0x00 前言
本文的出发点是希望在 gRPC 的框架中,加入核心数据监控的能力(Monitoring),目前预研的库有两个:
- prometheus
- open-falcon
这篇文章,介绍下如何将 gRPC 和 Prometheus 结合。Prometheus 的架构中常用的是 Pull 模式,当然 Push 也可以。这其实就是服务端(服务注册)和客户端(主动上报数据)的区别。在 Pull 模式中, 通过 HTTP 协议去采集指标,只要应用系统能够提供 HTTP 接口(一般使用 promhttp 创建 HttpServer)就可以接入监控系统,相比于私有协议或二进制协议来说更为简单。
相关基础知识介绍:理解 Prometheus 的基本数据类型及应用(基础篇)
0x01 Prometheus Metrics
Metrics 类型
Prometheus 常用 4 种 Metric 类型,前四种为:Counter,Gauge,Summary 和 Histogram,每种类型都有对应的 Vector 版本:GaugeVec, CounterVec, SummaryVec, HistogramVec。Vector 版本细化了 prometheus 数据模型,增加了 label 维度。现网项目中Vector形式更为常用。
0x02 Prometheus 包的用法
Prometheus 包提供了用于实现监控代码的 Metric 原型和用于注册 Metric 的 Registry。Promhttp 允许通过 HTTP 来暴露注册的 Metric 或将注册的 Metric 推送到 Pushgateway。
在 Prometheus 中,一般 Metric 对象采集的使用步骤如下:
- 初始化一个 Metric 对象
- Register 注册对象,常用
MustRegister方法注册 - 向对象中添加值
常用类型及方法
// 该类型实现了 error 接口,由 Register 返回,用于判断用于注册的 collector 是否已经被注册过
type AlreadyRegisteredError
// 用于采集 prometheus metric,如果运行多个相同的实例,则需要使用 ConstLabels 来注册这些实例。实现 collector 接口需要实现 Describe 和 Collect 方法,并注册 collector
type Collector
// 负责 collector 的注册和去注册,实现 custom registrer 时应该实现该接口
type Registerer
// 使用 DefaultRegisterer 来注册传入的 Collector
func Register(c Collector) error
// 使用 DefaultRegisterer 来移除传入的 Collector 的注册信息
func Unregister(c Collector) bool
此外,带 Must 的版本函数只是对不带 Must 函数的封装,增加了 panic 操作,如:
// MustRegister implements Registerer.
func (r *Registry) MustRegister(cs ...Collector) {
for _, c := range cs {
if err := r.Register(c); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
}
0x03 Counter && CouterVec
计数器(Counter)是表示单个单调递增计数器的累积量,其值只能增加或在重启时重置为零。 例如,可以使用计数器来表示服务的总请求数,已完成的任务或错误总数。 但是注意不要使用计数器来监控可能减少的值。CounterVec 是一组 Counter,这些计数器具有相同的描述,但它们的变量标签具有不同的值。 如果要计算按各种维度划分的相同内容(例如,响应代码和方法分区的 HTTP 请求数),则使用此方法。使用 NewCounterVec 创建实例。
Counter 主要两个方法,Inc 和 Add,
Inc() // 将 counter 值加 1
Add(float64) // 将指定值加到 counter 值上,如果指定值 < 0 会 panic
Counter 使用例子
// 初始化一个 Counter
pushCounter = prometheus.NewCounter(prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "repository_pushes",
Help: "Number of pushes to external repository.", // 注意,必须要定义 Help,否则会报错
})
// 注册
err = prometheus.Register(pushCounter)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Push counter couldn't be registered AGAIN, no counting will happen:", err)
return
}
collectChan := make(chan struct{})
for range collectChan {
// 向对象中写入(统计)值
pushCounter.Inc()
}
CounterVec 使用例子
同样的,建立 CounterVec 也遵循同样的三部曲:
// 第一步:建立 NewCounterVec,注意指定 label 为 slice 数组
httpReqs := prometheus.NewCounterVec(
prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "http_requests_total",
Help: "How many HTTP requests processed, partitioned by status code and HTTP method.",
},
[]string{"code", "method"},
)
// 第二步: 注册
prometheus.MustRegister(httpReqs)
// 调用 Add() 写入
httpReqs.WithLabelValues("404", "POST").Add(42)
// If you have to access the same set of labels very frequently, it
// might be good to retrieve the metric only once and keep a handle to
// it. But beware of deletion of that metric, see below!
// 第三步:写入值,调用 Inc() 写入
m := httpReqs.WithLabelValues("200", "GET")
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
m.Inc()
}
// Delete a metric from the vector. If you have previously kept a handle
// to that metric (as above), future updates via that handle will go
// unseen (even if you re-create a metric with the same label set
// later).
httpReqs.DeleteLabelValues("200", "GET")
// Same thing with the more verbose Labels syntax.
httpReqs.Delete(prometheus.Labels{"method": "GET", "code": "200"})
0x04 Gauge && GaugeVec
Gauge 可以用来存放一个可以任意变大变小的数值,通常用于测量值,例如 CPU-core 使用率或内存使用情况,或者运行的 goroutine 数量;如果需要一次性统计 N 个 cpu-core 的使用率,这个时候就适合使用 GaugeVec 来完成
Gauge 主要有以下四个方法:
// 将 Gauge 中的值设为指定值
Set(float64)
// 将 Gauge 中的值加 1
Inc()
// 将 Gauge 中的值减 1
Dec()
// 将指定值加到 Gauge 中的值上。(指定值可以为负数)
Add(float64)
// 将指定值从 Gauge 中的值减掉。(指定值可以为负数)
Sub(float64)
Gauge 使用例子
// 初始化
cpuUsage := prometheus.NewGauge(prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "CPU_Usage",
Help: "the Usage of CPU",
})
// 注册
prometheus.MustRegister(cpuUsage)
// 定时获取 cpu 温度并且写入到容器
func(){
tem = getCpuCurrentUsage()
// 向 cpuUsage 中写入值,调用 Set 方法
cpuUsage.Set(tem)
}
GaugeVec 使用例子
cpulistUsage := prometheus.NewGaugeVec(
prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "CPUs_Usage",
Help: "the Usage of ALL CPUs.",
},
[]string{
"cpuName",
},
)
prometheus.MustRegister(cpulistUsage)
cpulistUsage.WithLabelValues("cpu1").Set(cpu1_usage)
cpulistUsage.WithLabelValues("cpu2").Set(cpu2_usage)
cpulistUsage.WithLabelValues("cpu3").Set(cpu3_usage)
cpulistUsage.WithLabelValues("cpu4").Set(cpu4_usage)
0x05 Histogram
Histogram 主要用于表示一段时间范围内对数据进行采样,(通常是请求持续时间或响应大小),并能够对其指定区间以及总数进行统计,通常我们用它计算分位数的直方图。
temps := prometheus.NewHistogram(prometheus.HistogramOpts{
Name: "pond_temperature_celsius",
Help: "The temperature of the frog pond.", // Sorry, we can't measure how badly it smells.
Buckets: prometheus.LinearBuckets(20, 5, 5), // 5 buckets, each 5 centigrade wide.
})
// Simulate some observations.
for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ {
temps.Observe(30 + math.Floor(120*math.Sin(float64(i)*0.1))/10)
}
// Just for demonstration, let's check the state of the histogram by
// (ab)using its Write method (which is usually only used by Prometheus
// internally).
metric := &dto.Metric{}
temps.Write(metric)
fmt.Println(proto.MarshalTextString(metric))
0x06 Summary
Summary 从事件或样本流中捕获单个观察,并以类似于传统汇总统计的方式对其进行汇总:1。观察总和,2。观察计数,3。排名估计。典型的用例是观察请求延迟。 默认情况下,Summary 提供延迟的中位数。
temps := prometheus.NewSummary(prometheus.SummaryOpts{
Name: "pond_temperature_celsius",
Help: "The temperature of the frog pond.",
Objectives: map[float64]float64{0.5: 0.05, 0.9: 0.01, 0.99: 0.001},
})
// Simulate some observations.
for i := 0; i < 1000; i++ {
temps.Observe(30 + math.Floor(120*math.Sin(float64(i)*0.1))/10)
}
// Just for demonstration, let's check the state of the summary by
// (ab)using its Write method (which is usually only used by Prometheus
// internally).
metric := &dto.Metric{}
temps.Write(metric)
fmt.Println(proto.MarshalTextString(metric)
0x07 gRPC 与 Prometheus 结合
这小节,以 PULL 方式为例,看下如何在 gRPC 中通过 prometheus 实现监控。基本的框架如下:
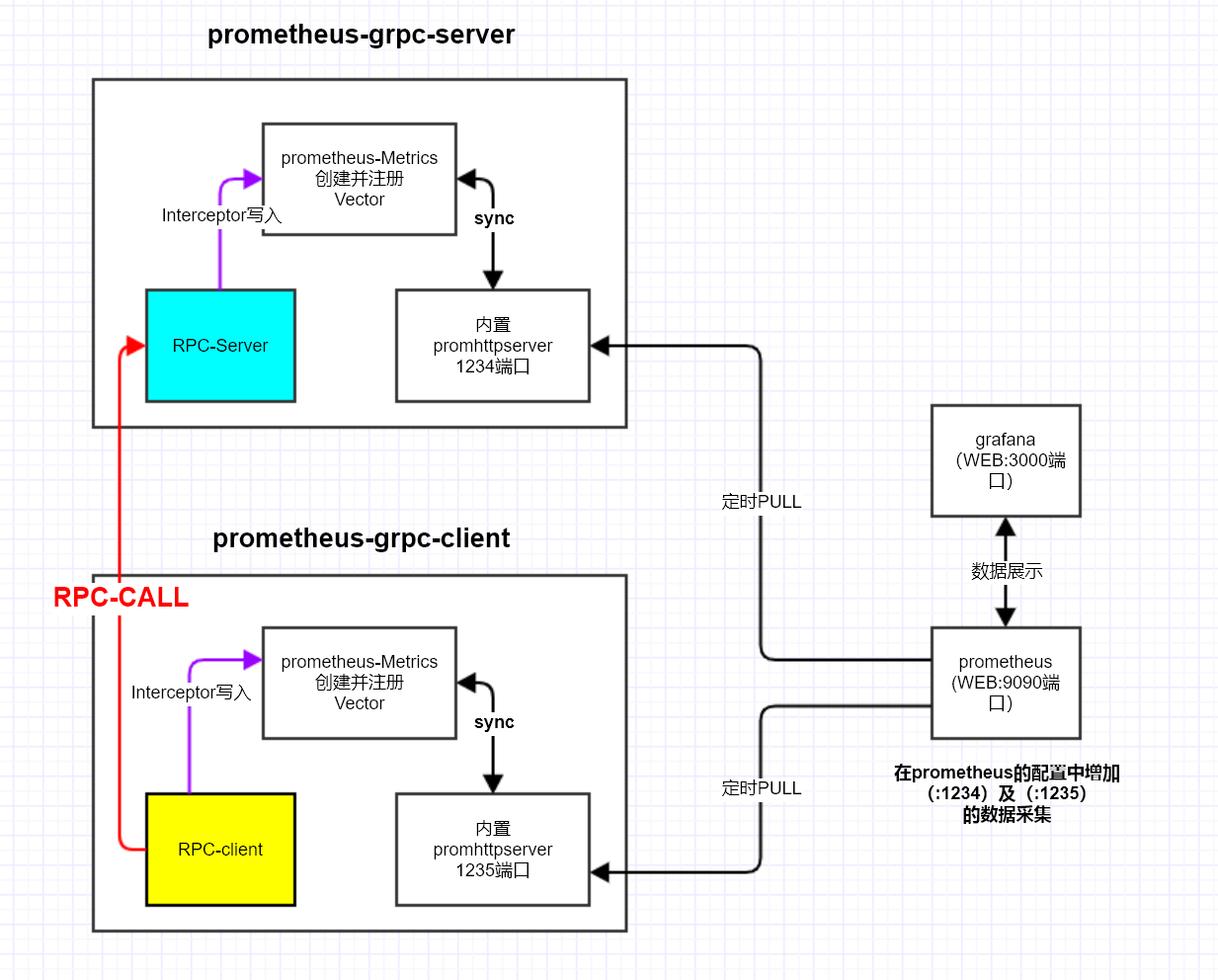
0x08 gRPC的metrics设计(思考)
指标
为了实时了解和监控gRPC服务的运行状况,需要重点关注如下指标:
- RPC接口请求耗时:
server_elapsed_ms - 服务器错误:
server_errors - 请求字节数:
server_bytes_transferred_in - 回包字节数:
server_bytes_transferred_out - 服务器状态码:
server_code
接下来,就是把上面的指标按照Prometheus的metrics表现出来:
- Counter:代表一种样本数据单调递增的指标,即只增不减,通常用来统计如服务的请求数,错误数等
- Gauge:代表一种样本数据可以任意变化的指标,即可增可减,通常用来统计如服务的CPU使用值,内存占用值等
- Histogram和Summary:用于表示一段时间内的数据采样和点分位图统计结果,通常用来统计请求耗时或响应大小等
label设计
- 组织(realm)
- 地域(region)
- 可用区域(available-zone)
- 发布环境(dev/beta/prod)
- 应用名称(appname)
- 主机名称(hostname)
- 方法(method)
- 返回码(retcode)
- 版本(app-version)
指标结合label所形成的多维度时间序列是各个维度监控/metrics的基础。
0x09 gRPC的metrics采集
本小节梳理下,如何利用gRPC拦截器简化Metrics的采集过程。考虑Metrics统计和Metrics采集两个逻辑的实现,参考项目go-grpc-prometheus
Metrics统计
Metrics的来源可能有如下两种。基于interceptor,可以在每一次请求前后都增加对应统计或处理:
- 服务自身的metrics
- 服务作为Metrics转换器,接收客户端上报的Metrics并转发(类似PUSH-GATEWAY的功能)
Metrics采集(PULL or PUSH)
服务完成metrics数据收集(转换)后,需要把数据上报到Prometheus服务器中:
1、主动拉取:服务侧提供接口暴露Metrics数据
func StartPrometheus(port, path string) *http.Server {
//......
if len(path) < 1 || !strings.HasPrefix(path, "/") {
// Invalid, use default
path = DefaultPath
}
// Register
prometheus.Register(Collector1)
prometheus.Register(Collector2)
prometheus.Register(Collector3)
httpMux := http.NewServeMux()
httpMux.Handle(path, promhttp.Handler())
server := &http.Server{
Addr: "0.0.0.0:" + port,
Handler: httpMux,
}
go func() {
server.ListenAndServe()
}()
return server
}
此外,通过声明Prometheus配置文件中的scrape_configs选项,指定Prometheus在运行时需要拉取指标的目标:
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape.
scrape_configs:
# 配置服务地址
- job_name: 'test-application-metrics'
scrape_interval: 2s
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:12345']
2、被动接收(PUSH模式)
主动拉取模式不一定适用所有场景,比如因防护墙限制无法提供采集服务,又或者定期对目标节点进行抓数据采集,可能存在任务节点还没来得及被拉取就运行完退出,导致数据丢失。为此,笔者封装了基于Prometheus提供了Pushgateway用于接收来自服务的主动上报接口,示例代码如下:
publisher := py_prom.NewPushGatewayPublisher(5*time.Second,prom_address)
publisher.Start()
guages := py_prom.ListGuage()
for i := range guages {
publisher.AddCollector(guages[i])
}
counters := py_prom.ListCounter()
for i := range counters {
publisher.AddCollector(counters[i])
}
histograms := py_prom.ListHistogram()
for i := range histograms {
publisher.AddCollector(histograms[i])
}
summay := py_prom.ListSummary()
for i := range summay {
publisher.AddCollector(summay[i])
}
prometheus的配置如下,配置成pushgateway的地址用于Prometheus拉取:
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape.
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'pushgateway'
scrape_interval: 10s
honor_labels: true
static_configs:
- targets: ['pushgateway:9091']