0x00 前言
asynq:Golang distributed task queue library,许多设计思想都来自sidekiq。官方文档给出的特点如下(省略了若干):
- 任务已写入Redis后会持久化(支持Redis Cluster/Sentinels)
- 任务执行失败自动 retry
- 支持任务优先级权重(加权优先级队列)
- 支持定时发送任务
- 可使用 unique-option 來避免任务重复执行
- UI及客户端、metrics支持(CLI检查和远程控制队列和任务)
- 支持任务设置执行时间or最长可运行的时间
asynq架构
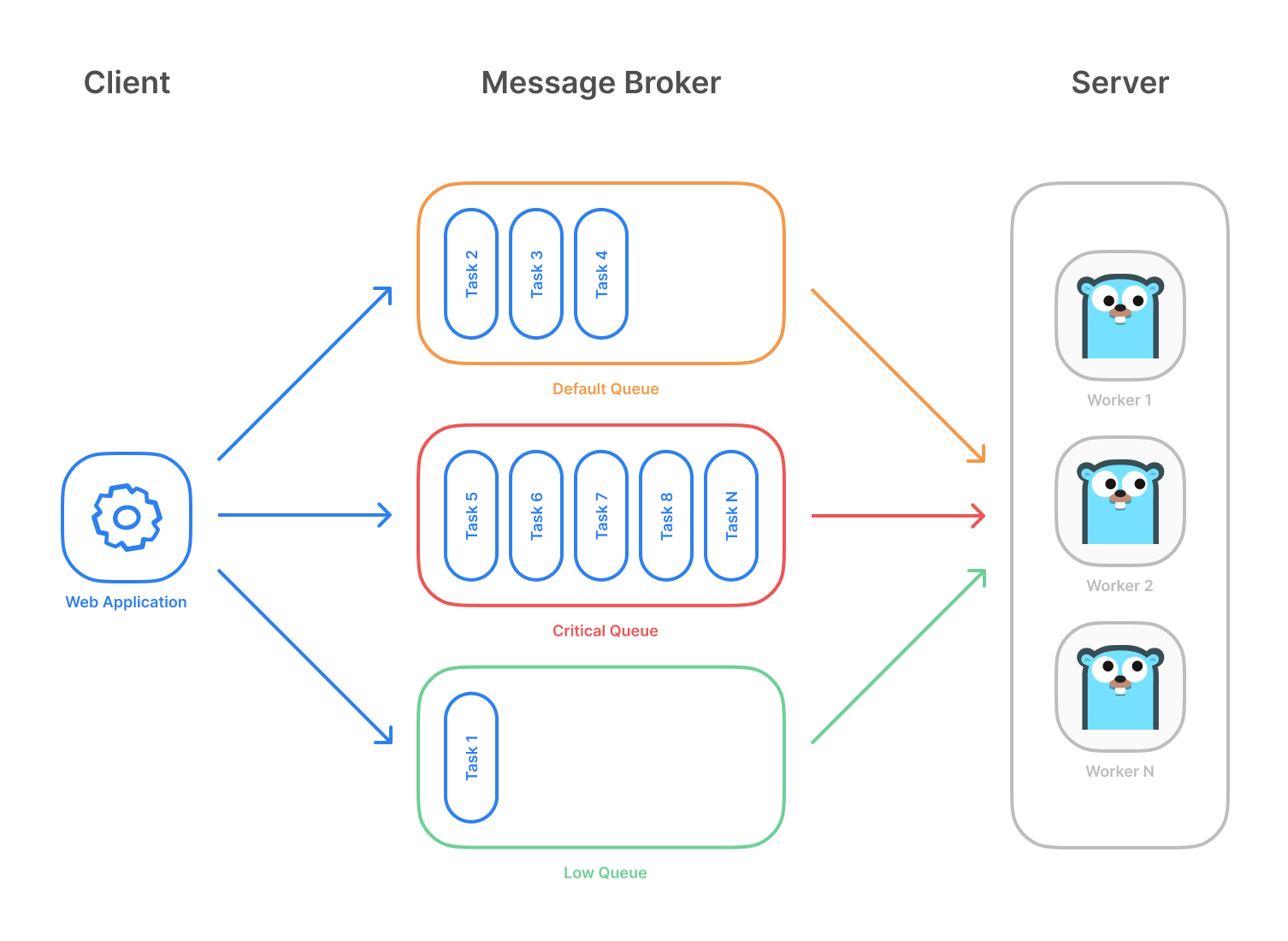
0x01 代码分析
asynq整体流程上和先前分析的中间件大同小异,并且该中间件严重依赖Redis,所有的原子化逻辑都是通过lua脚本实现的(如任务的出入队列等等),按照任务的状态划分了不同的redis数据结构及逻辑:
- active:asynq:{
}:active LIST类型 - pending:asynq:{
}:pending LIST类型 - lease:asynq:{
}:lease SortedSet类型 - completed:asynq:{
}: SortedSet类型 - paused:asynq:{
}:paused:HASHTABLE类型
此外,还有各种不同类型的结构,用来记录任务执行的状态、计数器等等
任务流
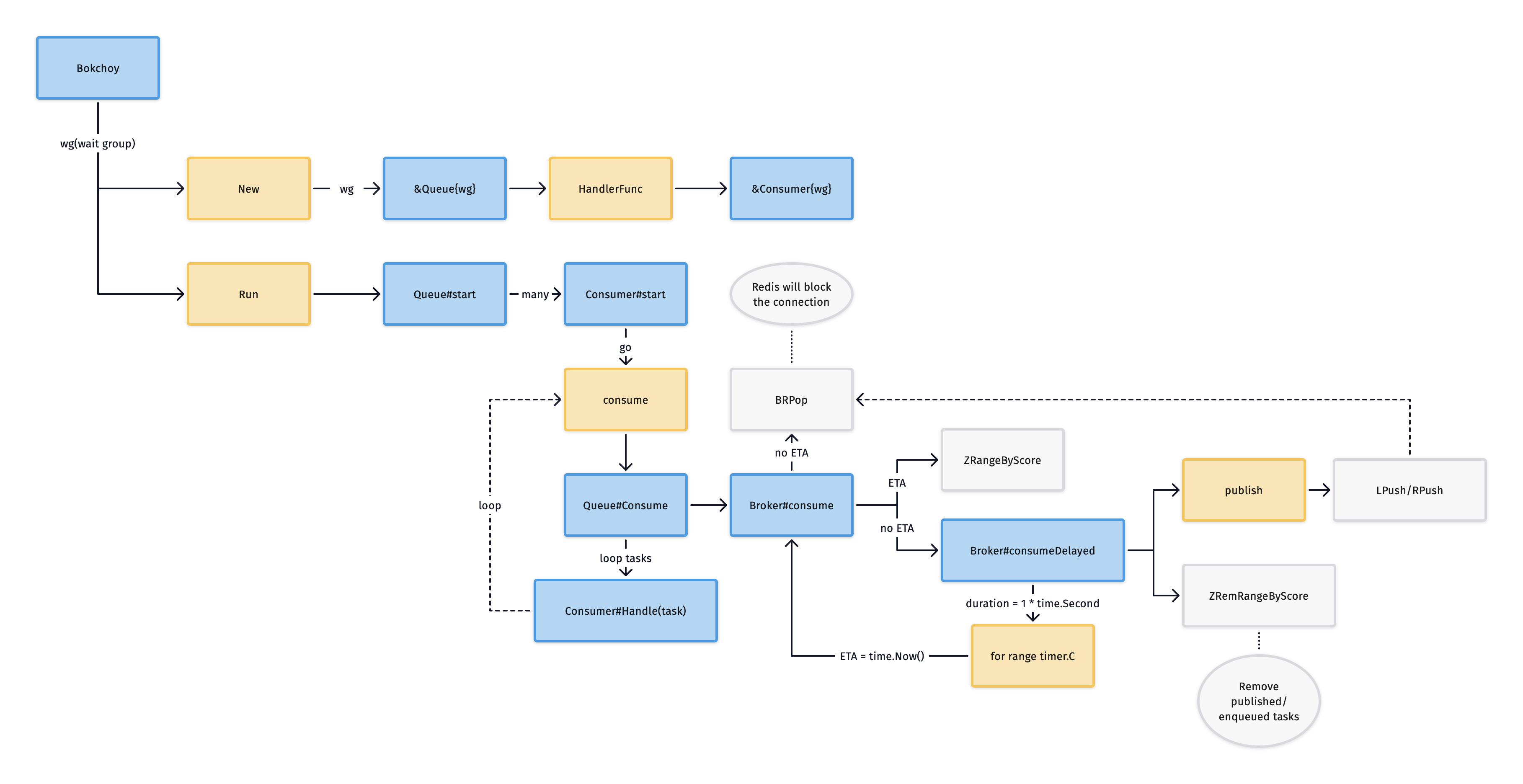
任务操作的Redis封装
1、dequeueCmd:用于把任务从pendingList取出,放到activeList中
// Input:
// KEYS[1] -> asynq:{<qname>}:pending
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:paused
// KEYS[3] -> asynq:{<qname>}:active
// KEYS[4] -> asynq:{<qname>}:lease
// --
// ARGV[1] -> initial lease expiration Unix time
// ARGV[2] -> task key prefix
//
// Output:
// Returns nil if no processable task is found in the given queue.
// Returns an encoded TaskMessage.
//
// Note: dequeueCmd checks whether a queue is paused first, before
// calling RPOPLPUSH to pop a task from the queue.
var dequeueCmd = redis.NewScript(`
if redis.call("EXISTS", KEYS[2]) == 0 then
local id = redis.call("RPOPLPUSH", KEYS[1], KEYS[3])
if id then
local key = ARGV[2] .. id
redis.call("HSET", key, "state", "active")
redis.call("HDEL", key, "pending_since")
redis.call("ZADD", KEYS[4], ARGV[1], id)
return redis.call("HGET", key, "msg")
end
end
return nil`)
2、markAsCompleteCmd方法:任务成功处理完成,通过HSET更新状态,同时删除activeLIST的数据
// KEYS[1] -> asynq:{<qname>}:active
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:lease
// KEYS[3] -> asynq:{<qname>}:completed
// KEYS[4] -> asynq:{<qname>}:t:<task_id>
// KEYS[5] -> asynq:{<qname>}:processed:<yyyy-mm-dd>
// KEYS[6] -> asynq:{<qname>}:processed
//
// ARGV[1] -> task ID
// ARGV[2] -> stats expiration timestamp
// ARGV[3] -> task exipration time in unix time
// ARGV[4] -> task message data
// ARGV[5] -> max int64 value
var markAsCompleteCmd = redis.NewScript(`
if redis.call("LREM", KEYS[1], 0, ARGV[1]) == 0 then
return redis.error_reply("NOT FOUND")
end
if redis.call("ZREM", KEYS[2], ARGV[1]) == 0 then
return redis.error_reply("NOT FOUND")
end
if redis.call("ZADD", KEYS[3], ARGV[3], ARGV[1]) ~= 1 then
redis.redis.error_reply("INTERNAL")
end
redis.call("HSET", KEYS[4], "msg", ARGV[4], "state", "completed")
local n = redis.call("INCR", KEYS[5])
if tonumber(n) == 1 then
redis.call("EXPIREAT", KEYS[5], ARGV[2])
end
local total = redis.call("GET", KEYS[6])
if tonumber(total) == tonumber(ARGV[5]) then
redis.call("SET", KEYS[6], 1)
else
redis.call("INCR", KEYS[6])
end
return redis.status_reply("OK")
`)
核心结构
1、processor结构
type processor struct {
logger *log.Logger
broker base.Broker
clock timeutil.Clock
handler Handler
baseCtxFn func() context.Context
queueConfig map[string]int
// orderedQueues is set only in strict-priority mode.
orderedQueues []string
retryDelayFunc RetryDelayFunc
isFailureFunc func(error) bool
errHandler ErrorHandler
shutdownTimeout time.Duration
// channel via which to send sync requests to syncer.
syncRequestCh chan<- *syncRequest
// rate limiter to prevent spamming logs with a bunch of errors.
errLogLimiter *rate.Limiter
// sema is a counting semaphore to ensure the number of active workers
// does not exceed the limit.
sema chan struct{}
// channel to communicate back to the long running "processor" goroutine.
// once is used to send value to the channel only once.
done chan struct{}
once sync.Once
// quit channel is closed when the shutdown of the "processor" goroutine starts.
quit chan struct{}
// abort channel communicates to the in-flight worker goroutines to stop.
abort chan struct{}
// cancelations is a set of cancel functions for all active tasks.
cancelations *base.Cancelations
starting chan<- *workerInfo
finished chan<- *base.TaskMessage
}
任务的状态
每个任务的唯一keyasynq:{<qname>}:t:<task_id>,在Redis数据结构为HashTable,有如下字段:
msg:任务关联数据state:任务状态(pending、active、completed、aggregating、scheduled、retry、archived)pending_since:unique_key:group:result:
1、Enqueue方法,关联enqueueCmd
// enqueueCmd enqueues a given task message.
//
// Input:
// KEYS[1] -> asynq:{<qname>}:t:<task_id>
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:pending
// --
// ARGV[1] -> task message data
// ARGV[2] -> task ID
// ARGV[3] -> current unix time in nsec
//
// Output:
// Returns 1 if successfully enqueued
// Returns 0 if task ID already exists
var enqueueCmd = redis.NewScript(`
if redis.call("EXISTS", KEYS[1]) == 1 then
return 0
end
redis.call("HSET", KEYS[1],
"msg", ARGV[1],
"state", "pending",
"pending_since", ARGV[3])
redis.call("LPUSH", KEYS[2], ARGV[2])
return 1
`)
2、enqueueUniqueCmd
// enqueueUniqueCmd enqueues the task message if the task is unique.
//
// KEYS[1] -> unique key
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:t:<taskid>
// KEYS[3] -> asynq:{<qname>}:pending
// --
// ARGV[1] -> task ID
// ARGV[2] -> uniqueness lock TTL
// ARGV[3] -> task message data
// ARGV[4] -> current unix time in nsec
//
// Output:
// Returns 1 if successfully enqueued
// Returns 0 if task ID conflicts with another task
// Returns -1 if task unique key already exists
var enqueueUniqueCmd = redis.NewScript(`
local ok = redis.call("SET", KEYS[1], ARGV[1], "NX", "EX", ARGV[2])
if not ok then
return -1
end
if redis.call("EXISTS", KEYS[2]) == 1 then
return 0
end
redis.call("HSET", KEYS[2],
"msg", ARGV[3],
"state", "pending",
"pending_since", ARGV[4],
"unique_key", KEYS[1])
redis.call("LPUSH", KEYS[3], ARGV[1])
return 1
`)
3、dequeueCmd
// Input:
// KEYS[1] -> asynq:{<qname>}:pending
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:paused
// KEYS[3] -> asynq:{<qname>}:active
// KEYS[4] -> asynq:{<qname>}:lease
// --
// ARGV[1] -> initial lease expiration Unix time
// ARGV[2] -> task key prefix
//
// Output:
// Returns nil if no processable task is found in the given queue.
// Returns an encoded TaskMessage.
//
// Note: dequeueCmd checks whether a queue is paused first, before
// calling RPOPLPUSH to pop a task from the queue.
var dequeueCmd = redis.NewScript(`
if redis.call("EXISTS", KEYS[2]) == 0 then
local id = redis.call("RPOPLPUSH", KEYS[1], KEYS[3])
if id then
local key = ARGV[2] .. id
redis.call("HSET", key, "state", "active")
redis.call("HDEL", key, "pending_since")
redis.call("ZADD", KEYS[4], ARGV[1], id)
return redis.call("HGET", key, "msg")
end
end
return nil`)
举例来说,redis数据如下:
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "asynq:servers:{VM_120_245_centos:20022:69678348-e2e8-4a40-a729-6f50b8180194}"
2) "asynq:{critical}:processed:2022-10-17"
3) "asynq:servers"
4) "asynq:{low}:scheduled"
5) "asynq:{low}:processed:2022-10-17"
6) "asynq:workers"
7) "asynq:{critical}:processed:2022-10-08"
8) "dq_queue_order"
9) "asynq:{low}:processed:2022-10-08"
10) "1570239831121"
11) "15702398321"
12) "asynq:queues"
13) "asynq:{default}:processed:2022-10-08"
核心流程
1、processor.exec
asynq没有使用 brpop/rpop 指令(前者阻塞,后者轮询),而是通过 channel 实现信号量去控制对 Redis 的轮询。参见下面的processor.exec方法,该方法独立运行,会先尝试获取一个允许继续执行的信号,如果有则调用 broker的Dequeue 方法查询待执行的任务信息,否则就停下来等待信号。如果队列是空的,那么会time.Sleep(time.Second),以免不断的查询 Redis 。此外,执行信号的个数也是可配置(默认机器核数),这里就是普通的限制取任务并发
// exec pulls a task out of the queue and starts a worker goroutine to
// process the task.
func (p *processor) exec() {
select {
case <-p.quit:
return
case p.sema <- struct{}{}: // acquire token
qnames := p.queues()
//从broker中取任务数据
msg, leaseExpirationTime, err := p.broker.Dequeue(qnames...)
switch {
case errors.Is(err, errors.ErrNoProcessableTask):
p.logger.Debug("All queues are empty")
// Queues are empty, this is a normal behavior.
// Sleep to avoid slamming redis and let scheduler move tasks into queues.
// Note: We are not using blocking pop operation and polling queues instead.
// This adds significant load to redis.
time.Sleep(time.Second)
<-p.sema // release token
return
case err != nil:
if p.errLogLimiter.Allow() {
p.logger.Errorf("Dequeue error: %v", err)
}
<-p.sema // release token
return
}
lease := base.NewLease(leaseExpirationTime)
deadline := p.computeDeadline(msg)
p.starting <- &workerInfo{msg, time.Now(), deadline, lease}
go func() {
defer func() {
p.finished <- msg
<-p.sema // release token
}()
ctx, cancel := asynqcontext.New(p.baseCtxFn(), msg, deadline)
p.cancelations.Add(msg.ID, cancel)
defer func() {
cancel()
p.cancelations.Delete(msg.ID)
}()
// check context before starting a worker goroutine.
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
// already canceled (e.g. deadline exceeded).
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, ctx.Err())
return
default:
}
resCh := make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
task := newTask(
msg.Type,
msg.Payload,
&ResultWriter{
id: msg.ID,
qname: msg.Queue,
broker: p.broker,
ctx: ctx,
},
)
resCh <- p.perform(ctx, task)
}()
select {
case <-p.abort:
// time is up, push the message back to queue and quit this worker goroutine.
p.logger.Warnf("Quitting worker. task id=%s", msg.ID)
p.requeue(lease, msg)
return
case <-lease.Done():
cancel()
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, ErrLeaseExpired)
return
case <-ctx.Done():
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, ctx.Err())
return
case resErr := <-resCh:
if resErr != nil {
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, resErr)
return
}
p.handleSucceededMessage(lease, msg)
}
}()
}
}
2、任务执行
任务的执行也是异步的
func (p *processor) exec() {
//...
go func() {
task := newTask(
msg.Type,
msg.Payload,
&ResultWriter{
id: msg.ID,
qname: msg.Queue,
broker: p.broker,
ctx: ctx,
},
)
resCh <- p.perform(ctx, task)
}()
//...
}
// perform calls the handler with the given task.
// If the call returns without panic, it simply returns the value,
// otherwise, it recovers from panic and returns an error.
func (p *processor) perform(ctx context.Context, task *Task) (err error) {
defer func() {
if x := recover(); x != nil {
p.logger.Errorf("recovering from panic. See the stack trace below for details:\n%s", string(debug.Stack()))
_, file, line, ok := runtime.Caller(1) // skip the first frame (panic itself)
if ok && strings.Contains(file, "runtime/") {
// The panic came from the runtime, most likely due to incorrect
// map/slice usage. The parent frame should have the real trigger.
_, file, line, ok = runtime.Caller(2)
}
// Include the file and line number info in the error, if runtime.Caller returned ok.
if ok {
err = fmt.Errorf("panic [%s:%d]: %v", file, line, x)
} else {
err = fmt.Errorf("panic: %v", x)
}
}
}()
return p.handler.ProcessTask(ctx, task)
}
func (fn HandlerFunc) ProcessTask(ctx context.Context, task *Task) error {
return fn(ctx, task)
}
3、等待任务执行结果
开头列举的,asynq支持任务的控制核心就在此实现,如;
p.abort:lease.Done():任务执行过期(超时)了ctx.Done():<-resCh:任务正常结束,获取结果成功/失败
func (p *processor) exec() {
//...
select {
case <-p.abort:
// time is up, push the message back to queue and quit this worker goroutine.
p.logger.Warnf("Quitting worker. task id=%s", msg.ID)
p.requeue(lease, msg)
return
case <-lease.Done():
cancel()
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, ErrLeaseExpired)
return
case <-ctx.Done():
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, ctx.Err())
return
case resErr := <-resCh:
if resErr != nil {
p.handleFailedMessage(ctx, lease, msg, resErr)
return
}
p.handleSucceededMessage(lease, msg)
}
//...
}
//处理结果
func (p *processor) handleSucceededMessage(l *base.Lease, msg *base.TaskMessage) {
if msg.Retention > 0 {
//
p.markAsComplete(l, msg)
} else {
p.markAsDone(l, msg)
}
}
注意:markAsComplete是
4、处理任务执行失败:handleFailedMessage
最终,需要retry重试的任务在p.retry方法中被打上下一次重试的时间,然后在retryCmd中通过ZADD添加到asynq:{<qname>}:retry对应的SortedSet中
func (p *processor) handleFailedMessage(ctx context.Context, l *base.Lease, msg *base.TaskMessage, err error) {
if p.errHandler != nil {
p.errHandler.HandleError(ctx, NewTask(msg.Type, msg.Payload), err)
}
if !p.isFailureFunc(err) {
// retry the task without marking it as failed
p.retry(l, msg, err, false /*isFailure*/)
return
}
if msg.Retried >= msg.Retry || errors.Is(err, SkipRetry) {
p.logger.Warnf("Retry exhausted for task id=%s", msg.ID)
p.archive(l, msg, err)
} else {
//调用p.retry重试
p.retry(l, msg, err, true /*isFailure*/)
}
}
func (p *processor) retry(l *base.Lease, msg *base.TaskMessage, e error, isFailure bool) {
if !l.IsValid() {
// If lease is not valid, do not write to redis; Let recoverer take care of it.
return
}
ctx, _ := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), l.Deadline())
//计算下一次重试触发的时间
d := p.retryDelayFunc(msg.Retried, e, NewTask(msg.Type, msg.Payload))
retryAt := time.Now().Add(d)
//调用broker的retry的方法
err := p.broker.Retry(ctx, msg, retryAt, e.Error(), isFailure)
if err != nil {
errMsg := fmt.Sprintf("Could not move task id=%s from %q to %q", msg.ID, base.ActiveKey(msg.Queue), base.RetryKey(msg.Queue))
p.logger.Warnf("%s; Will retry syncing", errMsg)
p.syncRequestCh <- &syncRequest{
fn: func() error {
return p.broker.Retry(ctx, msg, retryAt, e.Error(), isFailure)
},
errMsg: errMsg,
deadline: l.Deadline(),
}
}
}
// Retry moves the task from active to retry queue.
// It also annotates the message with the given error message and
// if isFailure is true increments the retried counter.
func (r *RDB) Retry(ctx context.Context, msg *base.TaskMessage, processAt time.Time, errMsg string, isFailure bool) error {
var op errors.Op = "rdb.Retry"
now := r.clock.Now()
modified := *msg
if isFailure {
modified.Retried++
}
modified.ErrorMsg = errMsg
modified.LastFailedAt = now.Unix() //下一次触发的时间,属性关联于Redis的SortSet
encoded, err := base.EncodeMessage(&modified)
if err != nil {
return errors.E(op, errors.Internal, fmt.Sprintf("cannot encode message: %v", err))
}
expireAt := now.Add(statsTTL)
keys := []string{
base.TaskKey(msg.Queue, msg.ID),
base.ActiveKey(msg.Queue),
base.LeaseKey(msg.Queue),
base.RetryKey(msg.Queue),
base.ProcessedKey(msg.Queue, now),
base.FailedKey(msg.Queue, now),
base.ProcessedTotalKey(msg.Queue),
base.FailedTotalKey(msg.Queue),
}
argv := []interface{}{
msg.ID,
encoded,
processAt.Unix(),
expireAt.Unix(),
isFailure,
int64(math.MaxInt64),
}
return r.runScript(ctx, op, retryCmd, keys, argv...)
}
// KEYS[1] -> asynq:{<qname>}:t:<task_id>
// KEYS[2] -> asynq:{<qname>}:active
// KEYS[3] -> asynq:{<qname>}:lease
// KEYS[4] -> asynq:{<qname>}:retry
// KEYS[5] -> asynq:{<qname>}:processed:<yyyy-mm-dd>
// KEYS[6] -> asynq:{<qname>}:failed:<yyyy-mm-dd>
// KEYS[7] -> asynq:{<qname>}:processed
// KEYS[8] -> asynq:{<qname>}:failed
// -------
// ARGV[1] -> task ID
// ARGV[2] -> updated base.TaskMessage value
// ARGV[3] -> retry_at UNIX timestamp
// ARGV[4] -> stats expiration timestamp
// ARGV[5] -> is_failure (bool)
// ARGV[6] -> max int64 value
var retryCmd = redis.NewScript(`
if redis.call("LREM", KEYS[2], 0, ARGV[1]) == 0 then
return redis.error_reply("NOT FOUND")
end
if redis.call("ZREM", KEYS[3], ARGV[1]) == 0 then
return redis.error_reply("NOT FOUND")
end
redis.call("ZADD", KEYS[4], ARGV[3], ARGV[1])
redis.call("HSET", KEYS[1], "msg", ARGV[2], "state", "retry")
if tonumber(ARGV[5]) == 1 then
local n = redis.call("INCR", KEYS[5])
if tonumber(n) == 1 then
redis.call("EXPIREAT", KEYS[5], ARGV[4])
end
local m = redis.call("INCR", KEYS[6])
if tonumber(m) == 1 then
redis.call("EXPIREAT", KEYS[6], ARGV[4])
end
local total = redis.call("GET", KEYS[7])
if tonumber(total) == tonumber(ARGV[6]) then
redis.call("SET", KEYS[7], 1)
redis.call("SET", KEYS[8], 1)
else
redis.call("INCR", KEYS[7])
redis.call("INCR", KEYS[8])
end
end
return redis.status_reply("OK")`)
0x02 metrics指标
本小节主要看下asynq定义的metrics,一款异步队列中间件需要考虑哪些指标
指标定义与说明
// Descriptors used by QueueMetricsCollector
var (
tasksQueuedDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "tasks_enqueued_total"),
"Number of tasks enqueued; broken down by queue and state.",
[]string{"queue", "state"}, nil,
)
queueSizeDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "queue_size"),
"Number of tasks in a queue",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
queueLatencyDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "queue_latency_seconds"),
"Number of seconds the oldest pending task is waiting in pending state to be processed.",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
queueMemUsgDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "queue_memory_usage_approx_bytes"),
"Number of memory used by a given queue (approximated number by sampling).",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
tasksProcessedTotalDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "tasks_processed_total"),
"Number of tasks processed (both succeeded and failed); broken down by queue",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
tasksFailedTotalDesc = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "tasks_failed_total"),
"Number of tasks failed; broken down by queue",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
pausedQueues = prometheus.NewDesc(
prometheus.BuildFQName(namespace, "", "queue_paused_total"),
"Number of queues paused",
[]string{"queue"}, nil,
)
)
0x03 总结
本文介绍了asynq的实现,asynq的代码非常值得一读,实现思路非常清晰