0x00 前言
命名空间用来实现内核对资源进行隔离,本文基于v4.11.6的源码分析下Mnt Namespace的若干细节
0x01 一个容器的case
几个问题:
- 容器内的进程pid的分配过程
- 容器(容器内进程)创建的过程,
pivot_root/chroot的区别 - 容器内挂载树(mount tree)的生成过程
0x02 pidnamespace:容器内进程pid的创建
前文已经学习过pidnamespace场景中pid的分配,这里先回顾下几个问题:
- 容器进程中的 pid 是如何申请?
- 内核如何显示容器中的进程号?
- 容器pid与宿主机pid的申请区别?
从copy_process的实现可知,当在容器内创建一个进程时,本质上还是在宿主机内核调用_do_fork等一系列指令,最终复制出一个task_struct结构(并不是宿主机、容器单独各一个task_struct结构),并且通过struct pid及其柔性数组成员upid的扩展,使得不同level的pidnamespace拥有不同的pid
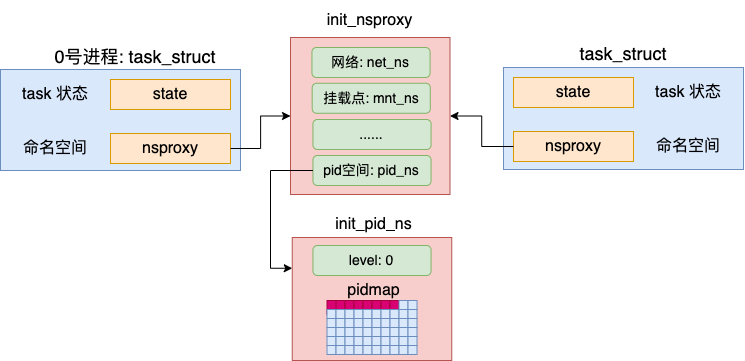
内核启动时:默认的pidnamespace
Linux内核启动的时候会有一套默认的命名空间init_nsproxy以及默认的 pidnamespace init_pid_ns,定义如下:
struct task_struct {
...
/* namespaces */
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
}
struct nsproxy init_nsproxy = {
.count = ATOMIC_INIT(1),
.uts_ns = &init_uts_ns,
.ipc_ns = &init_ipc_ns,
.mnt_ns = NULL,
.pid_ns = &init_pid_ns,
.net_ns = &init_net,
};
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/pid.c#L71
struct pid_namespace init_pid_ns = {
.kref = {
.refcount = ATOMIC_INIT(2),
},
.pidmap = {
[ 0 ... PIDMAP_ENTRIES-1] = { ATOMIC_INIT(BITS_PER_PAGE), NULL }
},
.last_pid = 0,
.level = 0,
.child_reaper = &init_task,
.user_ns = &init_user_ns,
.proc_inum = PROC_PID_INIT_INO,
};
而pid_namespace的定义如下:
level:当前 pid 命名空间的层级,默认命名空间的 level 初始化是0(根节点)。这是一个表示树的层次结构的节点(parent表示父节点)。如果有多个命名空间构成一棵树结构pidmap:用于标识pid分配的bitmap(位置1表示被分配出去)
struct pid_namespace {
struct kref kref;
struct pidmap pidmap[PIDMAP_ENTRIES];
struct rcu_head rcu;
int last_pid;
unsigned int nr_hashed;
struct task_struct *child_reaper;
struct kmem_cache *pid_cachep;
unsigned int level; // 本命名空间的level
struct pid_namespace *parent;
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS //for procfs
struct vfsmount *proc_mnt;
struct dentry *proc_self;
struct dentry *proc_thread_self;
#endif
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
struct ucounts *ucounts;
struct work_struct proc_work;
kgid_t pid_gid;
int hide_pid;
int reboot; /* group exit code if this pidns was rebooted */
struct ns_common ns;
};
INIT_TASK 即0号进程(idle 进程),默认绑定init_nsproxy,若创建进程时不指定命名空间,所有进程使用的都是使用默认命名空间
#define INIT_TASK(tsk) \
{
.state = 0, \
.stack = &init_thread_info, \
.usage = ATOMIC_INIT(2), \
.flags = PF_KTHREAD, \
.prio = MAX_PRIO-20, \
.static_prio = MAX_PRIO-20, \
.normal_prio = MAX_PRIO-20, \
...
.nsproxy = &init_nsproxy, \
......
}
Docker容器下的进程创建
参考Linux 容器底层工作机制:从 500 行 C 代码到生产级容器运行时
创建Docker容器进程(或者在容器中启动进程)时,通常要指定如下选项。其中指定了 CLONE_NEWPID 要创建一个独立的 pid 命名空间出来
int flags = CLONE_NEWNS | CLONE_NEWCGROUP | CLONE_NEWPID | CLONE_NEWIPC | CLONE_NEWNET | CLONE_NEWUTS;
// fork process
child_pid = clone(child, stack + STACK_SIZE, flags | SIGCHLD, &config);
新进程、命名空间的创建过程
主要涉及的内核函数如下:
copy_process
|- copy_namespaces
|- alloc_pid
|- attach_pid
1、copy_process,进程id涉及三个关键流程
- 拷贝进程的命名空间 nsproxy,
copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p) - 申请 pid,
pid = alloc_pid(p->nsproxy->pid_ns) - 记录 pid,
p->pid = pid_nr(pid);p->tgid = p->pid;attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID, pid)
static __latent_entropy struct task_struct *copy_process(
unsigned long clone_flags,
unsigned long stack_start,
unsigned long stack_size,
int __user *child_tidptr,
struct pid *pid,
int trace,
unsigned long tls,
int node)
{
int retval;
// new task_struct
struct task_struct *p;
retval = security_task_create(clone_flags);
if (retval)
goto fork_out;
retval = -ENOMEM;
// 复制一份task_struct
p = dup_task_struct(current, node);
if (!p)
goto fork_out;
ftrace_graph_init_task(p);
rt_mutex_init_task(p);
......
// 复制 creds信息
retval = copy_creds(p, clone_flags);
if (retval < 0)
goto bad_fork_free;
......
/* Perform scheduler related setup. Assign this task to a CPU. */
retval = sched_fork(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;
retval = perf_event_init_task(p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;
retval = audit_alloc(p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_perf;
/* copy all the process information */
shm_init_task(p);
retval = copy_semundo(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_audit;
retval = copy_files(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_semundo;
retval = copy_fs(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_files;
retval = copy_sighand(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_fs;
retval = copy_signal(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_sighand;
retval = copy_mm(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_signal;
// 拷贝进程的命名空间 nsproxy
retval = copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;
retval = copy_io(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces;
retval = copy_thread_tls(clone_flags, stack_start, stack_size, p, tls);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_io;
// 重要:申请及分配pid
if (pid != &init_struct_pid) {
pid = alloc_pid(p->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children);
if (IS_ERR(pid)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(pid);
goto bad_fork_cleanup_thread;
}
}
......
/* ok, now we should be set up.. */
p->pid = pid_nr(pid);
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {
p->exit_signal = -1;
p->group_leader = current->group_leader;
p->tgid = current->tgid;
} else {
if (clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT)
p->exit_signal = current->group_leader->exit_signal;
else
p->exit_signal = (clone_flags & CSIGNAL);
p->group_leader = p;
p->tgid = p->pid;
}
p->nr_dirtied = 0;
p->nr_dirtied_pause = 128 >> (PAGE_SHIFT - 10);
p->dirty_paused_when = 0;
p->pdeath_signal = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->thread_group);
p->task_works = NULL;
cgroup_threadgroup_change_begin(current);
/*
* Ensure that the cgroup subsystem policies allow the new process to be
* forked. It should be noted the the new process's css_set can be changed
* between here and cgroup_post_fork() if an organisation operation is in
* progress.
*/
retval = cgroup_can_fork(p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_free_pid;
/*
* Make it visible to the rest of the system, but dont wake it up yet.
* Need tasklist lock for parent etc handling!
*/
write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
/* CLONE_PARENT re-uses the old parent */
if (clone_flags & (CLONE_PARENT|CLONE_THREAD)) {
p->real_parent = current->real_parent;
p->parent_exec_id = current->parent_exec_id;
} else {
p->real_parent = current;
p->parent_exec_id = current->self_exec_id;
}
spin_lock(¤t->sighand->siglock);
/*
* Copy seccomp details explicitly here, in case they were changed
* before holding sighand lock.
*/
copy_seccomp(p);
......
if (likely(p->pid)) {
ptrace_init_task(p, (clone_flags & CLONE_PTRACE) || trace);
init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID, pid);
if (thread_group_leader(p)) {
init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PGID, task_pgrp(current));
init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_SID, task_session(current));
if (is_child_reaper(pid)) {
ns_of_pid(pid)->child_reaper = p;
p->signal->flags |= SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE;
}
p->signal->leader_pid = pid;
p->signal->tty = tty_kref_get(current->signal->tty);
/*
* Inherit has_child_subreaper flag under the same
* tasklist_lock with adding child to the process tree
* for propagate_has_child_subreaper optimization.
*/
p->signal->has_child_subreaper = p->real_parent->signal->has_child_subreaper ||
p->real_parent->signal->is_child_subreaper;
list_add_tail(&p->sibling, &p->real_parent->children);
list_add_tail_rcu(&p->tasks, &init_task.tasks);
attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PGID);
attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_SID);
__this_cpu_inc(process_counts);
} else {
current->signal->nr_threads++;
atomic_inc(¤t->signal->live);
atomic_inc(¤t->signal->sigcnt);
list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group,
&p->group_leader->thread_group);
list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_node,
&p->signal->thread_head);
}
attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID);
nr_threads++;
}
total_forks++;
spin_unlock(¤t->sighand->siglock);
syscall_tracepoint_update(p);
write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
proc_fork_connector(p);
cgroup_post_fork(p);
cgroup_threadgroup_change_end(current);
perf_event_fork(p);
trace_task_newtask(p, clone_flags);
uprobe_copy_process(p, clone_flags);
return p;
//各类错误case的处理
......
}
2、copy_namespaces函数:创建进程时,构造新命名空间,注意flags参数常用值
CLONE_NEWPID: 是否创建新的进程编号命名空间,以便与宿主机的进程 PID 进行隔离CLONE_NEWNS: 是否创建新的挂载点(文件系统)命名空间,以便隔离文件系统和挂载点CLONE_NEWNET: 是否创建新的网络命名空间,以便隔离网卡、IP、端口、路由表等网络资源CLONE_NEWUTS: 是否创建新的主机名与域名命名空间,以便在网络中独立标识自己CLONE_NEWIPC: 是否创建新的 IPC 命名空间,以便隔离信号量、消息队列和共享内存
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/fork.c#L1491
int copy_namespaces(unsigned long flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct nsproxy *old_ns = tsk->nsproxy;
struct user_namespace *user_ns = task_cred_xxx(tsk, user_ns);
struct nsproxy *new_ns;
// 参数
if (likely(!(flags & (CLONE_NEWNS | CLONE_NEWUTS | CLONE_NEWIPC |
CLONE_NEWPID | CLONE_NEWNET |
CLONE_NEWCGROUP)))) {
get_nsproxy(old_ns);
return 0;
}
if (!ns_capable(user_ns, CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
if ((flags & (CLONE_NEWIPC | CLONE_SYSVSEM)) ==
(CLONE_NEWIPC | CLONE_SYSVSEM))
return -EINVAL;
//
new_ns = create_new_namespaces(flags, tsk, user_ns, tsk->fs);
if (IS_ERR(new_ns))
return PTR_ERR(new_ns);
tsk->nsproxy = new_ns;
return 0;
}
3、create_new_namespaces:创建新的namespace
static struct nsproxy *create_new_namespaces(unsigned long flags,
struct task_struct *tsk, struct user_namespace *user_ns,
struct fs_struct *new_fs)
{
struct nsproxy *new_nsp;
int err;
//申请新的 nsproxy
new_nsp = create_nsproxy();
if (!new_nsp)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
new_nsp->mnt_ns = copy_mnt_ns(flags, tsk->nsproxy->mnt_ns, user_ns, new_fs);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->mnt_ns)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->mnt_ns);
goto out_ns;
}
new_nsp->uts_ns = copy_utsname(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->uts_ns);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->uts_ns)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->uts_ns);
goto out_uts;
}
new_nsp->ipc_ns = copy_ipcs(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->ipc_ns);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->ipc_ns)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->ipc_ns);
goto out_ipc;
}
// copy_pid_ns:创建 PID 命名空间
new_nsp->pid_ns_for_children =
copy_pid_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->pid_ns_for_children)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->pid_ns_for_children);
goto out_pid;
}
new_nsp->cgroup_ns = copy_cgroup_ns(flags, user_ns,
tsk->nsproxy->cgroup_ns);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->cgroup_ns)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->cgroup_ns);
goto out_cgroup;
}
new_nsp->net_ns = copy_net_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->net_ns);
if (IS_ERR(new_nsp->net_ns)) {
err = PTR_ERR(new_nsp->net_ns);
goto out_net;
}
return new_nsp;
......
}
// copy_pid_ns
struct pid_namespace *copy_pid_ns(unsigned long flags,
struct user_namespace *user_ns, struct pid_namespace *old_ns)
{
if (!(flags & CLONE_NEWPID))
return get_pid_ns(old_ns);
if (task_active_pid_ns(current) != old_ns)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
return create_pid_namespace(user_ns, old_ns);
}
4、create_new_namespaces->copy_pid_ns->create_pid_namespace:完成新的pidnamespace创建过程,从实现看,新命名空间namespace和旧命名空间通过 parent、level 等字段组成了一棵树,其中 parent 指向了上一级命名空间,自己的 level 用来表示层次,并设置成为上一级 level+1

//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/pid_namespace.c#L95
static struct pid_namespace *create_pid_namespace(struct user_namespace *user_ns,
struct pid_namespace *parent_pid_ns)
{
struct pid_namespace *ns;
//新 pid namespace level 值:在原level基础上加1
unsigned int level = parent_pid_ns->level + 1;
struct ucounts *ucounts;
int i;
int err;
err = -ENOSPC;
if (level > MAX_PID_NS_LEVEL)
goto out;
ucounts = inc_pid_namespaces(user_ns);
if (!ucounts)
goto out;
err = -ENOMEM;
// 申请内存
ns = kmem_cache_zalloc(pid_ns_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ns == NULL)
goto out_dec;
// 为新pid命名空间的 pidmap 申请内存
ns->pidmap[0].page = kzalloc(PAGE_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ns->pidmap[0].page)
goto out_free;
// 初始化pid bitmap
ns->pid_cachep = create_pid_cachep(level + 1);
if (ns->pid_cachep == NULL)
goto out_free_map;
err = ns_alloc_inum(&ns->ns);
if (err)
goto out_free_map;
ns->ns.ops = &pidns_operations;
kref_init(&ns->kref);
//设置新命名空间 level 值
ns->level = level;
// 重要:新命名空间和旧命名空间组成一棵树
ns->parent = get_pid_ns(parent_pid_ns);
ns->user_ns = get_user_ns(user_ns);
ns->ucounts = ucounts;
ns->nr_hashed = PIDNS_HASH_ADDING;
INIT_WORK(&ns->proc_work, proc_cleanup_work);
// 初始化新的pidnamespace的pid bitmap
set_bit(0, ns->pidmap[0].page);
atomic_set(&ns->pidmap[0].nr_free, BITS_PER_PAGE - 1);
for (i = 1; i < PIDMAP_ENTRIES; i++)
atomic_set(&ns->pidmap[i].nr_free, BITS_PER_PAGE);
return ns;
......
}
5、继续回到copy_process主过程,创建及初始化完命名空间后,调用alloc_pid函数申请分配pid,注意传入参数是上面新建的pid_namespace,其ns->level值已经是加1的了
注意,在alloc_pid中通过for (i = ns->level; i >= 0; i--){......}就构造了前文描述的内核struct pid多层次结构。考虑容器这类场景,容器内进程其关联自下而上的pidnamespace中都需要存在一个进程id,首先在当前层次的命名空间申请一个 pid 出来,然后顺着命名空间的父节点,每一层也都要申请一个,并都记录到 pid->numbers 数组(upid记录了进程id)中
struct pid
{
atomic_t count;
unsigned int level;
/* lists of tasks that use this pid */
struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct upid numbers[1];
};
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/pid.c#L296
struct pid *alloc_pid(struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
//申请 pid 内核对象
struct pid *pid;
enum pid_type type;
int i, nr;
struct pid_namespace *tmp;
struct upid *upid;
int retval = -ENOMEM;
//申请 pid 内核对象(注意pid的复合结构)
pid = kmem_cache_alloc(ns->pid_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pid)
return ERR_PTR(retval);
tmp = ns;
pid->level = ns->level;
// 注意是从child pidnamespace向parent pidnamespace
// 自下而上申请并创建pid
for (i = ns->level; i >= 0; i--) {
// alloc_pidmap:分配一个空闲的pid
nr = alloc_pidmap(tmp);
if (nr < 0) {
retval = nr;
goto out_free;
}
pid->numbers[i].nr = nr;
pid->numbers[i].ns = tmp;
tmp = tmp->parent;
}
if (unlikely(is_child_reaper(pid))) {
if (pid_ns_prepare_proc(ns))
goto out_free;
}
get_pid_ns(ns);
atomic_set(&pid->count, 1);
/*
enum pid_type
{
PIDTYPE_PID, //0
PIDTYPE_PGID, //1
PIDTYPE_SID, //2
PIDTYPE_MAX
};
*/
// 注意这里:在struct pid中构tasks成员的关系,如pid/pgid/sid的全局hashtable的链表关系
// 这里不是level的关系
for (type = 0; type < PIDTYPE_MAX; ++type)
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&pid->tasks[type]);
upid = pid->numbers + ns->level;
spin_lock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
if (!(ns->nr_hashed & PIDNS_HASH_ADDING))
goto out_unlock;
for ( ; upid >= pid->numbers; --upid) {
hlist_add_head_rcu(&upid->pid_chain,
&pid_hash[pid_hashfn(upid->nr, upid->ns)]);
upid->ns->nr_hashed++;
}
spin_unlock_irq(&pidmap_lock);
return pid;
......
}
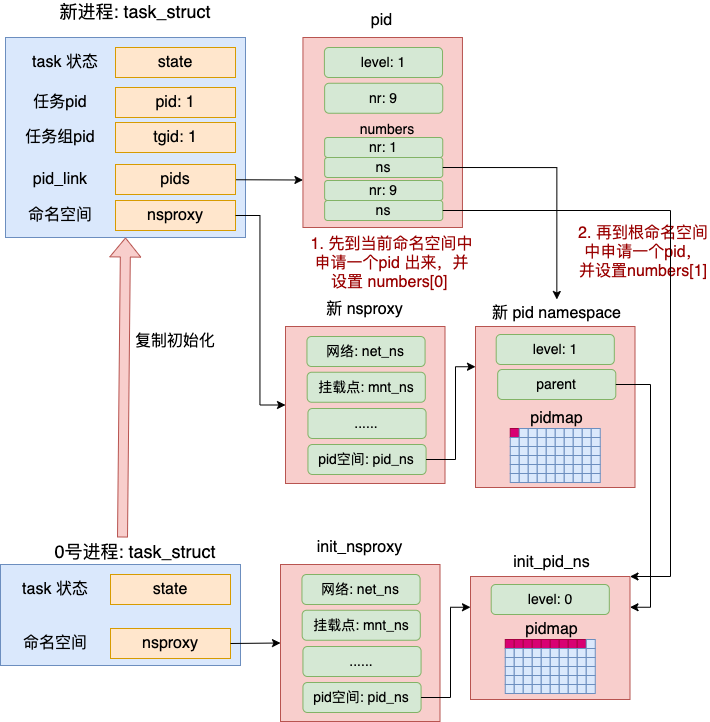
6、设置整数格式 pid:当申请并构造完 struct pid 结构后,将其关联在 task_struct 上,即新建的task_struct结构
// pid_nr:获取的根 pid 命名空间下的 pid 编号
static inline pid_t pid_nr(struct pid *pid)
{
pid_t nr = 0;
if (pid)
nr = pid->numbers[0].nr;
return nr;
}
// attach_pid:把申请到的 pid 结构挂到自己的 pids[PIDTYPE_PID] 链表中
void attach_pid(struct task_struct *task, enum pid_type type)
{
// 注意:task->pids 本身就是是一组链表结构
struct pid_link *link = &task->pids[type];
hlist_add_head_rcu(&link->node, &link->pid->tasks[type]);
}
static struct task_struct *copy_process(...)
{
......
// p指向当前新建的task_struct
//申请 pid
pid = alloc_pid(p->nsproxy->pid_ns);
......
// 记录 pid
p->pid = pid_nr(pid);
p->tgid = p->pid;
attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID, pid);
......
}
容器进程 pid 查看
内核提供函数pid_vnr来实现在容器中查看进程 pid,pid_vnr 调用 pid_nr_ns 来查看进程在特定命名空间里的进程id,厘清这里的关系参考前文已经给出的关系图
这里详细描述下,对于struct pid结构,如果level=2,那么说明该task_struct所在的层级为2(容器内),struct upid numbers[1]数组的长度也为2,numbers数组,numbers[0].ns指向0层的pid_namespace,numbers[0].nr是宿主机上该容器进程的pid;numbers[1].ns指向1层的pid_namespace,numbers[1].nr是容器内该容器进程的pid,numbers[0].ns与numbers[1].ns这两个pid_namespace构成了命名空间上的父子关系。此外,一个struct pid,该结构体的level是确定的,而且对应任意level上的进程,内核中有且仅有一个struct pid
struct pid
{
atomic_t count;
unsigned int level;
/* lists of tasks that use this pid */
struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct upid numbers[1];
};
struct upid {
/* Try to keep pid_chain in the same cacheline as nr for find_vpid */
int nr; //是`pid`的值, 即 `task_struct` 中 `pid_t pid` 域的值
struct pid_namespace *ns; // 所属的pid namespace(归属,其中包含了在每个namespace管理进程分配的bitmap)
struct hlist_node pid_chain;
};
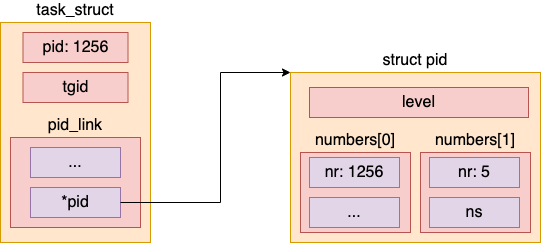
注意到,函数 pid_nr_ns 两个参数:
struct pid *pid:全局结构,保存了进程里记录的 pid 对象(以及在各个层次申请到的 pid 号)struct pid_namespace *ns:当前调用的task_struct指定的 pid 命名空间(通过task_active_pid_ns(current)获取)- 对于
current而言,调用方所在的level层级一定是明确的(宿主机或者容器),所以current->pid->level的值也是明确的(比如为0或1)
涉及到的核心代码如下,其中注意task_pid这个函数,是获取当前task_struct指向(关联的)struct pid指针,那么task_active_pid_ns(current)就是返回当前current所在的pid_namespace
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/kernel/pid.c#L388
pid_t pid_vnr(struct pid *pid)
{
return pid_nr_ns(pid, task_active_pid_ns(current));
}
struct pid_namespace *task_active_pid_ns(struct task_struct *tsk)
{
return ns_of_pid(task_pid(tsk));
}
static inline struct pid_namespace *ns_of_pid(struct pid *pid)
{
struct pid_namespace *ns = NULL;
if (pid){
// ns为某个指定level上的进程id
// pid->level是确定的
ns = pid->numbers[pid->level].ns;
}
return ns;
}
// task_pid
static inline struct pid *task_pid(struct task_struct *task)
{
// 获取调用方所在task_struct的pid结构
// 主要目的是为了获取pid->level
return task->pids[PIDTYPE_PID].pid;
}
pid_t pid_nr_ns(struct pid *pid, struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
struct upid *upid;
pid_t nr = 0;
// ns->level:命名空间
// pid->level:进程唯一的level
// 通常情况下,一定有ns->level<=pid->level 成立
if (pid && ns->level <= pid->level) {
upid = &pid->numbers[ns->level];
if (upid->ns == ns)
nr = upid->nr;
}
return nr;
}
0x03 Mnt namespace
独立挂载
先思考下这个问题,按下述命令在容器启动后,容器内会自动创建/soft的目录,这里对VFS、mnt namespace节点关系的影响是什么?
#冒号:前面的目录是宿主机目录,后面的目录是容器内目录
docker run -it -v /test:/soft centos /bin/bash
数据结构
//https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.11.6/source/fs/mount.h#L7
struct mnt_namespace {
atomic_t count;
struct ns_common ns;
struct mount * root; //指向本namespace中根目录 / 指向的mount结构
struct list_head list; //用来存储该mnt space中所有的挂载点链表(比如上述的独立挂载等)
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
struct ucounts *ucounts;
u64 seq; /* Sequence number to prevent loops */
wait_queue_head_t poll;
u64 event;
unsigned int mounts; /* # of mounts in the namespace */
unsigned int pending_mounts;
};
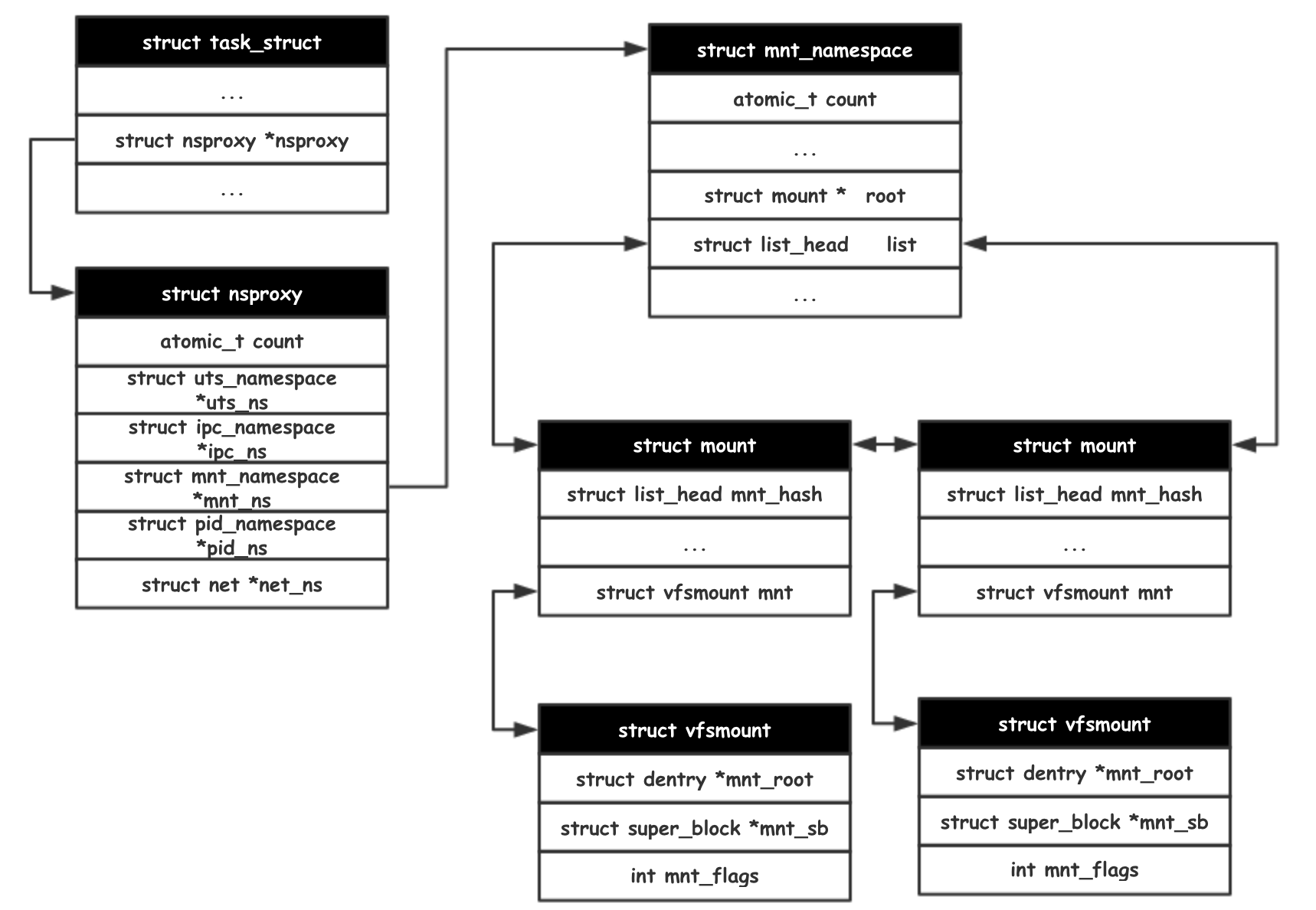
多命名空间下的mount树,如容器化场景,内核为了支持 mnt_namespace,把 mount 树扩展成了多棵。每个 mnt_namespace 拥有一棵独立的 mount 树。从下图可以看到
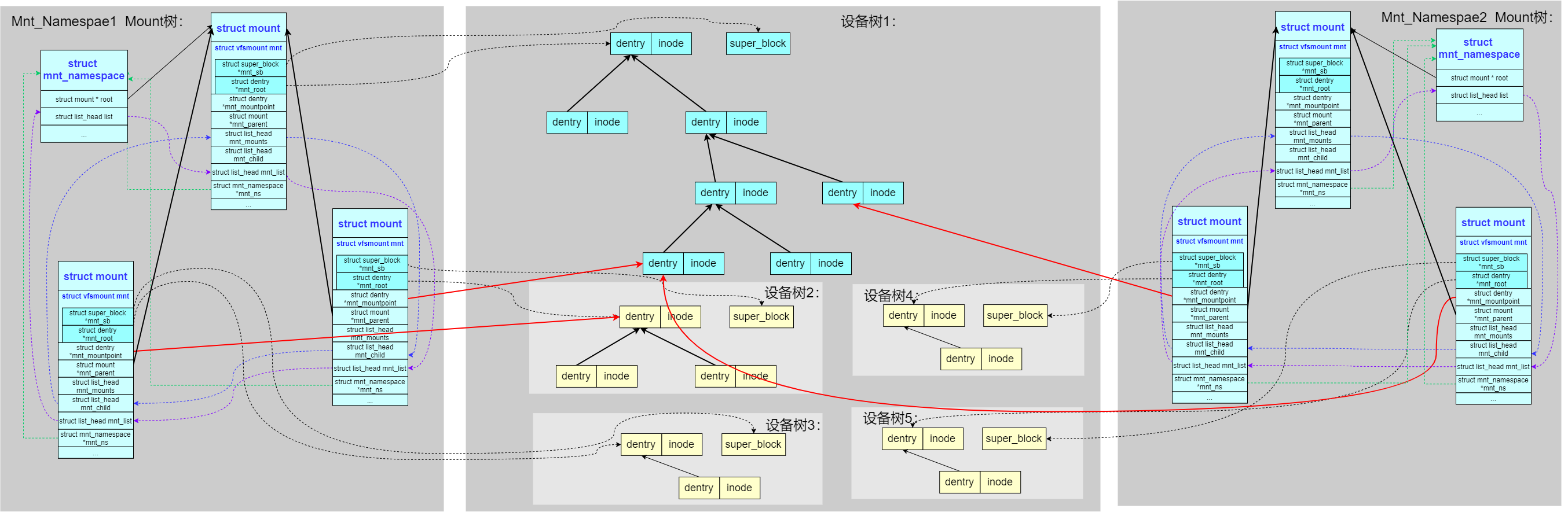
- 每个namespace的mount树都是独立的(mnt_namespace1与mnt_namespace2),对应于不同容器的不同的挂载根目录节点(容器创建时一般通过
pivot_root切换根目录) - 红色的线可能表示容器中的宿主机独立挂载,比如将宿主机上某个路径以独立挂载的方式挂载到容器中(对容器内的进程可见),这些独立挂载需要以链表节点形式link到本
mnt_namespace的struct list_head list成员 - 宿主机可以看到容器内部分路径,如通过挂载点(绑定挂载)访问、Docker的数据卷(Volumes)