() decide; we'll be
* dropping this one anyway.
*/
}
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_lock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_lock_shared(dir->d_inode);
// lookup_open:核心处理逻辑
error = lookup_open(nd, &path, file, op, got_write, opened);
if (open_flag & O_CREAT)
inode_unlock(dir->d_inode);
else
inode_unlock_shared(dir->d_inode);
if (error <= 0) {
if (error)
goto out;
if ((*opened & FILE_CREATED) ||
!S_ISREG(file_inode(file)->i_mode))
will_truncate = false;
audit_inode(nd->name, file->f_path.dentry, 0);
goto opened;
}
if (*opened & FILE_CREATED) {
/* Don't check for write permission, don't truncate */
// 如果这个文件就是本次新建的
// 那么就要清除 O_TRUNC 位
open_flag &= ~O_TRUNC;
will_truncate = false;
// 已经成功的创建了新文件
// 那么写权限也没必要检查了
acc_mode = 0;
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
//直接跳转到标号 finish_open_created 处完成打开
goto finish_open_created;
}
/*
* If atomic_open() acquired write access it is dropped now due to
* possible mount and symlink following (this might be optimized away if
* necessary...)
*/
if (got_write) {
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
got_write = false;
}
error = follow_managed(&path, nd);
if (unlikely(error < 0))
return error;
if (unlikely(d_is_negative(path.dentry))) {
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -ENOENT;
}
/*
* create/update audit record if it already exists.
*/
audit_inode(nd->name, path.dentry, 0);
if (unlikely((open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_CREAT)) == (O_EXCL | O_CREAT))) {
// 如果这个文件本来就存在
// 检查 O_EXCL 和 O_CREAT 这两个标志位
// 因为 O_EXCL 标志位要求必须创建成功
// 所以这里就会返回File exists”错误
path_to_nameidata(&path, nd);
return -EEXIST;
}
seq = 0; /* out of RCU mode, so the value doesn't matter */
inode = d_backing_inode(path.dentry);
finish_lookup:
error = step_into(nd, &path, 0, inode, seq);
if (unlikely(error))
return error;
finish_open:
/* Why this, you ask? _Now_ we might have grown LOOKUP_JUMPED... */
error = complete_walk(nd);
if (error)
return error;
audit_inode(nd->name, nd->path.dentry, 0);
error = -EISDIR;
if ((open_flag & O_CREAT) && d_is_dir(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
error = -ENOTDIR;
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
if (!d_is_reg(nd->path.dentry))
will_truncate = false;
if (will_truncate) {
error = mnt_want_write(nd->path.mnt);
if (error)
goto out;
got_write = true;
}
finish_open_created:
// 最后 may_open 检查相应的权限
// 然后 vfs_open 完成打开
error = may_open(&nd->path, acc_mode, open_flag);
if (error)
goto out;
......
error = vfs_open(&nd->path, file, current_cred());
if (error)
goto out;
*opened |= FILE_OPENED;
opened:
error = open_check_o_direct(file);
if (!error)
error = ima_file_check(file, op->acc_mode, *opened);
if (!error && will_truncate)
error = handle_truncate(file);
out:
if (unlikely(error) && (*opened & FILE_OPENED))
fput(file);
if (unlikely(error > 0)) {
WARN_ON(1);
error = -EINVAL;
}
if (got_write)
mnt_drop_write(nd->path.mnt);
return error;
}
static int lookup_open(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path,
struct file *file,
const struct open_flags *op,
bool got_write, int *opened)
{
struct dentry *dir = nd->path.dentry;
struct inode *dir_inode = dir->d_inode;
int open_flag = op->open_flag;
struct dentry *dentry;
int error, create_error = 0;
umode_t mode = op->mode;
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(dir_inode)))
return -ENOENT;
//先清除改变量的 FILE_CREATED 位
//如果该文件不存在的话会被重新赋上 FILE_CREATED,表示文件是这次创建的
*opened &= ~FILE_CREATED;
dentry = d_lookup(dir, &nd->last);
for (;;) {
if (!dentry) {
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, &nd->last, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry))
return PTR_ERR(dentry);
}
if (d_in_lookup(dentry))
break;
error = d_revalidate(dentry, nd->flags);
if (likely(error > 0))
break;
if (error)
goto out_dput;
d_invalidate(dentry);
dput(dentry);
dentry = NULL;
}
if (dentry->d_inode) {
/* Cached positive dentry: will open in f_op->open */
goto out_no_open;
}
if (open_flag & O_CREAT) {
if (!IS_POSIXACL(dir->d_inode))
mode &= ~current_umask();
if (unlikely(!got_write)) {
create_error = -EROFS;
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (open_flag & (O_EXCL | O_TRUNC))
goto no_open;
/* No side effects, safe to clear O_CREAT */
} else {
create_error = may_o_create(&nd->path, dentry, mode);
if (create_error) {
open_flag &= ~O_CREAT;
if (open_flag & O_EXCL)
goto no_open;
}
}
} else if ((open_flag & (O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY|O_RDWR)) &&
unlikely(!got_write)) {
/*
* No O_CREATE -> atomicity not a requirement -> fall
* back to lookup + open
*/
goto no_open;
}
if (dir_inode->i_op->atomic_open) {
error = atomic_open(nd, dentry, path, file, op, open_flag,mode, opened);
if (unlikely(error == -ENOENT) && create_error)
error = create_error;
return error;
}
no_open:
if (d_in_lookup(dentry)) {
struct dentry *res = dir_inode->i_op->lookup(dir_inode, dentry,nd->flags);
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (IS_ERR(res)) {
error = PTR_ERR(res);
goto out_dput;
}
dput(dentry);
dentry = res;
}
}
/* Negative dentry, just create the file */
if (!dentry->d_inode && (open_flag & O_CREAT)) {
// 重新补入FILE_CREATED位
*opened |= FILE_CREATED;
audit_inode_child(dir_inode, dentry, AUDIT_TYPE_CHILD_CREATE);
if (!dir_inode->i_op->create) {
error = -EACCES;
goto out_dput;
}
// struct dentry * dir = nd->path.dentry; 指的是当前要创建 dentry 的父目录的 dentry
// 所以这里是调用父目录 dentry 的 inode_operations.create
// create 会调用文件系统的 inode_operations.create函数真正创建这个文件
error = dir_inode->i_op->create(dir_inode, dentry, mode,
open_flag & O_EXCL);
if (error)
goto out_dput;
fsnotify_create(dir_inode, dentry);
}
if (unlikely(create_error) && !dentry->d_inode) {
error = create_error;
goto out_dput;
}
out_no_open:
path->dentry = dentry;
path->mnt = nd->path.mnt;
return 1;
out_dput:
dput(dentry);
return error;
}
0x07 附录
d_lookup函数
d_lookup函是一个导出的内核函数(在open内核实现中没有直接调用),用于在dcache中查找dentry。它通常被用于慢速路径查找或其他需要显式查找的场景;d_lookup函数内部会调用__d_lookup,但增加了序列锁(rename_lock)的保护,以确保在重命名操作下的安全性
struct dentry *d_lookup(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
unsigned seq;
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&rename_lock);
dentry = __d_lookup(parent, name);
if (dentry)
break;
} while (read_seqretry(&rename_lock, seq));
return dentry;
}
d_invalidate函数
d_invalidate函数用于使目录项(dentry)及其子树无效的核心函数。它会递归地使指定 dentry 及其所有子 dentry 从目录缓存(dcache)中移除,并处理相关的挂载点分离,d_invalidate只会出现在ref-walk模式中,思考一下为什么?
d_invalidate调用场景如下(通常位于d_revalidate返回错误的case之后):
- 文件系统卸载:当卸载文件系统时,需要使所有相关 dentry 无效,确保后续访问不会使用过时的缓存
- 目录重命名/删除:当目录被重命名或删除时,需要使该目录及其所有子项的 dentry 无效
- 网络文件系统缓存失效:当服务器端文件状态改变时,客户端需要使相关 dentry 无效
- 强制刷新缓存:用户空间程序(如
drop_caches)可能触发 dentry 无效化来释放内存
void d_invalidate(struct dentry *dentry)
{
/*
* If it's already been dropped, return OK.
*/
//1. 初始检查
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
//检查 dentry 是否已经被丢弃(不在哈希表中)
if (d_unhashed(dentry)) {
//如果 d_unhashed(dentry)返回 true,表示 dentry 已经被移除,直接返回无需进一步处理
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
return;
}
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
/* Negative dentries can be dropped without further checks */
//2. 负 dentry 处理
//处理负 dentry(表示不存在的文件)
if (!dentry->d_inode) {
//如果 dentry 没有关联的 inode(dentry->d_inode为 NULL),直接调用 d_drop将其从哈希表中移除并返回
// 处于negtive dentry状态的,无子树,处理较为简单
d_drop(dentry);
return;
}
//3. positive dentry 处理(主循环),处理 dentry 子树
for (;;) {
//a. 初始化数据结构
struct detach_data data;
data.mountpoint = NULL; //用于记录需要分离的挂载点
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&data.select.dispose); //链表头,用于收集需要处理的 dentry
data.select.start = dentry; //设置起始 dentry
data.select.found = 0; //计数器,记录找到的 dentry 数量
//b. 递归的遍历 dentry 树
//回调函数detach_and_collect:分离挂载点并收集需要处理的 dentry
//回调函数check_and_drop:检查 dentry 是否需要被丢弃
d_walk(dentry, &data, detach_and_collect, check_and_drop);
// c. 处理收集到的 dentry
if (data.select.found)
shrink_dentry_list(&data.select.dispose);
//d. 处理挂载点,分离挂载点并释放相关资源
if (data.mountpoint) {
//分离挂载在指定 dentry 上的所有文件系统
detach_mounts(data.mountpoint);
dput(data.mountpoint);
}
if (!data.mountpoint && !data.select.found){
//当没有挂载点需要分离且没有 dentry 需要处理时,退出循环
break;
}
//在每次循环后提供调度机会,避免长时间占用 CPU
cond_resched();
}
}
do_last中的跟随目录检查(Trailing Slash Check)
目录跟随检查是内核路径查找中一个重要的语义解析步骤,它的作用是检测用户提供的路径是否以斜杠结尾。如果是,则强制要求查找的最终目标必须是一个真正的目录,否则就使操作失败。在 do_last函数中,目录跟随检查主要涉及到下面的代码:
if (nd->last.name[nd->last.len])
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_FOLLOW | LOOKUP_DIRECTORY;
先回顾一下,nd->last 是一个 struct qstr类型,它保存了当前正在处理的路径组件的名称和长度。nd->last.name指向组件字符串的起始地址(比如对于路径 /tmp/foo/,处理最后一个组件时,它指向 foo);nd->last.len是这个组件的有效长度(如strlen("foo") = 3);nd->last.name[nd->last.len]表示的是有效长度之后的一个字节
所以,代码中if (nd->last.name[nd->last.len])意义是判断当前路径组件的名称字符串,在有效长度之后,是否还有一个非结束符的字符(非\0),那么大概率这种场景是路径的末尾是/(如/tmp/foo/),由于/在Linux中表示目录,于是这个检查的目的是当检测到路径末尾有多余的斜杠时,强制后续的查找逻辑必须将目标当作一个目录来处理
假设要打开的路径是/tmp/foo/,路径查找器会一步步解析组件:/-> tmp-> foo,当处理最后一个组件 foo时,nd->last.name指向字符串 foo/(注意内核可能不会单独拷贝字符串,而是直接在原路径字符串上操作),nd->last.len被设置为 3( foo的长度是 3),那么 nd->last.name[nd->last.len]就是 foo/这个字符串的第 4 个字符(索引为 3),也就是 '/'
在 do_last函数的后面,有一个关键检查(如下),如果设置了 LOOKUP_DIRECTORY标志,但最终找到的 dentry 不是一个可以通过 d_can_lookup判断的目录(一个普通文件),那么这次查找就会失败,并返回 -ENOTDIR(不是一个目录)错误
error = -ENOTDIR;
if ((nd->flags & LOOKUP_DIRECTORY) && !d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))
goto out;
在实践中,假设cat /tmp/regular_file/时,即使文件存在,也会得到Not a directory的错误,就是因为内核在 do_last中做了这个检查并设置了 LOOKUP_DIRECTORY标志
follow_managed函数
TODO
__follow_mount_rcu函数
static bool __follow_mount_rcu(struct nameidata *nd, struct path *path,
struct inode **inode, unsigned *seqp)
{
for (;;) {
struct mount *mounted;
/*
* Don't forget we might have a non-mountpoint managed dentry
* that wants to block transit.
*/
switch (managed_dentry_rcu(path)) {
case -ECHILD:
default:
return false;
case -EISDIR:
return true;
case 0:
break;
}
if (!d_mountpoint(path->dentry))
return !(path->dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_NEED_AUTOMOUNT);
mounted = __lookup_mnt(path->mnt, path->dentry);
if (!mounted)
break;
path->mnt = &mounted->mnt;
path->dentry = mounted->mnt.mnt_root;
nd->flags |= LOOKUP_JUMPED;
*seqp = read_seqcount_begin(&path->dentry->d_seq);
/*
* Update the inode too. We don't need to re-check the
* dentry sequence number here after this d_inode read,
* because a mount-point is always pinned.
*/
*inode = path->dentry->d_inode;
}
return !read_seqretry(&mount_lock, nd->m_seq) &&
!(path->dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_NEED_AUTOMOUNT);
}
小结:do_filp_open中的查找模式
do_filp_open对path_openat的调用模式与path_openat内部的lookup_fast/lookup_slow组合,这些策略的设计目的是在效率(无锁RCU模式)和兼容性(带锁的ref-walk模式)之间动态平衡,实际组合共4种场景(RCU独立成功、RCU回退、标准模式、REVAL模式),核心策略如下:
1、RCU模式(LOOKUP_RCU)
- 触发条件:
do_filp_open首次调用path_openat时设置LOOKUP_RCU | LOOKUP_FOLLOW - 核心流程:通过
lookup_fast->__d_lookup_rcu在无锁状态下查询dcache,若dcache命中且通过RCU校验(如read_seqcount_retry),直接返回成功 - 失败场景:dcache未命中或校验失败,返回
-ECHILD,触发回退至ref-walk模式
2、RCU回退至ref-walk模式
- 触发条件:RCU模式返回
-ECHILD后,do_filp_open重新调用path_openat(无LOOKUP_RCU标志) - 核心流程
- Step 1:
lookup_fast(ref-walk版),在dcache中带锁查找(lookup_fast->__d_lookup),若成功则更新nameidata - Step 2:
lookup_slow(文件系统级查找),若lookup_fast失败,调用具体文件系统的->lookup钩子(如ext4_lookup)从磁盘加载inode
- Step 1:
3、标准ref-walk模式
- 触发条件:RCU模式未启用或已回退后
- 核心流程:同RCU回退模式(
lookup_fast->lookup_slow),但无RCU前置尝试 - 典型场景:非首次查找、或进程已持有锁无法使用RCU
4、 REVAL模式(LOOKUP_REVAL)
- 触发条件:标准模式返回
-ESTALE(inode可能过期),在lookup_slow中强制重新验证inode有效性(如NFS场景) - 核心流程:与标准ref-walk模式一致,但增加有效性校验逻辑
handle_dots
TODO
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L1679
static inline int handle_dots(struct nameidata *nd, int type)
{
if (type == LAST_DOTDOT) {
if (!nd->root.mnt)
set_root(nd);
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
// RCU
return follow_dotdot_rcu(nd);
} else
return follow_dotdot(nd);
}
return 0;
}
operations 成员(ext4文件系统)
针对ext4系统,相应注册的inode实例化方法如下
const struct inode_operations ext4_dir_inode_operations = {
.create = ext4_create,
.lookup = ext4_lookup,
.link = ext4_link,
.unlink = ext4_unlink,
.symlink = ext4_symlink,
.mkdir = ext4_mkdir,
.rmdir = ext4_rmdir,
.mknod = ext4_mknod,
.tmpfile = ext4_tmpfile,
.rename = ext4_rename2,
.setattr = ext4_setattr,
.getattr = ext4_getattr,
.listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
.get_acl = ext4_get_acl,
.set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
.fiemap = ext4_fiemap,
};
以inode的创建函数ext4_create为例,核心调用关系如下:
ext4_create
--ext4_new_inode_start_handle
--ext4_add_nondir
--ext4_add_nondir
--d_instantiate
ext4_new_inode_start_handle:为新创建的文件分配一个inode结构,接着为该文件找一个有空闲inode和空闲block的块组group,然后在该块组的inode bitmap找一个空闲inode编号,最后把该inode编号赋值给inode->i_inoext4_add_nondir: 把dentry和inode对应的文件或目录添加到它父目录的ext4_dir_entry_2结构里
绑定dentry与inode的方法__d_set_inode_and_type:
static inline void __d_set_inode_and_type(struct dentry *dentry,
struct inode *inode,
unsigned type_flags)
{
unsigned flags;
dentry->d_inode = inode;
flags = READ_ONCE(dentry->d_flags);
flags &= ~(DCACHE_ENTRY_TYPE | DCACHE_FALLTHRU);
flags |= type_flags;
WRITE_ONCE(dentry->d_flags, flags);
}
对 dcache 的操作(lookup_slow)
通过上面可以知道对路径的查找过程,也是对 dcache 树的不断的追加、修改过程(即对于不存在于 dcache 的 dentry 节点,需要先通过 filename 找到其文件系统磁盘的 inode,然后建立内存 inode 及 dentry 结构,然后建立内存 dentry 到 inode 的关系),对于 lookup_slow 逻辑会涉及到如下操作 dcache 的逻辑:
- 分配 dentry,从 slab 分配器分配内存,初始化 dentry 对象
- 绑定 inode,关联 dentry 与 inode,并加入 dcache 树
- 处理别名,解决硬链接冲突
- 链接到父目录,将 dentry 加入父目录的
d_subdirs链表
1、d_alloc_parallel->d_alloc->__d_alloc
struct dentry *d_alloc(struct dentry * parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct dentry *dentry = __d_alloc(parent->d_sb, name);
if (!dentry)
return NULL;
dentry->d_flags |= DCACHE_RCUACCESS;
spin_lock(&parent->d_lock);
/*
* don't need child lock because it is not subject
* to concurrency here
*/
__dget_dlock(parent);
dentry->d_parent = parent; // 将新建节点的 dentry->d_parent 设置为 parent
list_add(&dentry->d_child, &parent->d_subdirs); // 将 dentry 加入父目录的 d_subdirs 链表
spin_unlock(&parent->d_lock);
return dentry;
}
struct dentry *__d_alloc(struct super_block *sb, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
char *dname;
int err;
dentry = kmem_cache_alloc(dentry_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dentry)
return NULL;
dentry->d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1] = 0;
if (unlikely(!name)) {
static const struct qstr anon = QSTR_INIT("/", 1);
name = &anon;
dname = dentry->d_iname;
} else if (name->len > DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1) {
size_t size = offsetof(struct external_name, name[1]);
struct external_name *p = kmalloc(size + name->len,
GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT);
if (!p) {
kmem_cache_free(dentry_cache, dentry);
return NULL;
}
atomic_set(&p->u.count, 1);
dname = p->name;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DCACHE_WORD_ACCESS))
kasan_unpoison_shadow(dname,
round_up(name->len + 1, sizeof(unsigned long)));
} else {
dname = dentry->d_iname;
}
dentry->d_name.len = name->len;
dentry->d_name.hash = name->hash;
memcpy(dname, name->name, name->len);
dname[name->len] = 0;
/* Make sure we always see the terminating NUL character */
smp_wmb();
dentry->d_name.name = dname;
dentry->d_lockref.count = 1;
dentry->d_flags = 0;
spin_lock_init(&dentry->d_lock);
seqcount_init(&dentry->d_seq);
dentry->d_inode = NULL;
dentry->d_parent = dentry;
dentry->d_sb = sb;
dentry->d_op = NULL;
dentry->d_fsdata = NULL;
INIT_HLIST_BL_NODE(&dentry->d_hash);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_lru);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_subdirs);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&dentry->d_u.d_alias);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_child);
d_set_d_op(dentry, dentry->d_sb->s_d_op);
if (dentry->d_op && dentry->d_op->d_init) {
err = dentry->d_op->d_init(dentry);
if (err) {
if (dname_external(dentry))
kfree(external_name(dentry));
kmem_cache_free(dentry_cache, dentry);
return NULL;
}
}
this_cpu_inc(nr_dentry);
return dentry;
}
2、d_splice_alias->__d_instantiate->__d_set_inode_and_type:将 dentry 和 inode 绑定,即将 inode 赋值给 dentry 的 d_inode 成员
void d_instantiate(struct dentry *entry, struct inode * inode)
{
BUG_ON(!hlist_unhashed(&entry->d_u.d_alias));
if (inode) {
security_d_instantiate(entry, inode);
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
__d_instantiate(entry, inode);
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
}
}
static void __d_instantiate(struct dentry *dentry, struct inode *inode)
{
unsigned add_flags = d_flags_for_inode(inode);
WARN_ON(d_in_lookup(dentry));
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
hlist_add_head(&dentry->d_u.d_alias, &inode->i_dentry);
raw_write_seqcount_begin(&dentry->d_seq);
__d_set_inode_and_type(dentry, inode, add_flags);
raw_write_seqcount_end(&dentry->d_seq);
fsnotify_update_flags(dentry);
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
}
static inline void __d_set_inode_and_type(struct dentry *dentry,
struct inode *inode,
unsigned type_flags)
{
unsigned flags;
// 设置 dentry 与 inode 的绑定关系
dentry->d_inode = inode;
flags = READ_ONCE(dentry->d_flags);
flags &= ~(DCACHE_ENTRY_TYPE | DCACHE_FALLTHRU);
flags |= type_flags;
WRITE_ONCE(dentry->d_flags, flags);
}
d_alloc_parallel的实现
d_alloc_parallel 函设计核心是通过无锁并发机制优化目录项(dentry)的分配与查找,完全在内存中操作,属于快速路径(fast path)的一部分
- 并行查找:通过 RCU(Read-Copy-Update)机制无锁遍历哈希桶,直接检查目标 dentry 是否已存在于父目录的哈希链表中
- 条件分配:若 dentry 不存在,则分配一个新 dentry 并尝试将其插入哈希链;若已存在,则直接返回现有 dentry(通过
res参数返回) - 无磁盘 I/O:整个过程仅操作内存中的 dentry 缓存,不触发文件系统底层的磁盘读取或复杂逻辑(如加载 inode)
为什么经常调用d_revalidate?
d_revalidate的实现如下,经常在各种*lookup*方法之后调用,其作用是什么?
//返回值:1表示有效
static inline int d_revalidate(struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags)
{
//NFS等
if (unlikely(dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_REVALIDATE))
//调用文件系统的d_revalidate方法
return dentry->d_op->d_revalidate(dentry, flags);
else
return 1; //大部分的系统,如ext4,都走到此
}
d_revalidate是 VFS中目录缓存(dcache)一致性保障的核心机制之一,作用是检查一个已经从目录缓存(dcache)中找到的目录项(dentry)是否仍然有效,防止进程使用过时或无效的缓存数据。为什么需要重新验证呢?目录缓存(dcache)是为了提升路径查找性能的内存缓存,缓存中的数据可能会过时,与磁盘上的真实情况不一致。例如,比如
- 文件被删除:另一个进程可能已经删除了这个文件
- 文件被重命名:另一个进程可能更改了文件名
- 权限被更改:文件的访问权限(rwx)可能已被修改
- 符号链接目标改变:符号链接指向的路径可能已更改
- 网络文件系统(如NFS, CIFS等):文件状态可能被网络上的其他客户端改变,服务器端的更改客户端可能不知道
如果内核不进行验证,直接使用过期的缓存数据,会导致应用程序看到错误的信息(如看到已删除的文件),或者违反权限控制(如访问了已无权限访问的文件)
此外,当d_revalidate验证失败表示dentry 已失效,调用者需要将此 dentry 从缓存中无效化(d_invalidate),并重新进行查找
d_revalidate是路径查找阶段的早期验证,用于提高效率,避免基于过时缓存继续操作。但是仍然无法避免d_revalidate之后出现了并发修改导致dentry失效的问题,内核会提供其他的校验机制来检测
open实现中的回退视角:局部回退 VFS 全局回退
思考一个问题,对路径/a/b/c/d/e的查找过程中,假设a、b都已经成功的使用RCU模式查找,此时c查找过程中使用RCU方式失败,那么回退之后的查询过程是如何的?
回到上面的walk_component函数,这里有一个容易被忽视的小细节:
static int walk_component(struct nameidata *nd, int flags)
{
struct path path;
struct inode *inode;
unsigned seq;
int err;
//lookup_fast
err = lookup_fast(nd, &path, &inode, &seq);
if (unlikely(err <= 0)) {
if (err < 0)
return err;
path.dentry = lookup_slow(&nd->last, nd->path.dentry,
nd->flags);
......
}
......
}
细节1:lookup_fast中包含了rcu与ref两种模式的实现,根据选项二选一,这里为什么不采用rcu回退到ref的策略?什么情况下会局部回退到ref?什么情况下会触发回退到全局ref(从头开始ref)?
细节2:lookup_fast的返回值err<=0决定了是全局回退到ref,还是局部回退到ref
unlazy_walk的意义到底是什么?
unlazy_walk函数的作用是:将路径查找从无锁、易失效的 RCU-walk 模式,安全原子地切换到稳定可靠的 Ref-walk 模式。这是一个模式切换器,确保在切换过程中,之前以 RCU 方式读取的所有关键数据(如dentry、mount点)保持有效,并通过获取引用和锁来固定其状态,防止在后续操作中被并发修改或释放。该函数成功返回0,失败返回-ECHILD
先简单分析下unlazy_walk的实现:
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/namei.c#L672
static int unlazy_walk(struct nameidata *nd)
{
struct dentry *parent = nd->path.dentry;
BUG_ON(!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU));
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU;
if (unlikely(!legitimize_links(nd)))
goto out2;
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->path, nd->seq)))
goto out1;
if (nd->root.mnt && !(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT)) {
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->root, nd->root_seq)))
goto out;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
BUG_ON(nd->inode != parent->d_inode);
return 0;
out2:
nd->path.mnt = NULL;
nd->path.dentry = NULL;
out1:
if (!(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT))
nd->root.mnt = NULL;
out:
rcu_read_unlock();
return -ECHILD;
}
/* path_put is needed afterwards regardless of success or failure */
static bool legitimize_path(struct nameidata *nd,
struct path *path, unsigned seq)
{
int res = __legitimize_mnt(path->mnt, nd->m_seq);
if (unlikely(res)) {
if (res > 0)
path->mnt = NULL;
path->dentry = NULL;
return false;
}
if (unlikely(!lockref_get_not_dead(&path->dentry->d_lockref))) {
path->dentry = NULL;
return false;
}
return !read_seqcount_retry(&path->dentry->d_seq, seq);
}
static bool legitimize_links(struct nameidata *nd)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nd->depth; i++) {
struct saved *last = nd->stack + i;
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &last->link, last->seq))) {
drop_links(nd);
nd->depth = i + 1;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
TODO
场景1:在 open 系统调用中,什么情况下会走到 unlazy_walk?这里分为局部回退与全局回退来说明
1、局部回退的情况(unlazy_walk 成功),当 unlazy_walk成功执行时,实现的是局部回退,即只有当前路径分量的查找从 RCU 模式切换到 Ref 模式,之前的查找进度保持不变,在整个open的实现中,有下面的case会触发局部回退:
1.1:DCache 查找未命中的情况,需要文件系统查找。即RCU 模式下在 dcache 中找不到目标 dentry,成功退出 RCU 模式后,在 Ref 模式下调用文件系统的 ->lookup方法继续查找(参考上面lookup_fast->lookup_slow的触发条件),这样只有当前分量重新查找,之前的分量进度保留
static int lookup_fast(struct nameidata *nd,
struct path *path, struct inode **inode,
unsigned *seqp)
{
......
// 在 lookup_fast 的 RCU 分支中
dentry = __d_lookup_rcu(parent, &nd->last, &seq);
if (unlikely(!dentry)) {
if (unlazy_walk(nd)) // 尝试局部回退
return -ECHILD; // 失败则全局回退
return 0; // 成功,触发上层调用 lookup_slow
}
......
}
1.2:符号链接解析需要阻塞操作,即文件系统的 ->get_link方法需要阻塞(如磁盘 I/O),所以这里退出 RCU 模式,在 Ref 模式下重新获取链接内容,局部的回退让符号链接解析在 Ref 模式下继续
static __always_inline
const char *get_link(struct nameidata *nd)
{
......
// 在 get_link 函数中
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
res = get(NULL, inode, &last->done);
if (res == ERR_PTR(-ECHILD)) {
if (unlikely(unlazy_walk(nd))) // 尝试局部回退
return ERR_PTR(-ECHILD);
res = get(dentry, inode, &last->done); // Ref模式下重试
}
......
}
}
2、需要全局回退的情况(unlazy_walk 调用失败),当 unlazy_walk失败时(返回 -ECHILD),触发全局回退,整个路径查找在 Ref 模式下重新开始(回退到path_openat),主要case如下:
2.1:序列号验证失败,检测到 dentry 在 RCU 读取期间被并发修改。unlazy_walk失败,返回 -ECHILD,触发全局回退
static bool legitimize_path(struct nameidata *nd,
struct path *path, unsigned seq)
{
......
// 在 legitimize_path 等函数中
if (read_seqcount_retry(&dentry->d_seq, seq)) {
// 无法安全退出 RCU 模式
return -ECHILD;
}
......
}
2.2:无法获取必要引用,即无法增加 dentry 或 mount 的引用计数。unlazy_walk失败,全局回退
static bool legitimize_path(struct nameidata *nd,
struct path *path, unsigned seq)
{
......
// 在 legitimize_path 中尝试获取引用
if (!dget(dentry)) {
// 引用获取失败,可能 dentry 正在被释放
return -ECHILD;
}
......
}
场景2:为什么 unlazy_walk 执行成功内核就可以(认为)安全地将 RCU 切换到 Ref模式?unlazy_walk成功意味着它完成了如下四类关键的安全保障步骤,确保从无锁的 RCU 模式安全过渡到有锁的 Ref 模式
1、数据一致性验证(序列号检查),检查在 RCU 模式下读取的 dentry、mount 点等数据的序列号是否变化。如果序列号未变,证明数据在读取期间没有被并发修改,可以安全使用
// 验证所有关键数据的序列号
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->path, nd->seq)))
goto fail;
if (nd->root.mnt && !(nd->flags & LOOKUP_ROOT)) {
if (unlikely(!legitimize_path(nd, &nd->root, nd->root_seq)))
goto fail;
}
2、资源生命周期保障(引用计数),增加所有关键数据结构的引用计数,防止这些资源在后续 Ref 模式操作中被意外释放,确保它们在整个 Ref 模式查找期间保持有效
// 在 legitimize_path 内部
dget(dentry); // 增加 dentry 引用计数
mntget(mnt); // 增加 mount 点引用计数
3、锁状态安全转换,在所有验证和引用获取完成后才释放 RCU 锁。确保在退出 RCU 保护之前,所有关键资源都已处于安全状态
rcu_read_unlock(); // 安全释放 RCU 读锁
4、模式标志更新,更新查找状态,标记现在处于 Ref 模式。后续操作基于 Ref 模式的规则执行(如可以获取锁、执行阻塞操作)
nd->flags &= ~LOOKUP_RCU; // 清除 RCU 标志
所以,unlazy_walk成功执行的本质就总结为如下两点:
- 数据有效性:序列号验证确保数据没有被并发修改
- 资源稳定性:引用计数确保资源不会被释放
这使得后续的 Ref 模式操作可以:
- 安全地获取锁(不会死锁,因为资源存在)
- 执行阻塞操作(如磁盘 I/O,因为资源被固定)
场景3:在link_path_walk中的片段:
if (unlikely(!d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry))) {
if (nd->flags & LOOKUP_RCU) {
if (unlazy_walk(nd)){
//unlazy_walk失败了
return -ECHILD;
}
//为什么在 unlazy_walk成功后,直接返回-ENOTDIR,而不是回退到ref-walk?
}
//直接返回错误:ENOTDIR
return -ENOTDIR;
}
......
疑问是为什么在 unlazy_walk成功后,直接返回-ENOTDIR,而不是回退到ref-walk?分两点回答:
1、错误条件的本质
d_can_lookup(nd->path.dentry)检查的是当前 dentry 是否是一个可以查找的目录。这个条件在短时间内不会改变:
- 如果 dentry 不是目录(例如是普通文件),它不会因为模式切换而变成目录
d_can_lookup函数检查的是 dentry 的固有属性,不是临时状态
2、unlazy_walk的目的:其主要目的不是改变 dentry 的性质,而是安全地退出 RCU 模式。在 RCU 模式下,数据读取是无锁的,可能看到不一致的状态。unlazy_walk确保在返回错误时,所有必要的锁和引用都已获取,避免资源泄漏或竞态条件
3、d_can_lookup错误返回的语义,-ENOTDIR 表示不是一个目录,这是一个永久性错误。即使切换到 ref-walk 模式重新检查,结果也不会改变;重试检查只会浪费 CPU 周期,不会改变结果
问题:能否不通过全局挂载表定位到挂载点的/节点?
TODO
__lookup_hash的实现及应用场景
TODO
小结:path walk的策略
前文描述了内核实现path walk的策略,首先 Kernel 会在 rcu-walk 模式下进入 lookup_fast 进行尝试,如果失败了那么就尝试就地转入 ref-walk,如果还是不行就回到 do_filp_open 从头开始。Kernel 在 ref-walk 模式下会首先在内存缓冲区查找相应的目标(lookup_fast),如果找不到就启动具体文件系统自己的 lookup 进行查找(lookup_slow)。注意,在 rcu-walk 模式下是不会进入 lookup_slow 的。如果这样都还找不到的话就一定是是出错了,那就报错返回吧,这时屏幕就会出现 No such file or directory
0x0 open中涉及到的mount操作
__follow_mount_rcufollow_mount- ` __lookup_mnt`
real_mount
0x08 参考
- open 系统调用(一)
- 走马观花: Linux 系统调用 open 七日游
- Open() 函数的内核追踪
- Linux Kernel 文件系统写 I/O 流程代码分析(二)
- linux 内核 open 文件流程
- 文件系统缓存
- Linux 的 VFS 实现 - 番外 [一] - dcache
- Linux Kernel 文件系统写 I/O 流程代码分析(一)
- vfs dentry cache 模块实现分析
- open 系统调用实现
- open(2) — Linux manual page
- Linux Open系统调用 篇二
- Linux Open系统调用 篇三
- Linux Open系统调用 篇四
- 图解 Binder:系统调用 open
- linux kernel 路径查询
- Parallel pathname lookups and the importance of testing