0x00 前言
Linux的IO 多路复用机制(I/O Multiplexing)是一种通过单个线程或进程同时管理多个 I/O 通道(如网络套接字、文件描述符)的机制,用来解决大量并发文件描述符fd场景下,如何快速发现哪些fd触发了事件(读/写)。为了解决遍历fds导致的性能浪费,内核提供了select、poll、epoll这几类机制,本文就以内核的角度来拆解下epoll机制的实现
本文代码基于 v4.11.6 版本
epoll 简单服务端示例
void epoll_server_run(){
//....
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
struct sockaddr_in srv_addr;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr;
struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENTS];
listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
set_sockaddr(&srv_addr);
bind(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr *)&srv_addr, sizeof(srv_addr));
//注意需要设置为NON-BLOCK
setnonblocking(listen_sock);
listen(listen_sock, MAX_CONN);
//1. 创建epoll fd 并对listener fd加入监听
epfd = epoll_create(1);
epoll_ctl_add(epfd, listen_sock, EPOLLIN | EPOLLOUT | EPOLLET);
socklen = sizeof(cli_addr);
for (;;) {
//2. 调用epoll_wait并等待返回就绪事件
nfds = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
//3. 处理就绪事件(读、写、退出等),要区分是否为listener fd或者accept fd
for (i = 0; i < nfds; i++) {
if (events[i].data.fd == listen_sock) {
/* handle new connection */
// 若为listenfd,在ET模式下
// 用 while 循环包裹住 accept 调用,处理完 TCP 就绪队列中的所有连接后再退出循环
// 如何知道是否处理完就绪队列中的所有连接呢?
// accept 返回 -1 并且 errno 设置为 EAGAIN 就表示所有连接都处理完
// 当然读/写在ET模式下也是一样
//读:只要可读, 就一直读, 直到返回 0, 或者 errno = EAGAIN
//写:只要可写, 就一直写, 直到数据发送完, 或者 errno = EAGAIN
while(1){
conn_sock =
accept(listen_sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr,
&socklen);
if (conn_sock == -1) {
if ((errno == EAGAIN) || (errno == EWOULDBLOCK)) {
break; // We have processed all incoming connections.
} else {
perror("accept");
break;
}
}
inet_ntop(AF_INET, (char *)&(cli_addr.sin_addr),
buf, sizeof(cli_addr));
printf("[+] connected with %s:%d\n", buf,
ntohs(cli_addr.sin_port));
setnonblocking(conn_sock);
epoll_ctl_add(epfd, conn_sock,
EPOLLIN | EPOLLET | EPOLLRDHUP |
EPOLLHUP);
//check epoll_ctl_add return value
}
} else if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
/* handle EPOLLIN event */
for (;;) {
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
n = read(events[i].data.fd, buf,
sizeof(buf));
if (n <= 0 /* || errno == EAGAIN */ ) {
break;
} else {
printf("[+] data: %s\n", buf);
write(events[i].data.fd, buf,
strlen(buf));
}
}
} else {
printf("[+] unexpected\n");
}
/* check if the connection is closing */
if (events[i].events & (EPOLLRDHUP | EPOLLHUP)) {
printf("[+] connection closed\n");
// 将fd移除epoll监听
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL,
events[i].data.fd, NULL);
close(events[i].data.fd);
continue;
}
}
}
}
0x01 前置知识 && 问题
1、struct socket/sock/sock_common等结构与struct file关系
2、struct sock的等待队列sock->wq的作用及何时被唤醒、唤醒条件是什么?这里分为两种socket,其一是listener fd,其二是通过accept拿到的fd
3、epoll(通过epoll_create创建)的等待队列的作用及机制,调用epoll_wait系统调用的进程何时主动让出CPU(睡眠)?何时被唤醒?唤醒之后的流程是什么?
4、同步阻塞IO机制下的收包流程,在软中断核心逻辑中,当数据包送到某个socket(sock)关联的接收队列上时,内核是如何通知应用层有数据到达的?参考此文深入理解高性能网络开发路上的绊脚石 - 同步阻塞网络 IO
5、内核协议栈的收包过程,前文已描述
6、epoll机制下,各个内核struct之间的关系以及回调函数(赋值为何种函数)
7、epoll机制下,为何要使用红黑树而不是hashtable?
struct sock/socket/sock_comm
struct sock结构关联的等待队列socket_wq,包含了内核等待队列的头节点:
struct socket_wq {
/* Note: wait MUST be first field of socket_wq */
wait_queue_head_t wait;
......
};
epoll的API
1、epoll_create:创建一个 epoll 对象,返回fd
2、epoll_ctl:向 epoll 对象中添加要管理的连接,在代码示例中主要涉及到操作两类fd,第一类是listnerfd(服务端绑定socket),第二类是acceptfd(客户端新连接)
3、epoll_wait:等待其管理的连接上的 IO 事件
0x02 epoll_create实现
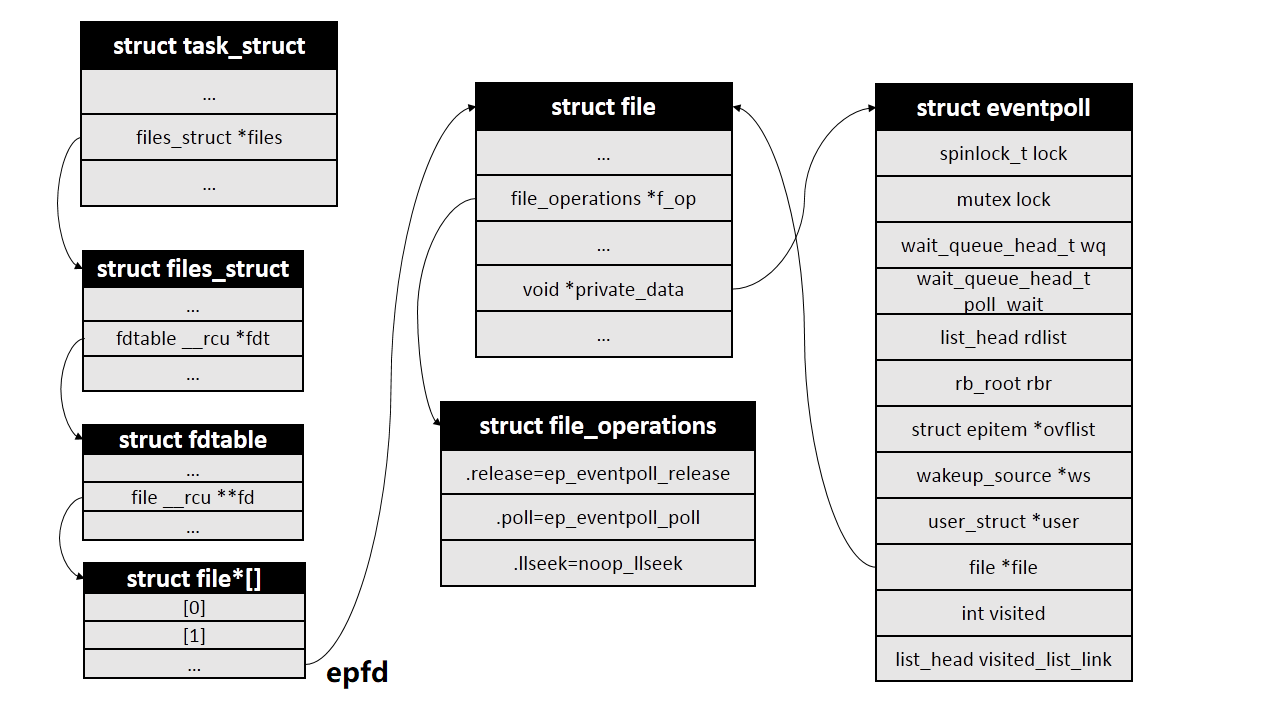
在用户进程调用 epoll_create 函数时,内核会创建一个 struct eventpoll 的内核结构对象,注意epoll_create成功时会返回一个fd,内核也会把它关联到当前进程的已打开文件列表fdtable中
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L1793
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags)
{
int error, fd;
struct eventpoll *ep = NULL;
struct file *file;
// ...
//1. 创建一个 eventpoll 对象
error = ep_alloc(&ep);
if (error < 0)
return error;
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (fd < 0) {
error = fd;
goto out_free_ep;
}
file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
error = PTR_ERR(file);
goto out_free_fd;
}
ep->file = file;
//安装fd
fd_install(fd, file);
return fd;
//....
}
eventpoll结构
struct eventpoll的定义如下,这里重点看下面几个成员:
wait_queue_head_t wq:epoll_wait/sys_epoll_wait用到的等待队列(链表),内核软中断运行过程中,当数据就绪的时候会通过此wq来找到阻塞在epoll对象上的用户进程struct list_head rdllist:接收就绪的描述符都会放到这里,即存放就绪的描述符的链表。当有连接就绪的时候,内核会把就绪的连接放到rdllist链表里。这样应用进程只需要遍历rdllist链表就能找出就绪进程,而不用去遍历整棵树struct rb_root rbr:每个epoll对象中都有一颗红黑树,为了支持对海量连接的高效查找、插入和删除,eventpoll内部使用了一棵红黑树并通过这棵树来管理用户进程下添加进来的所有 socket 连接(红黑树的key为fd)
struct eventpoll {
/* Protect the access to this structure */
spinlock_t lock;
/*
* This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations.
*/
struct mutex mtx;
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
/* List of ready file descriptors */
struct list_head rdllist;
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root rbr;
/*
* This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that
* happened while transferring ready events to userspace w/out
* holding ->lock.
*/
struct epitem *ovflist;
/* wakeup_source used when ep_scan_ready_list is running */
struct wakeup_source *ws;
/* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */
struct user_struct *user;
struct file *file;
/* used to optimize loop detection check */
int visited;
struct list_head visited_list_link;
};
ep_alloc的实现
ep_alloc的实现如下,其中包含了上面列出的重要成员的初始化工作
static int ep_alloc(struct eventpoll **pep)
{
int error;
struct user_struct *user;
struct eventpoll *ep;
user = get_current_user();
error = -ENOMEM;
//1. 申请 epollevent 内存
ep = kzalloc(sizeof(*ep), GFP_KERNEL);
if (unlikely(!ep))
goto free_uid;
spin_lock_init(&ep->lock);
mutex_init(&ep->mtx);
//2. 初始化等待队列头
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->wq);
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->poll_wait);
//3. 初始化就绪列表
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ep->rdllist);
//4. 初始化红黑树指针
ep->rbr = RB_ROOT;
ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
ep->user = user;
*pep = ep;
return 0;
free_uid:
free_uid(user);
return error;
}
至此,完成了epoll机制最核心的管理结构struct eventpoll的创建及初始化工作,进程打开的epfd在内核的关系如下图:
0x03 服务端accept新连接(fd)
前文Linux 内核之旅(十二):内核视角下的三次握手已经介绍了服务端accept的内核实现,这里再回顾下accept时struct socket 内核结构的创建、以及和内核已存在的struct sock关联的主要过程:
- 初始化
struct socket对象,并使用listnerfd关联的socket信息初始化(如type、ops等) - 为新
struct socket对象申请struct file结构,关联sock->file指针,在accept方法里会调用sock_alloc_file函数来申请内存并初始化,该指针的主要目的是通过task_struct->fdtable(fd)->file(private)->socket->sock....,即通过进程+fd找到对应的struct socket/sock结构 - 在
sock_alloc_file->alloc_file函数中,会把socket_file_ops赋值给新建的socket->file->f_op - 调用
sock->ops->accept(即inet_accept)接收新连接 - 调用
fd_install将accept返回的新连接fd加到当前进程打开文件列表fdtable
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(accept4, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, upeer_sockaddr,
int __user *, upeer_addrlen, int, flags)
{
struct socket *sock, *newsock;
//根据 fd 查找到监听的 socket
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
//1、申请并初始化新的 socket
newsock = sock_alloc();
//2、把 listen 状态的 socket 对象(关联AF_INET)上的协议操作函数集合 ops等赋值给新的 socket
newsock->type = sock->type;
newsock->ops = sock->ops;
//3、 申请新的 file 对象,并设置到新 socket 上
// sock_alloc_file最终会完成 sock->file = file
//
newfile = sock_alloc_file(newsock, flags, sock->sk->sk_prot_creator->name);
......
//4、 接收连接
err = sock->ops->accept(sock, newsock, sock->file->f_flags);
//5、 添加新文件到当前进程的打开文件列表
fd_install(newfd, newfile);
新建立socket/file结构
上文说到,在accept里创建的新 struct socket 成员file,即struct file的f_op成员(类型为struct file_operations),被赋值为下面socket_file_ops的方法:
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read_iter = sock_read_iter,
.write_iter = sock_write_iter,
.poll = sock_poll, //记住这个sock_poll函数
.unlocked_ioctl = sock_ioctl,
.mmap = sock_mmap,
.release = sock_close,
.fasync = sock_fasync,
.sendpage = sock_sendpage,
.splice_write = generic_splice_sendpage,
.splice_read = sock_splice_read,
};
记住上面这个sock_poll函数:在accept里创建的新 socket 里的 file->f_op->poll 函数指向的是 sock_poll
接收新连接
这里只列举sock->ops->accept中几个关键赋值结点:
内核在三次握手完成时会从全连接队列(已完成TCP连接建立)中取出,关联函数为inet_csk_accept,从这里可以看到,这个struct sock对象sk是内核在三次握手完成就已经创建完成的(这点与系统调用socket的流程不一样),在系统调用accept中只是将上层的struct socket与这个sk做了关联而已(实现函数为sock_graft)
还需要记住的一个细节,内核创建struct sock结构时同样是调用sock_init_data完成,注意其中的sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable;这段代码,这段代码的意义是告诉内核,当前的sk上有数据了,该怎么处理(调用sock_def_readable回调函数)
struct sock *inet_csk_accept(struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err, bool kern)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct request_sock_queue *queue = &icsk->icsk_accept_queue;
struct request_sock *req;
struct sock *newsk;
// ......
/* 从已完成连接队列中移除 */
req = reqsk_queue_remove(queue, sk);
/* 设置新控制块指针 */
/* sk为 struct sock *sk 类型*/
newsk = req->sk;
// ......
/* 返回找到的连接控制块 */
return newsk;
}
void sock_init_data(struct socket *sock, struct sock *sk)
{
sk->sk_wq = NULL;
sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable;
}
0x04 epoll_ctl 实现:操作fd
这一步是epoll机制的核心,在上面的示例代码中,通过epoll_ctl操作网络连接socket fd的内核大致过程描述如下:
- 分配一个红黑树节点对象
epitem - 添加等待事件到 socket 的等待队列中,其回调函数是
ep_poll_callback - 将
epitem插入到 epoll 对象管理结构eventpoll的红黑树
相关数据结构
epoll_ctl操作eventpoll对象时会涉及到多个数据结构:
struct epoll_filefdstruct epitemep_pqueue:临时粘合剂,传递epitem并注册回调到poll_tablestruct poll_table:标准化桥梁,触发文件操作并执行回调创建eppoll_entrystruct eppoll_entry:持久枢纽,绑定sock、sock等待队列与epitem,实现事件驱动的高效通知
其中,ep_pqueue、poll_table和eppoll_entry这三者完成了初始化 -> 注册 -> 持久监听的高效机制,非常优雅(这三者关系见附录描述)
1、epitem,从其成员定义易知,这就是红黑树的元素节点
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L141
struct epitem {
union {
/* RB tree node links this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */
struct rb_node rbn;
/* Used to free the struct epitem */
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */
struct list_head rdllink;
/*
* Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
* single linked chain of items.
*/
struct epitem *next;
/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
int nwait;
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct list_head pwqlist;
/* The "container" of this item */
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
struct list_head fllink;
/* wakeup_source used when EPOLLWAKEUP is set */
struct wakeup_source __rcu *ws;
/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
struct epoll_event event;
};
2、eppoll_entry
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L230
struct eppoll_entry {
/* List header used to link this structure to the "struct epitem" */
struct list_head llink;
/* The "base" pointer is set to the container "struct epitem" */
struct epitem *base;
/*
* Wait queue item that will be linked to the target file wait
* queue head.
*/
wait_queue_t wait;
/* The wait queue head that linked the "wait" wait queue item */
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};
3、poll_table
typedef struct poll_table_struct {
poll_queue_proc _qproc;
unsigned long _key;
} poll_table;
4、ep_pqueue
/* Wrapper struct used by poll queueing */
struct ep_pqueue {
poll_table pt;
struct epitem *epi;
};
epoll_ctl系统调用
epoll_ctl的主要过程如下:
- 根据传入参数
ebpf、fd找到eventpoll、socket相关的内核对象 - 调用
ep_*完成fd关联的socket/sock结构的注册(等待队列的事件就绪回调函数) - 操作rbtree
对于EPOLL_CTL_ADD选项而言,主要调用函数链为epoll_ctl()->ep_insert()
// epoll_ctl的参数包括两个fd
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
struct epoll_event __user *, event)
{
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct file *file, *tfile;
//根据 epfd 找到 eventpoll 内核对象
file = fget(epfd);
ep = file->private_data; // 又一次看到了private_data
//根据 socket 句柄号, 找到其 file 内核对象
tfile = fget(fd);
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
// for add
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);
} else
error = -EEXIST;
clear_tfile_check_list();
break;
//.....
}
EPOLL_CTL_ADD的过程(重点)
ep_insert又是epoll_ctl函数的核心实现过程,所有的注册都是在这个函数中完成的。ep_insert的核心逻辑:
- 将需要监听的fd(不区分listenfd或acceptfd)包装为
epitem对象,这个结构是作为eventpoll管理结构红黑树上的某个树节点 ep_insert的最终目的是让告诉内核,这个fd上面发生了事件(读写错误等),要怎么处理。所以涉及到事件及事件的回调方法注册,这里还包含了一个隐藏的细节,当fd有事件发生时,还需要具备(内核)能够通过这个fd找到其归属的task_struct(进程),然后唤醒它,让它来干活(处理连接)了- 根据上面的描述,所以
ep_insert就会利用内核的机制(如waitqueue)把上面的工作完成 - 内核还需要考虑,如何在海量fd的集合中快速的定位到
fd节点(epoll_ctl针对fd的CRUD操作)
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep,
struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd)
{
//1、分配并初始化 epitem
struct epitem *epi; //分配一个epi对象
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
return -ENOMEM;
//对分配的epi进行初始化
//epi->ffd中存了句柄号和struct file对象地址
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
// 设置epitem的ep成员指向eventpoll管理对象
epi->ep = ep;
// 设置epitem的ffd 指向要添加的fd 相关对象
ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
//2、设置 socket 等待队列
//定义并初始化 ep_pqueue 对象
struct ep_pqueue epq;
epq.epi = epi;
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
//调用 ep_ptable_queue_proc 注册回调函数
//实际注入的函数为 ep_poll_callback
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt);
......
//3、将epi插入到 eventpoll 对象中的红黑树中
ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi);
......
}
对于上面的ep_insert的实现代码,这里拆开来分析:
1、初始化epitem,建立成员关系
// 参数ffd为 新建的epitem成员
// 参数file/fd为 要添加监听的socket成员(epoll_ctl的操作对象)
static inline void ep_set_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *ffd,
struct file *file, int fd)
{
ffd->file = file;
ffd->fd = fd;
}
2、设置epoll_ctl监控fd(socket)对象的struct socket/sock的等待队列(非常重要)
在创建 epitem 并初始化之后,ep_insert 会设置 socket 对象上的等待任务队列,并把函数 ep_poll_callback 设置为数据就绪时候的回调函数,这里需要搞懂几个细节
init_poll_funcptr的参数是什么?ep_ptable_queue_proc是什么?- 内核设计
struct ep_pqueue epq这个结构的意义是什么?
static int ep_insert(...)
{
...
// 新建一个 ep_pqueue 对象
struct ep_pqueue epq;
// 将新建的epitem挂在 epq上
// 记住ep_pqueue结构包含了两个成员:
// 1、poll_table pt
// 2、struct epitem *epi
epq.epi = epi;
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
...
//ep_item_poll:核心
//作用:调用 ep_ptable_queue_proc 注册回调函数(实际注入的函数为 ep_poll_callback)
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt);
// ......
}
static inline void init_poll_funcptr(poll_table *pt,
poll_queue_proc qproc)
{
pt->_qproc = qproc; // 这里的qproc就是ep_ptable_queue_proc
pt->_key = ~0UL; /* all events enabled */
}
在ep_insert的实现中,ep_item_poll函数在init_poll_funcptr之后被调用,注意它的参数是struct ep_pqueue的两个成员
ep_item_poll中,走到epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll调用,对应的函数是sock_poll,这个epi是关联epoll_ctl操作的那个fdsock_poll中,走到sock->ops->poll调用,对应的函数是tcp_polltcp_poll中,走到sock_poll_wait调用
static inline unsigned int ep_item_poll(struct epitem *epi, poll_table *pt)
{
//......
pt->_key = epi->event.events;
// 重要:epi->ffd.file->f_op 找到被操作的fd的f_op成员
// sock_poll
return epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, pt) & epi->event.events;
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/net/socket.c#L1041
static unsigned int sock_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait)
{
struct socket *sock;
sock = file->private_data;
// ......
//tcp_poll
return sock->ops->poll(file, sock, wait);
}
unsigned int tcp_poll(struct file *file, struct socket *sock, poll_table *wait)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
// ......
sock_poll_wait(file, sk_sleep(sk), wait);
}
在进入sock_poll_wait函数之前,先看下sk_sleep(sk)获取的是啥结构?从实现来看,返回结果为wait_queue_head_t *结构,在此函数它获取了 struct sock 对象下的等待队列列表头 wait_queue_head_t,待会等待队列项就插入这里,还是需要强调两点:
- 这个
struct sock是epoll_ctl函数操作的目标fd(listenfd或acceptfd) - 这个等待队列是 socket/sock 的等待队列,非 epoll 对象的等待队列,二者的作用完全不同(见附录说明)
static inline wait_queue_head_t *sk_sleep(struct sock *sk)
{
BUILD_BUG_ON(offsetof(struct socket_wq, wait) != 0);
return &rcu_dereference_raw(sk->sk_wq)->wait;
}
分析下sock_poll_wait->poll_wait的实现(记住调用路径为ep_item_poll->sock_poll->tcp_poll->sock_poll_wait),其参数为:
file *filp:p->_qproc的回调参数之一,需要操作哪个fd的file结构wait_queue_head_t *wait_address:等待队列的头部poll_table *p:需要使用到p->_qproc成员
终于在poll_wait中看到调用了前面在init_poll_funcptr函数中注册的回调函数ep_ptable_queue_proc
static inline void sock_poll_wait(struct file *filp,
wait_queue_head_t *wait_address, poll_table *p)
{
//poll_wait
poll_wait(filp, wait_address, p);
}
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p)
{
if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address)
// qproc 为函数指针,
// 在前面的 init_poll_funcptr 调用时被设置成了 ep_ptable_queue_proc 函数
// 调用其实是ep_ptable_queue_proc方法
p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}
所以,ep_insert最终的逻辑是在 ep_ptable_queue_proc 函数中,新建了一个等待队列项,并注册其回调函数为 ep_poll_callback 函数,然后再将这个等待项添加到fd关联的 socket 的等待队列中
继续分析,回调函数ep_ptable_queue_proc真正完成了socket等待队列的初始化及添加等工作,注意到参数whead是socket等待队列的头结点,等待队列项最终会通过whead插入
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,
poll_table *pt)
{
//新建一个eppoll_entry对象
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
f (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
//初始化回调方法
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
//将ep_poll_callback放入socket的等待队列whead(注意不是epoll的等待队列)
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
}
//....
}
ep_ptable_queue_proc调用init_waitqueue_func_entry初始化一个等待队列项,等待队列项中仅仅只设置了回调函数 q->func 为 ep_poll_callback,其定义在ep_poll_callback
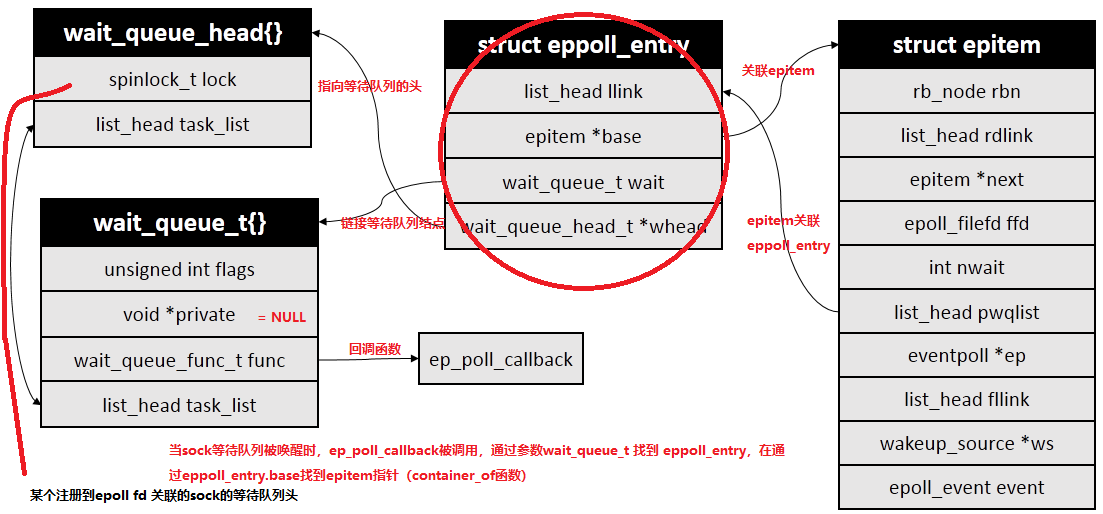
在内核软中断ksoftirqd将数据收到 socket 的接收队列后,内核会唤醒这个socket等待队列上的所有项,会通过注册的这个 ep_poll_callback 函数来回调(依次调用其注册的回调函数),进而通知到 epoll 对象
此外,这里思考下为何在epoll机制下的init_waitqqueue_func_entry中q->private要设置为NULL?首先这个private的意义是的内核实现等待队列机制中,当等待条件可能就绪时内核要唤醒的进程结构task_struct,但是在epoll机制中,socket是由epoll统一管理的,不需要在一个 socket 就绪的时候就唤醒进程(这样效率也极低),所以这里的 q->private 没意义就设置成了 NULL
static inline void init_waitqqueue_func_entry(
wait_queue_t *q, wait_queue_func_t func)
{
q->flags = 0;
// 这里为什么是NULL?
q->private = NULL;
//ep_poll_callback 注册到 wait_queue_t对象上
//有数据到达的时候调用 q->func
q->func = func;
}
3、将epitem对象插入epoll的红黑树
分配完 epitem 对象后,最后通过ep_rbtree_insert函数把它插入到红黑树eventpoll.rbr中,注意eventpoll红黑树的key为epitem.ffd(即epoll_ctl操作的fd)
static void ep_rbtree_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{
int kcmp;
struct rb_node **p = &ep->rbr.rb_node, *parent = NULL;
struct epitem *epic;
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
epic = rb_entry(parent, struct epitem, rbn);
kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&epi->ffd, &epic->ffd);
if (kcmp > 0)
p = &parent->rb_right;
else
p = &parent->rb_left;
}
rb_link_node(&epi->rbn, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
}
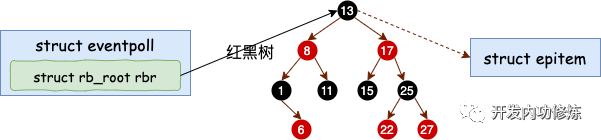
总结下epoll_ctl(ADD)的过程:
- 建立epoll机制的事件结构,并为其建立关联关系(这样某个
sk上有数据到达时,内核可以通过此sk找到对应的fd,从而告知epoll哪些fd上有事件发生了) - 为操作参数fd关联的socket的等待队列,注册等待队列项及数据就绪时候的回调函数
- 操作eventpoll的红黑树,变更信息
0x05 epoll_wait实现:等待就绪connection
epoll_wait 系统调用的核心流程如下,核心调用链为sys_epoll_wait->ep_poll
epoll_wait的主要工作流程是它会检查 eventpoll->rdllist 链表里有无数据,有数据就返回,没有数据就创建一个等待队列项,将其添加到 eventpoll 的等待队列上,然后把自己阻塞掉(让出CPU),等待唤醒重复上述过程
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,
int, maxevents, int, timeout)
{
int error;
struct fd f;
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
f = fdget(epfd);
if (!f.file)
return -EBADF;
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the fd
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file.
*/
error = -EINVAL;
if (!is_file_epoll(f.file))
goto error_fput;
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = f.file->private_data;
/* Time to fish for events ... */
error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);
//.....
}
epoll_wait的核心工作都在ep_poll中完成,ep_poll的实现亦是一个典型的等待-唤醒模式
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0;
unsigned long flags;
u64 slack = 0;
// 定义一个等待队列
wait_queue_t wait;
ktime_t expires, *to = NULL;
//.......
fetch_events:
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
//1、判断就绪队列上有没有事件就绪
if (!ep_events_available(ep)) {
//2、定义等待事件并关联当前进程(current为当前进程)
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
//3、 把新 waitqueue 添加到 epoll->wq 链表(eventpoll的等待队列)里
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
//4、启动等待-唤醒 循环机制
for (;;) {
// 将当前进程状态设置为可打断状态
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
//5、current进入CPU切换前,先检查唤醒事件是否满足
// 满足则退出等待
// 不满足继续执行,让出CPU(进程调度切换)
if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out)
break;
if (signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
//6、让出CPU 主动进入睡眠状态
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS))
timed_out = 1;
//7、说明被唤醒了,拿到CPU的控制权,继续循环(检测等待条件是否满足....)
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
}
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
}
check_events:
/* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
* more luck.
*/
if (!res && eavail &&
!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && !timed_out)
goto fetch_events;
return res;
}
上面对ep_poll的核心流程都加了注释,这里再拆解下步骤:
1、判断就绪队列上有没有事件就绪
在ep_poll中首先调用 ep_events_available 来判断就绪链表eventpoll.rdllist中是否有可处理(已就绪)IO的事件
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L374
static inline int ep_events_available(struct eventpoll *ep)
{
return !list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
}
2、初始化定义等待队列事件(wait_queue_t结构)并关联当前进程current
当检测rdllist上没有已就绪的连接时,那就使用内核的等待队列把当前进程current挂到等待队列waitqueue上,此时epoll进程也会被阻塞
static inline void init_waitqueue_entry(wait_queue_t *q, struct task_struct *p)
{
q->flags = 0;
q->private = p; //current
q->func = default_wake_function; //等待被唤醒时的调用函数为default_wake_function
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/sched/core.c#L3665
int default_wake_function(wait_queue_t *curr, unsigned mode, int wake_flags,
void *key)
{
return try_to_wake_up(curr->private, mode, wake_flags);
}
3、添加等待队列结构wait_queue_t到eventpoll的等待队列wq中,注意这里的wait->flags是被强行加上了一个WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE参数的,WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE的作用见下文
static inline void __add_wait_queue_exclusive(wait_queue_head_t *q,
wait_queue_t *wait)
{
wait->flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE; //注意这个WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE
__add_wait_queue(q, wait);
}
4-5、等待-唤醒机制的经典循环以及唤醒时再检测
6、当前进程主动调用schedule让出CPU(schedule_hrtimeout_range),主动进入睡眠状态,调度流程可以参考前文
int __sched schedule_hrtimeout_range(ktime_t *expires,
unsigned long delta, const enum hrtimer_mode mode)
{
return schedule_hrtimeout_range_clock(
expires, delta, mode, CLOCK_MONOTONIC);
}
int __sched schedule_hrtimeout_range_clock(...)
{
//在 schedule 中选择下一个进程调度
schedule();
...
}
static void __sched __schedule(void)
{
next = pick_next_task(rq);
...
context_switch(rq, prev, next);
}
先埋个问题:这里epoll等待队列的唤醒的逻辑是由谁完成的?
0x06 connection到达后的流程
本节将分析下软中断softirq是如何处理协议栈数据以及处理完之后依次进入各个回调函数(包括唤醒阻塞等待在epoll_wait上的进程),最后通知到用户进程的
- 内核从协议栈收到数据之后完成的事情
- 内核如何通知上层应用数据就绪了
- 内核通知应用层的机制(epoll)
- ET/LT模式在内核层面的区别
- epoll惊群及解决
如何根据sk(有数据)找到epitem/eventpoll结构?
/* Get the "struct epitem" from a wait queue pointer */
static inline struct epitem *ep_item_from_wait(wait_queue_t *p)
{
return container_of(p, struct eppoll_entry, wait)->base;
}
epoll机制下的两类等待队列
- 等待队列1:当
epoll_ctl执行注册监听fd时,内核为每一个 socket关联的sock 成员上都添加了一个等待队列项 - 等待队列2:当
epoll_wait运行时,在eventpoll对象上添加了等待队列元素
唤醒1:协议栈数据到达,唤醒sock/socket的等待队列
回想下软中断线程softirqd接收数据的处理逻辑,三次握手完成后最终会根据数据包中的ip与端口信息寻找到对应的sk结构(struct sock),然后把数据挂在sk.sk_receive_queue即sock结构关联的接收队列上,这段核心逻辑位于tcp_v4_rcv->tcp_v4_do_rcv->tcp_rcv_established->tcp_queue_rcv
1、内核对已建立连接sock数据的处理,这里只关注如下调用链(正常有序数据包接收)
tcp_v4_rcv:处理从 IP 层传入的 TCP 数据包,完成基础校验、套接字查找和队列分发tcp_v4_do_rcv:根据套接字的状态(TCP_ESTABLISHED、TCP_LISTEN等)分发到具体处理逻辑tcp_rcv_established:处理已建立连接的数据包tcp_queue_rcv:将sk_buff加入套接字(sock)的sk_receive_queue,供应用读取tcp_data_queue:在慢速路径中处理乱序、窗口外数据等复杂场景
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c#L1605
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct sock *sk;
......
th = tcp_hdr(skb); //获取tcp header
iph = ip_hdr(skb); //获取ip header
//1、根据数据包 header 中的 ip、端口信息查找到对应的sock结构
sk = __inet_lookup_skb(&tcp_hashinfo, skb, __tcp_hdrlen(th), th->source,
th->dest, &refcounted);
......
//sock 未被用户锁定
if (!sock_owned_by_user(sk)) {
{
if (!tcp_prequeue(sk, skb))
//2、go tcp_v4_do_rcv
ret = tcp_v4_do_rcv(sk, skb);
}
}
......
}
//tcp_v4_do_rcv
int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_ESTABLISHED) {
// TCP_ESTABLISHED:执行连接状态下的数据处理
// 暂时只关注这个状态下的数据传输
if (tcp_rcv_established(sk, skb, tcp_hdr(skb), skb->len)) {
......
}
return 0;
}
//其它非 ESTABLISH 状态的数据包处理
......
}
//tcp_rcv_established:非常复杂,基于TCP FSM处理
int tcp_rcv_established(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct tcphdr *th, unsigned int len)
{
......
// 1、调用 tcp_queue_rcv ,将接收数据放到 sock 的接收队列sk_receive_queue
eaten = tcp_queue_rcv(sk, skb, tcp_header_len,
&fragstolen);
......
// 2、数据 ready,唤醒 sock 上阻塞掉的进程
sk->sk_data_ready(sk, 0);
......
}
//tcp_queue_rcv
static int __must_check tcp_queue_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, int hdrlen,
bool *fragstolen)
{
//1、把接收到的数据放到 sock 的接收队列的尾部
if (!eaten) {
__skb_queue_tail(&sk->sk_receive_queue, skb);
skb_set_owner_r(skb, sk);
}
return eaten;
}
2、对sk->sk_data_ready的处理,查找数据就绪时的回调函数,在前文 accept 函数创建 socket 并关联内核sock 这个流程里提到的 sock_init_data 函数,在该函数中会设置 sk_data_ready 为 sock_def_readable 函数,这就是默认的数据就绪处理函数,当某个 socket/sock 上数据就绪时候,内核将以 sock_def_readable 这个函数为入口,找到 epoll_ctl 添加 socket/fd 时在其上设置的回调函数 ep_poll_callback,接着就会进入ep_poll_callback的流程
先回看下,上文介绍epoll_ctl内核实现时,最终会调用poll_wait,在poll_wait中会调用p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p)即ep_ptable_queue_proc函数,如下代码:
在ep_ptable_queue_proc中会把一个fd关联的eppoll_entry对象,挂到该fd关联的sock结构的等待队列里面(简单理解eppoll_entry对象就是一个sock等待队列waitqueue的一个表项,其回调函数为ep_poll_callback)
// 参数whead 来自于fd关联的sock对象的等待队列头: (sk->sk_wq)->wait
// 在ep_ptable_queue_proc会把新建的eppoll_entry对象挂到上面这个等待队列链表里面
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead, poll_table *pt)
{
//新建一个eppoll_entry对象
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
f (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
//初始化pwq(eppoll_entry对象)回调方法
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
//将ep_poll_callback放入socket的等待队列whead(注意不是epoll的等待队列)
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
}
//....
}
// 初始化等待队列项wait_queue_t
static inline void
init_waitqueue_func_entry(wait_queue_t *q, wait_queue_func_t func)
{
q->flags = 0;
q->private = NULL; //注意!这里是NULL
q->func = func; // 这里是ep_poll_callback
}
// 追加到等待队列的成员task_list上
static inline void __add_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *head, wait_queue_t *new)
{
list_add(&new->task_list, &head->task_list);
}
当内核调用 tcp_queue_rcv 完成数据接收后,接着再调用 sk->sk_data_ready 来唤醒在 sock.sk_wq 等待队列上等待的用户进程。前面已经介绍过在sock_init_data函数中的这段代码sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable,先看下sock_def_readable的实现:
static void sock_def_readable(struct sock *sk, int len)
{
struct socket_wq *wq;
rcu_read_lock();
wq = rcu_dereference(sk->sk_wq);
//判断等待队列不为空
if (skwq_has_sleeper(wq))
//执行等待队列项上的回调函数
wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll(&wq->wait, POLLIN | POLLPRI |
POLLRDNORM | POLLRDBAND);
sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_WAITD, POLL_IN);
rcu_read_unlock();
}
sock_def_readable函数中,skwq_has_sleeper这里会检测sk->sk_wq及sock的等待队列上是否为空!list_empty(&q->task_list)
这里特别注明一点:对上面代码中的skwq_has_sleeper函数的实现,本质是判断 fd/socket/sock关联的等待队列成员task_list上是有不为空!list_empty(&q->task_list),分为两种情况:
- 对于同步+阻塞fd场景下,
recvfrom系统调用在内核的实现,如何无数据可读时,是会把当前进程挂在sock等待队列上(相关内核函数sk_wait_data的实现);唤醒时会唤醒睡眠的进程 - 对于epoll+非阻塞fd 场景下,从
ep_ptable_queue_proc函数实现可知并不会把current挂到sock的等待队列上去(q->private = NULL),那么唤醒的逻辑也只是检查 sock 等待队列是否为空,并不一定有进程阻塞。所以当判断sock等待队列不为空,在唤醒操作wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll中只是会进入到 sock 等待队列项上设置的回调函数,并没有唤醒进程的操作,相对第一种情况是非常高效的
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/include/linux/wait.h#L106
static inline int waitqueue_active(wait_queue_head_t *q)
{
return !list_empty(&q->task_list);
}
static inline bool wq_has_sleeper(wait_queue_head_t *wq)
{
smp_mb();
return waitqueue_active(wq);
}
static inline bool skwq_has_sleeper(struct socket_wq *wq)
{
return wq && wq_has_sleeper(&wq->wait);
}
继续分析下sock_def_readable函数中,当检测到等待队列不为空时,wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll的实现,核心调用链为wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll->__wake_up_sync_key->__wake_up_common,在 __wake_up_common 中,会遍历等待队列项task_list选出等待队列里注册的每个元素 curr, 调用回调函数 curr->func(注意在ep_insert 调用时会设置 func为 ep_poll_callback)
#define wake_up_interruptible_sync_poll(x, m) \
__wake_up_sync_key((x), TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1, (void *) (m))
void __wake_up_sync_key(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, void *key)
{
...
__wake_up_common(q, mode, nr_exclusive, wake_flags, key);
}
static void __wake_up_common(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key)
{
wait_queue_t *curr, *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &q->task_list, task_list) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
//curr->func 为 ep_poll_callback
// 注意ep_poll_callback的参数为
// wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key
if (curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key) &&
(flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
}
}
3、调用 sock 等待队列的就绪回调函数ep_poll_callback的实现
注意:内核会直接根据(遍历)已注册在sock等待队列上的等待项的成员,通过ep_item_from_wait函数直接定位到epitem结构,即在ep_poll_callback 根据等待任务队列项上的额外的 base 指针可以找到 epitem, 进而也可以找到 eventpoll对象
ep_poll_callback的主要流程为:
- 把自己的
epitem添加到epoll的就绪队列rdllist中 - 查看
eventpoll对象上的等待队列里是否有等待项(epoll_wait执行的时候会设置) - 如果有等待项,那就查找到等待项里设置的回调函数
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L1004
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{
// 1、根据sk的等待队列中的等待项wait_queue_t
// 获取 waitqueue 对应的 epitem(前文已述)
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
// 2、获取 epitem 对应的 eventpoll 结构体
struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
int ewake = 0;
//......
// 3、将当前 epitem 添加到 eventpoll 的就绪队列中(尾部)
if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
}
// 4、查看 eventpoll 的等待队列上是否有在等待
// waitqueue_active:ep->wq的等待队列不为空返回true
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) {
if ((epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE) &&
!((unsigned long)key & POLLFREE)) {
switch ((unsigned long)key & EPOLLINOUT_BITS) {
case POLLIN:
if (epi->event.events & POLLIN)
ewake = 1;
break;
case POLLOUT:
if (epi->event.events & POLLOUT)
ewake = 1;
break;
case 0:
ewake = 1;
break;
}
}
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
}
//.......
}
wake_up_locked的调用链为wake_up_locked->__wake_up_locked->__wake_up_common,其中在 __wake_up_common调用 curr->func,该func是在 epoll_wait 中传入的 default_wake_function 函数,此外需要格外注意wake_up_locked传入的参数是eventpoll的wq等待队列,__wake_up_common的主要工作也是和eventpoll有关的
static void __wake_up_common(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, int wake_flags, void *key)
{
wait_queue_t *curr, *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &q->task_list, task_list) {
unsigned flags = curr->flags;
//curr->func:default_wake_function
if (curr->func(curr, mode, wake_flags, key) &&
(flags & WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE) && !--nr_exclusive)
break;
}
}
唤醒2:根据sock.wq->epitem->eventpoll.wq,唤醒因epoll_wait睡眠的进程
4、执行 epoll 就绪通知(default_wake_function)
在default_wake_function 中找到等待队列项里的进程描述符,然后唤醒它,这里等待队列项 curr->private 指针是在 epoll 对象上等待而被阻塞掉的进程。上一小节提出的问题的答案就在这里,经过两步唤醒后,内核将epoll_wait进程推入CPU 可运行队列runqueue,等待内核重新调度进程,继而当epoll_wait对应的这个进程重新运行后,就从 schedule 恢复,继续执行下面的代码
int default_wake_function(wait_queue_t *curr, unsigned mode, int wake_flags, void *key)
{
return try_to_wake_up(curr->private, mode, wake_flags);
}
当因epoll_wait阻塞进程醒来后,继续从 epoll_wait 时暂停(schedule_hrtimeout_range(......)之后)的代码继续执行,把 rdlist 中就绪的事件返回给用户进程,
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
......
for (;;) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out)
// 就绪队列有事件了,所以condition成立,跳出for(;;)循环
break;
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS))
timed_out = 1;
// 唤醒后,继续从这里开始执行
}
// 将先前epoll_wait阻塞的进程,移除epoll的等待队列
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
check_events:
//返回就绪事件给用户进程
ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)
}
最后看下ep_send_events->ep_scan_ready_list的实现,其中在ep_scan_ready_list中遍历事件就绪列表,发送就绪事件到用户空间,注意到该函数的参数为函数指针ep_send_events_proc,这二者协作完成事件从内核到用户态的传递,同时确保并发安全和高效率
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L584
static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep,
struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents)
{
struct ep_send_events_data esed;
esed.maxevents = maxevents;
esed.events = events;
// 遍历事件就绪列表,发送就绪事件到用户空间
return ep_scan_ready_list(ep, ep_send_events_proc/**/, &esed, 0, false);
}
ep_scan_ready_list与ep_send_events_proc的核心流程如下。其中ep_scan_ready_list主要完成就绪事件的分割与回调调度,在 epoll_wait 调用时,从 eventpoll 的就绪队列rdllist中提取事件并分发给用户态,同时处理新到达事件的并发冲突
- 锁定与状态切换:通过自旋锁
spin_lock_irqsave锁定eventpoll实例,暂停事件回调向rdllist的写入,然后将ovflist(单链表)设置为临时接收区,后续新到达的事件会暂存于此(避免与当前处理冲突) - 分割就绪队列
rdllist,将rdllist中的事件全部转移到临时链表txlist中,并清空rdllist - 执行回调函数,调用传入的回调函数
sproc(ep_send_events_proc),将txlist作为参数传递,处理事件回传 - 处理新事件与回滚:遍历
ovflist,将未处理的就绪事件重新加入rdllist(如在回调执行期间新到达的事件),然后恢复ovflist为初始状态(EP_UNACTIVE_PTR),解自旋锁 - 唤醒等待进程,若回调处理后仍有事件未完成(如 LT 模式重入),唤醒阻塞在
epoll_wait的进程
static __poll_t ep_scan_ready_list(struct eventpoll *ep,
__poll_t (*sproc)(struct eventpoll *,
struct list_head *, void *),
void *priv, int depth, bool ep_locked) {
__poll_t res;
struct epitem *epi, *nepi;
LIST_HEAD(txlist);
......
// 将就绪队列分片链接到 txlist 链表中
//分割就绪队列`rdllist`,将 `rdllist` 中的事件全部转移到临时链表 `txlist` 中,并清空 `rdllist`
list_splice_init(&ep->rdllist, &txlist);
//CALL ep_send_events_proc
res = (*sproc)(ep, &txlist, priv);
......
// 在处理 sproc 回调处理过程中,可能产生新的就绪事件被写入 ovflist,将 ovflist 回写 rdllist
for (nepi = READ_ONCE(ep->ovflist); (epi = nepi) != NULL;
nepi = epi->next, epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
if (!ep_is_linked(epi)) {
list_add(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}
}
......
// txlist 在 epitem 回调中,可能没有完全处理完,那么重新放回到 rdllist,下次处理
list_splice(&txlist, &ep->rdllist);
......
}
ep_send_events_proc主要处理事件回传,将 txlist 中的事件逐个拷贝到用户空间,并根据触发模式(ET/LT)决定是否重新加入就绪队列
- 遍历事件链表,循环处理
txlist中的每个epitem(代表一个就绪的文件描述符) - 事件有效性校验,调用
ep_item_poll重新检查文件状态(避免状态变更导致无效事件) - 用户空间数据拷贝,通过
__put_user将事件类型revents和用户数据event.data拷贝到用户态数组,若copy失败,将事件重新链入txlist等待后续重试 - 针对触发模式处理(
ET/LT),对于ET边缘触发模式,事件处理后不重新加入rdllist,仅当文件状态再次变化时重新触发;而LT水平触发模式,事件处理后重新加入rdllist,确保下次epoll_wait会再次检查(即使数据未读完) - 额外对
EPOLLONESHOT处理,若设置单次触发,事件处理后禁用后续监听(需重新注册)
static int ep_send_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,
void *priv)
{
struct ep_send_events_data *esed = priv;
int eventcnt;
unsigned int revents;
struct epitem *epi;
struct epoll_event __user *uevent;
struct wakeup_source *ws;
poll_table pt;
......
for (eventcnt = 0, uevent = esed->events;
!list_empty(head) && eventcnt < esed->maxevents;) {
epi = list_first_entry(head, struct epitem, rdllink);
......
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt);
if (revents) {
// copy to 用户态
if (__put_user(revents, &uevent->events) ||
__put_user(epi->event.data, &uevent->data)) {
//copy error
//把未处理的事件,再加回rdllink
list_add(&epi->rdllink, head);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
return eventcnt ? eventcnt : -EFAULT;
}
eventcnt++;
uevent++;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLONESHOT)
epi->event.events &= EP_PRIVATE_BITS;
else if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLET)) {
// 非ET模式下,需要加回ep->rdllist
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}//ET模式,不加回
}
}
return eventcnt;
}
0x07 番外
EPOLL_CTL_DEL AND EPOLL_CTL_MOD的流程
EPOLL_CTL_DEL关联实现为ep_remove()函数,主要流程围绕解绑事件关联、清理数据结构、释放资源等
static int ep_remove(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct file *file = epi->ffd.file;
//1、解绑等待队列,移除事件回调
//从 sock 等待队列中移除 eppoll_entry(通过 epi->pwqlist 链表定位)
//解除事件回调函数 ep_poll_callback 的注册,确保后续事件不再触发通知
ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
/* Remove the current item from the list of epoll hooks */
spin_lock(&file->f_lock);
//将epitem从该fd关联的file结构的f_ep_links链表上移除
// 从文件的 f_ep_links 链表中移除 epi(反向链接关系)
// 解除文件与 epitem 的关联,确保文件关闭时不会误操作已移除的监听项
// 添加代码位于:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L1349
list_del_rcu(&epi->fllink);
spin_unlock(&file->f_lock);
//2、从红黑树中删除epitem节点,解除全局监听
//将 epi 从 epoll 实例的红黑树(rbr)中移除,此后内核不再监听该 fd 的事件
rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
//3、清理就绪队列,移除待处理事件(fd)
//若 epi 已就绪但尚未被 epoll_wait 处理,需将其移出队列,避免无效事件上报
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink); // 从 rdllist 中移除epi
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));
//5、释放资源:销毁 epitem,并减少文件引用计数
// 若文件无其他引用,可触发关闭操作
atomic_long_dec(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
return 0;
}
epoll机制中的等待队列
1、epoll_wait中的等待队列机制实现:epoll_wait->ep_poll,在ep_poll函数的实现中发现了经典的等待->唤醒机制的模式,类似于wait_event内核调用中的condition参数,这里可以看到condition为ep_events_available函数的实现,即检查eventpoll的就绪队列rdllist是否不为空!list_empty(&ep->rdllist),具体流程请看注释
// 检查就绪队列是否可用(不为空)
static inline int ep_events_available(struct eventpoll *ep)
{
return !list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
}
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/eventpoll.c#L1614
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0;
unsigned long flags;
u64 slack = 0;
wait_queue_t wait;
ktime_t expires, *to = NULL;
if (timeout > 0) {
struct timespec64 end_time = ep_set_mstimeout(timeout);
slack = select_estimate_accuracy(&end_time);
to = &expires;
*to = timespec64_to_ktime(end_time);
} else if (timeout == 0) {
/*
* Avoid the unnecessary trip to the wait queue loop, if the
* caller specified a non blocking operation.
*/
timed_out = 1;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
goto check_events;
}
fetch_events:
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
if (!ep_events_available(ep)) {
/*
* We don't have any available event to return to the caller.
* We need to sleep here, and we will be wake up by
* ep_poll_callback() when events will become available.
*/
// 1. 先初始化等待队列并移入
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
for (;;) {
/*
* We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us
* a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state
* to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.
*/
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
// 2. 检查condition条件是否成立
if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out)
// 3. 若condition成立,则跳出for(;;)循环
break;
if (signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
// 4. 走到这里说明condition不成立,那么就先让出CPU
// 进程第一调度定律
// 那么内核执行进程切换,上下文保存到堆栈至此
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS))
timed_out = 1;
//5. 执行到这里大概率说明内核通过wakeup机制唤醒了当前的进程,继续for(;;)循环
// 下一步是检查condition是否满足
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
}
// 6. 已经被唤醒了,且condition也满足了,那么就移除等待队列
// 且设置当前的进程的运行状态的TASK_RUNNING
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
}
check_events:
/* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
* more luck.
*/
if (!res && eavail &&
!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && !timed_out)
goto fetch_events;
return res;
}
epoll机制下的回调函数
epoll在内核的运作机制中主要使用到3类回调函数:
sock_def_readable:内核在三次握手创建完整的struct sock结构并初始化时,设置成员sk_data_ready的默认值ep_poll_callback:当调用epoll_ctl时添加到 socket/sock 上,本质是向struct sock的sk_wq等待队列头添加了一个等待项(.private为NULL,.func为ep_poll_callback)default_wake_function:当调用epoll_wait时,设置到epollevent等待队列上,本质是向struct eventpoll的wq等待队列头添加了一个等待项(.private为当前进程,.func为default_wake_function)
0x08 惊群问题(epoll_wait+IO多路复用机制下)
惊群问题的本质
解决方案一:EPOLLEXCLUSIVE选项
解决方案二:SO_REUSEPORT技术
0x09 总结
epoll 事件处理流程的完整步骤
1、构建内核eventpoll结构,其中包含了 epoll进程的等待队列wq、fd(epitem)管理结构rbtree(rbr)以及事件就绪链表rdllist等核心成员,并初始化这些成员
2、注册监听(epoll_ctl),当调用 epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd) 时,内核创建 epitem 结构体(封装 fd 及其监听事件),插入到 eventpoll 的红黑树(rbr)中,实现 O(logN) 的高效查找。这里有个关键流程是内核会同时创建 eppoll_entry 结构体,它作为桥梁,一端指向当前 epitem,另一端会通过 wait_queue_t 挂载到 socket 关联的 struct sock 的等待队列(socket.sock->sk_wq)上,这样当该socket(fd)发生可读可写事件时,内核会遍历该socket等待队列,对每个唤醒的结构(curr->func),调用其已注册的函数ep_poll_callback(在ep_insert 调用时会设置该 func为 ep_poll_callback)
3、事件触发与回调(ep_poll_callback)过程,当注册到epoll体系的 socket 发生可读/可写事件时(如收到数据),内核执行以下动作:
- 从 socket 关联的等待队列中获取
eppoll_entry,进而找到对应的epitem - 通过
epitem定位到所属的eventpoll对象(每个 epoll 实例一个) - 将
epitem加入eventpoll的就绪链表(rdllist),此处是O(1)操作 - 唤醒逻辑:检查
eventpoll->wq(阻塞在epoll_wait上的进程等待队列),若有进程等待,则唤醒它处理已经就绪的fds
4、进程处理就绪事件(epoll_wait),被唤醒的进程从 rdllist 中取出 epitem,将其从rdllist链表中移除(但仍在红黑树中),然后将就绪的 fd 和事件拷贝到用户空间(如 events 数组),最后返回就绪的 fd 数量,用户进程即可处理这些fds事件
Why rbtree?
epoll机制中,红黑树的作用主要是在epoll_ctl操作海量fd时能够快速的定位到相关epitem节点,此外还兼顾了查找效率、插入效率、内存开销等多方面因素
ep_pqueue、poll_table与eppoll_entry结构的关系
在介绍ep_insert的实现中,出现了三个数据结构ep_pqueue、poll_table 和 eppoll_entry(其中ep_pqueue包含了poll_table与epitem指针)这三者共同实现了高效的事件监听与回调机制。其中ep_pqueue 是临时桥梁,用于向文件注册回调;poll_table 是标准接口,传递回调函数;eppoll_entry 是持久纽带,绑定文件等待队列与 epoll 监听项
这里再稍微回顾下epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_ADD)的流程,当调用 epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_ADD) 添加监听fd时
步骤1:初始化 ep_pqueue 与 poll_table
1、内核创建 ep_pqueue 对象,其成员 epi 指向当前监听的 epitem
2、初始化 ep_pqueue.pt(即 poll_table),将其回调函数 poll_table._qproc 设为 ep_ptable_queue_proc
struct ep_pqueue {
poll_table pt; // 内含 _qproc 回调函数指针
struct epitem *epi; // 指向监听的 epitem
};
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc); // 关键初始化
步骤2:触发文件操作,创建 eppoll_entry(关联ep_item_poll())
1、调用目标文件(socket)的 f_op->poll() 方法(tcp_poll()),传入 poll_table 参数
2、文件操作内部调用 poll_table._qproc(即 ep_ptable_queue_proc)
3、ep_ptable_queue_proc 创建 eppoll_entry 对象并初始化
struct eppoll_entry {
struct epitem *base; // 指向 epitem(来自 ep_pqueue.epi)
wait_queue_entry_t wait; // 等待队列项,回调函数设为 ep_poll_callback
wait_queue_head_t *whead; // 指向文件的等待队列头
};
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback); // 注册回调
4、将 eppoll_entry.wait 加入文件的等待队列( socket 的 sk_wq)后,这里就返回了
步骤3:事件触发与回调,当文件事件(如数据到达)发生时
1、内核调用文件的等待队列回调函数 ep_poll_callback
2、通过 eppoll_entry.base 找到 epitem,将其加入 eventpoll 的就绪队列(rdllist)
3、唤醒阻塞在 epoll_wait() 的进程
| 结构 | 功能 | 依赖 | 存在周期 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ep_pqueue |
作为临时粘合的结构体,用于关联 poll_table 与 epitem,用于向sock注册回调函数 |
依赖 epitem 传递监听上下文 |
仅在 epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_ADD) 期间存在,临时结构 |
避免每次调用重复创建实体,仅作为注册回调的媒介,提升性能 |
poll_table |
作为标准轮询接口,封装回调函数指针(_qproc),由sock操作(tcp_poll())调用 |
作为 ep_pqueue 的成员被初始化 |
仅在 epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_ADD) 期间存在,临时结构 |
提供通用接口,兼容不同文件操作(如 socket、pipe等),解耦 epoll 与具体设备 |
eppoll_entry |
作为持久结构体,绑定sock等待队列与 epitem结构,事件发生时触发回调通知 epoll |
由 ep_pqueue 的回调函数创建 |
存在直到该fd监听被从epoll中移除 | 通过 wait 成员长期驻留文件等待队列,实现一次注册+永久监听的高效模型,此外,它还双向链接到 epitem.pwqlist,便于监听移除时清理资源(调用 ep_remove() 时遍历删除) |
listenfd 与 acceptfd
在 Linux 的 epoll 机制中,通过 epoll_ctl 注册的监听套接字(listenfd)和通过 accept 获取的客户端套接字(acceptfd)在内核数据结构、队列机制以及唤醒后的处理流程都是有差异的,如下表:
| - | listenfd(监听套接字) | acceptfd(客户端套接字) |
|---|---|---|
| 类型 | 被动套接字(仅监听),for accept | 主动套接字(数据通信),for read/write |
| 关联内核队列 | 全连接队列(Accept Queue),包含连接的 struct sock 结构 | 读/写缓冲区 |
| 等待队列触发条件 | 全连接队列非空(有新连接) | 读缓冲区有数据/写缓冲区有空闲空间 |
| 注册事件 | EPOLLIN(新连接到达) | EPOLLIN(可读)、EPOLLOUT(可写) |
对于sock等待队列机制与唤醒,二者些许区别:
1、对于acceptfd(sock):某个已经处于TCP_ESTABLISHED状态的socket上有数据到达时,经由tcp_rcv_established->tcp_queue_rcv数据被挂在sock的接收队列sk_receive_queue上,然后内核触发唤醒过程sk->sk_data_ready(sk, ...)
2、对于 listenfd(sock):新连接到达,内核完成TCP三次握手流程后加入全连接队列,由于全连接队列非空(有新连接就绪),会触发唤醒流程,内核唤醒 listenfd 的等待队列,调用 ep_poll_callback ,会把 epitem 加入 eventpoll 的就绪队列rdllist,从而 epoll_wait 返回 EPOLLIN 事件
但是注册、唤醒之后(到达应用层之前)的流程本质上是一样的,对于listenfd,epoll 将 ep_poll_callback 注册到等待队列,触发后会将 listenfd 对应的 epitem 加入 eventpoll 的就绪队列rdllist;而对于 acceptfd,同样注册 ep_poll_callback,当数据到达或缓冲区可写时,将 acceptfd 的 epitem 加入 rdllist
此外,对 listenfd而言,其本身无数据收发能力,其接收队列实为全连接队列,存储的是 struct sock 结构(代表已建立的连接),而非数据包。换句话说,listenfd 关联的sock结构的sk_receive_queue接收队列实际上是没用的